2 The Three Major Components Of The Microbial Diversity Download

2 The Three Major Components Of The Microbial Diversity Download In this chapter, we will discuss the diversity of environmental microorganisms, how they interact with other organisms and the environment, and how their diversity and interactions impact microbial adaptation, ecosystem function and the discovery of natural products such as antibiotics. 19.2. microbial diversity in natural systems. 2. biogeography of microbial diversity. the diversity of microbial communities varies within habitats as much as between habitats . this variation can even occur within a few millimetres, suggesting that microbial diversity encompasses more than the documented evidence available. hence, biogeography is gaining importance as a field of study.

2 The Three Major Components Of The Microbial Diversity Diversity in natural ecosy stems. according to bhardwaj and garg [6], microbial. diversity existing in natural ecosystems has the. following major applications: 9.1.1 cycling of matter. Download scientific diagram | 2 the three major components of the microbial diversity. from publication: microbial ecology in sustainable fruit growing: genetic, functional, and metabolic. 2.2 toward a trait based approach of microbial functional diversity biodiversity is generally seen as a triad composed of taxonomic, phylogenetic, and functional diversity. taxonomic and phylogenetic microbial diversities are both estimated using a single, highly conserved, marker genes (e.g., 16s rrna for bacteria and archaea, its for fungi. The term ‘microbial diversity’ or biodiversity has become so well known that a public servant is also aware about it. microbial diversity is defined as the variability among living organisms. the main key of microbial diversity on earth is due to evolution. the structural and functional diversity of any cell represents its evolutionary.
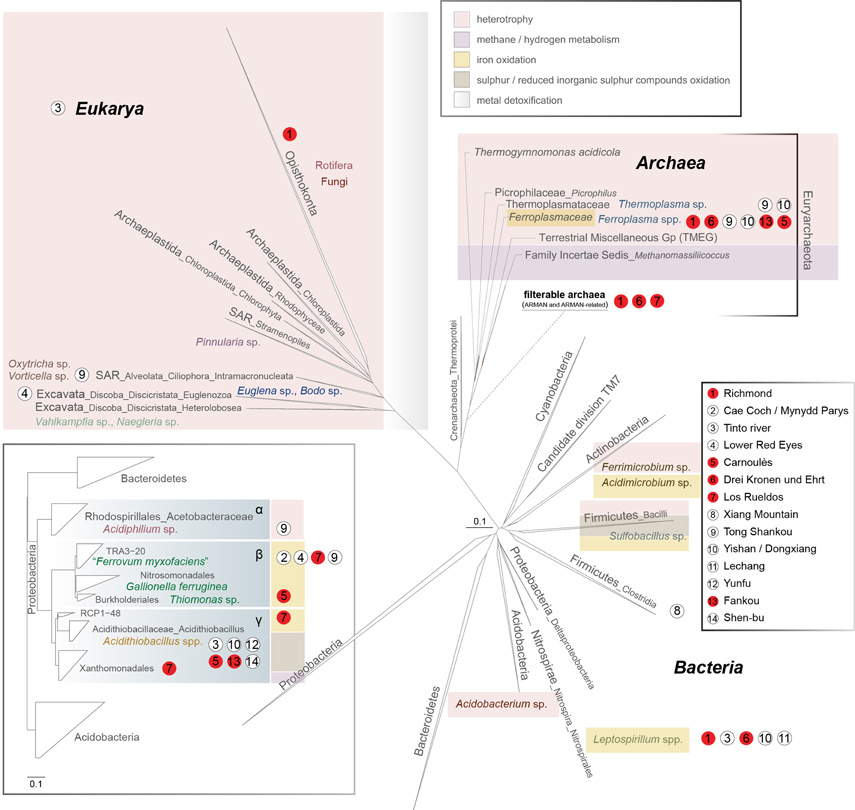
2 The Three Major Components Of The Microbial Diversity Download 2.2 toward a trait based approach of microbial functional diversity biodiversity is generally seen as a triad composed of taxonomic, phylogenetic, and functional diversity. taxonomic and phylogenetic microbial diversities are both estimated using a single, highly conserved, marker genes (e.g., 16s rrna for bacteria and archaea, its for fungi. The term ‘microbial diversity’ or biodiversity has become so well known that a public servant is also aware about it. microbial diversity is defined as the variability among living organisms. the main key of microbial diversity on earth is due to evolution. the structural and functional diversity of any cell represents its evolutionary. Abstract. a wide array of microorganisms, including many novel, phylogenetically deeply rooted taxa, survive and thrive in extreme environments. these unique and reduced complexity ecosystems. The relationship between biodiversity and biomass has been a long standing debate in ecology. soil biodiversity and biomass are essential drivers of ecosystem functions. however, unlike plant.
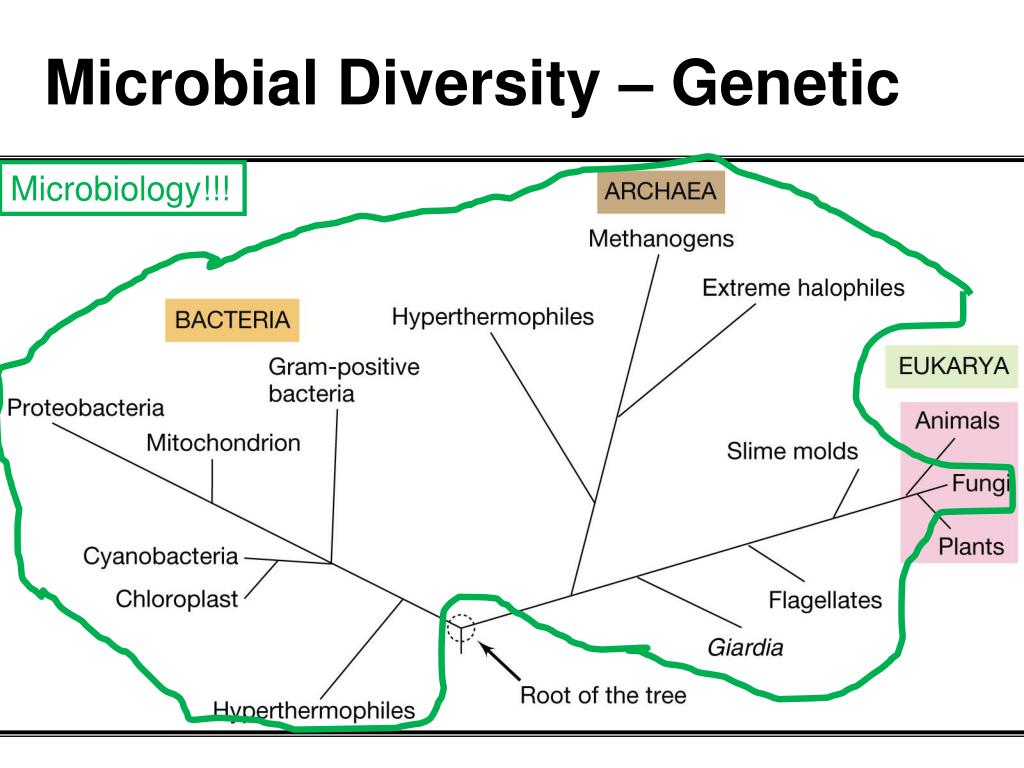
2 The Three Major Components Of The Microbial Diversity Abstract. a wide array of microorganisms, including many novel, phylogenetically deeply rooted taxa, survive and thrive in extreme environments. these unique and reduced complexity ecosystems. The relationship between biodiversity and biomass has been a long standing debate in ecology. soil biodiversity and biomass are essential drivers of ecosystem functions. however, unlike plant.

Comments are closed.