2 3 Tissues Anatomy Physiology
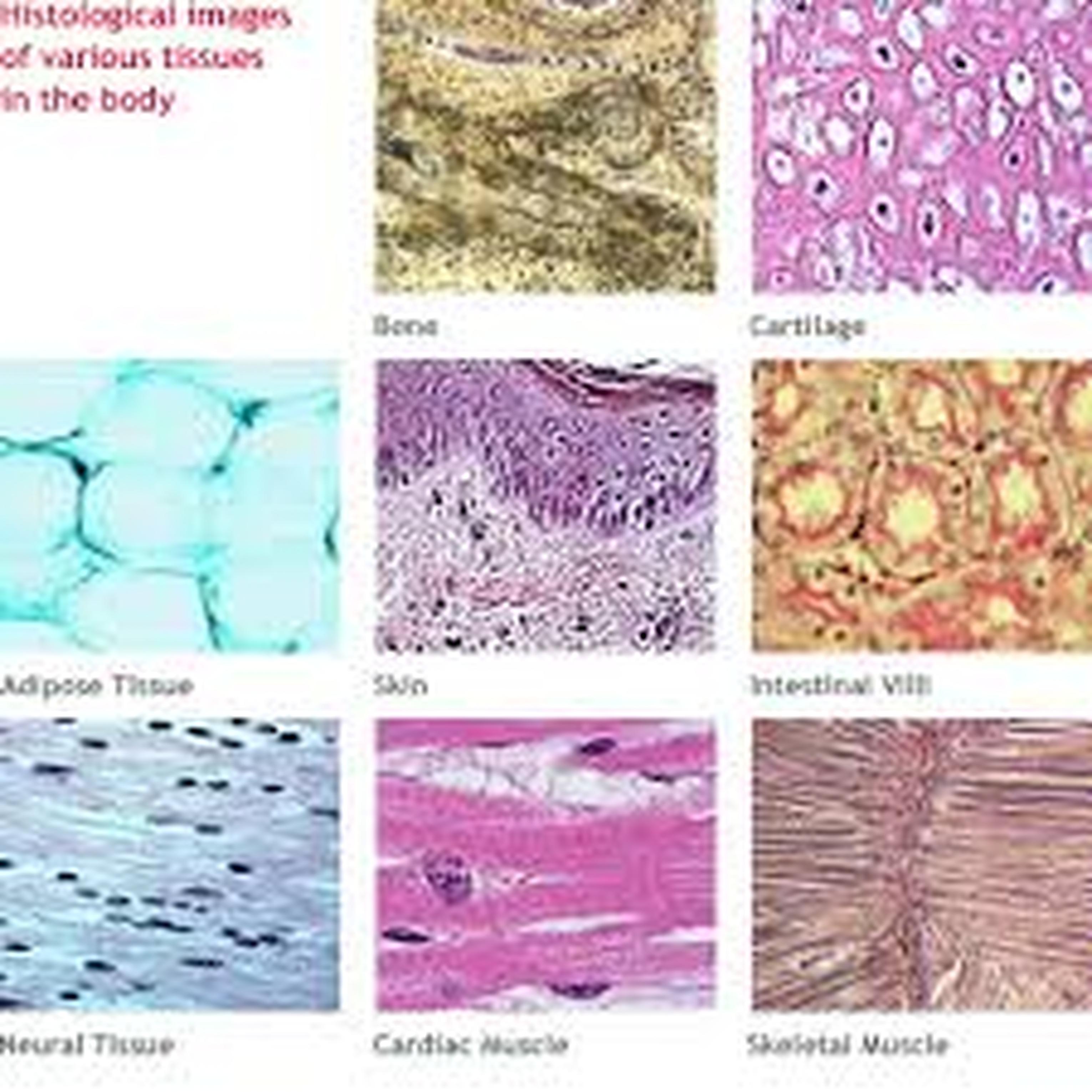
2 3 Tissues Anatomy Physiology Muscle tissue. a body tissue that contracts or shortens, making body parts move; has cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscles. epithelial tissue. tissue that forms boundaries between different environments, protects, secretes, absorbs, and filters; located in glands, skin surface, and lining of hollow organs. Figure 3.2.1 3.2. 1: four types of tissue: body. the four types of tissues are exemplified in nervous tissue, stratified squamous epithelial tissue, cardiac muscle tissue, and connective tissue in small intestine. clockwise from nervous tissue, lm × 872, lm × 282, lm × 460, lm × 800.
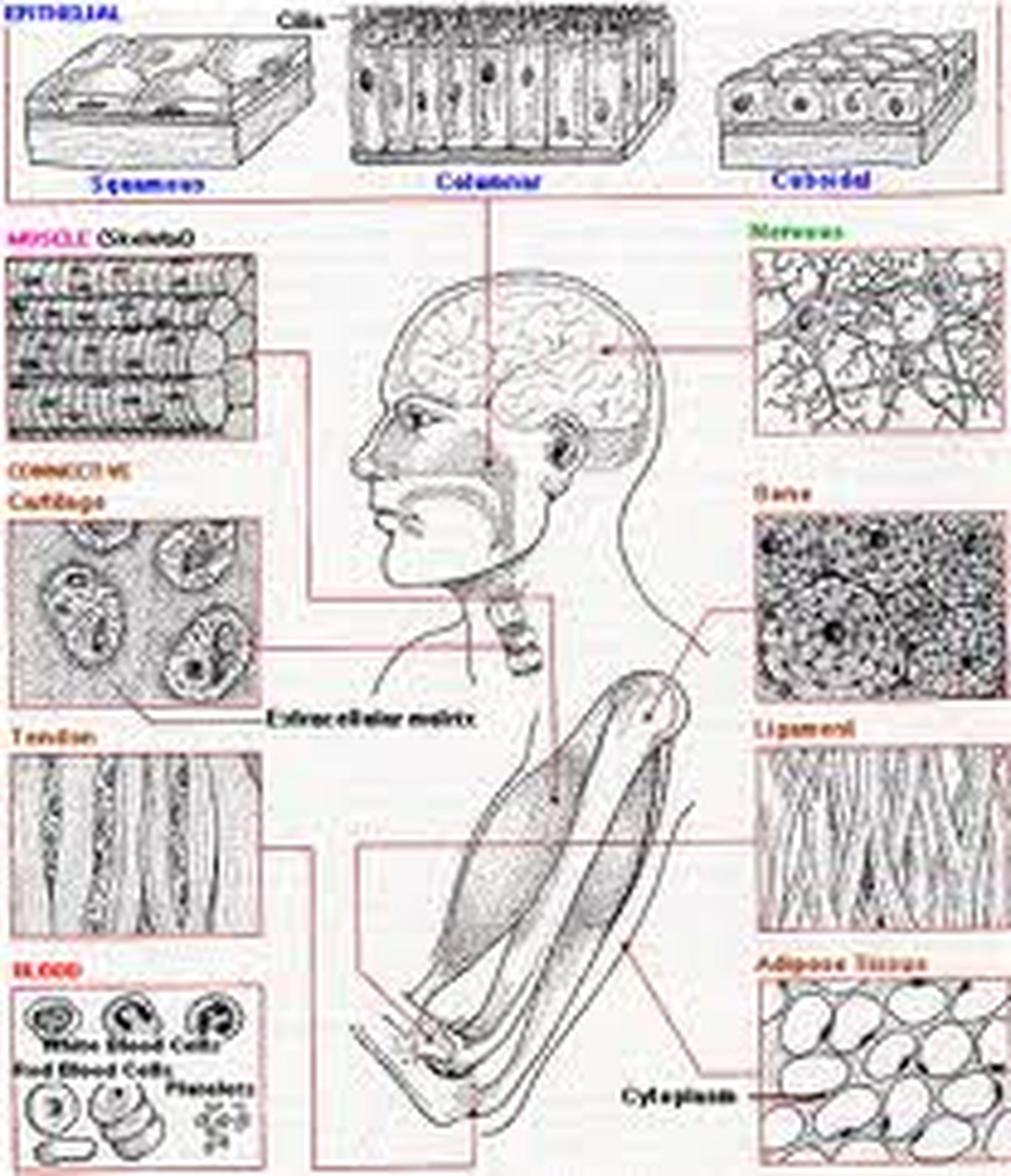
2 3 Tissues Anatomy Physiology The four types of tissues in the body are epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. epithelial tissue is made of layers of cells that cover the surfaces of the body that come into contact with the exterior world, line internal cavities, and form glands. connective tissue binds the cells and organs of the body together and performs many. Muscle and nervous tissues will be discussed only briefly in this chapter. figure 3.1.1. four types of tissue: body. the four types of tissues are exemplified in nervous tissue, stratified squamous epithelial tissue, cardiac muscle tissue, and connective tissue in small intestine. clockwise from nervous tissue, lm × 872, lm × 282, lm × 460. Tissue types. overview of the main cellular components and tissues. a tissue is a group of cells, in close proximity, organized to perform one or more specific functions. there are four basic tissue types defined by their morphology and function: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. Figure 4.3 shows the types of tissues and organs associated with the each of the three germ layers. note that epithelial tissue originates in all three layers, whereas nervous tissue derives primarily from the ectoderm and muscle tissue from mesoderm.

2 3 Tissues Anatomy Physiology Tissue types. overview of the main cellular components and tissues. a tissue is a group of cells, in close proximity, organized to perform one or more specific functions. there are four basic tissue types defined by their morphology and function: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. Figure 4.3 shows the types of tissues and organs associated with the each of the three germ layers. note that epithelial tissue originates in all three layers, whereas nervous tissue derives primarily from the ectoderm and muscle tissue from mesoderm. Muscle and nervous tissues will be discussed only briefly in this chapter. figure 4.1.1: four types of tissue: body.the four types of tissues are exemplified in nervous tissue, stratified squamous epithelial tissue, cardiac muscle tissue, and connective tissue in small intestine. clockwise from nervous tissue, lm × 872, lm × 282, lm × 460. 1 loose connective tissue. areolar (between tissue & organ) adipose (beneath skin; around organs) 2 dense connective tissue. regular (tendons & ligaments) irregular (dermis of skin; joint capsule) 3 reticular connective tissue. (lymphatic organs & liver) cartilage.

Comments are closed.