_____ Are Secondary Consumers

Secondary Consumer Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary Secondary consumers can be sorted into two groups: carnivores and omnivores. carnivores only eat meat, or other animals. some secondary consumers are large predators, but even the smaller ones often eat herbivores bigger than they are in order to get enough energy. spiders, snakes, and seals are all examples of carnivorous secondary consumers. Secondary consumer b. primary consumer c. detritivore d. producer e. tertiary consumer. e. a seal that just ate a clam is eaten by a shark. the shark is acting as a.
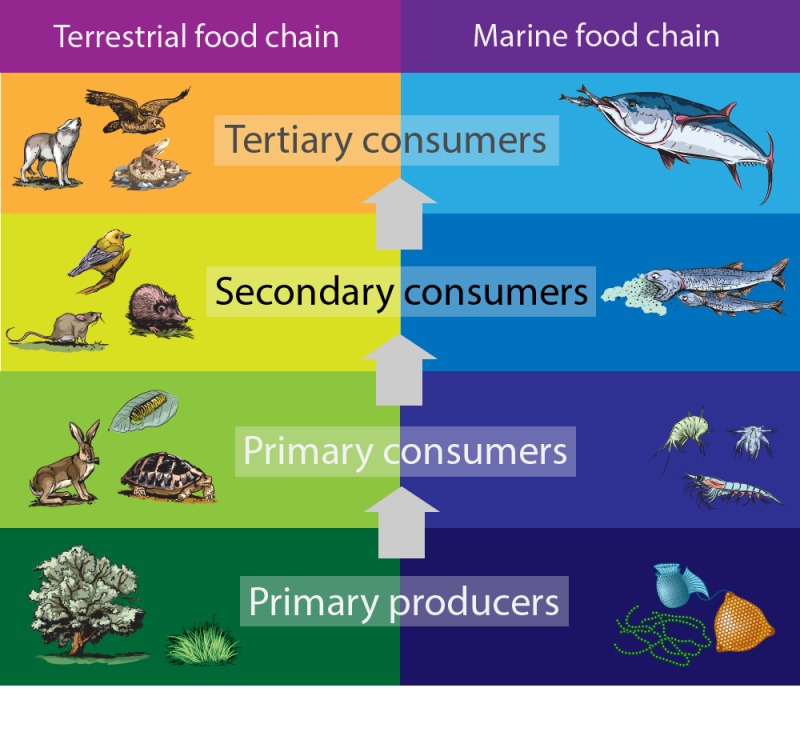
Secondary Consumers Definition Types And Examples Secondary consumers can be defined as a group of living organisms that mainly feed on primary consumers or herbivores to get energy. they are placed on the third trophic level in a food chain. some secondary consumers also feed on both producers and primary consumers. so, secondary consumers range from carnivores that consume meat to omnivores. Secondary consumers are those that predate upon primary consumers, and tertiary consumers predate upon secondary consumers. secondary consumers are either carnivores (which eat meat) or omnivores. Functions of secondary consumers. secondary consumers have an integral role to play in the food network. they are deeply involved in the regulation of the primary consumers’ populations in an ecosystem as they eat them for energy. moreover, secondary consumers also act as a source of nutrients and energy to the tertiary consumers. Definition of secondary consumers. secondary consumers are organisms that primarily feed on primary consumers, which are herbivores, in a food chain. they occupy the third trophic level and can be either carnivores, who eat only other animals, or omnivores, who consume both animal and plant matter. their role is vital in transferring energy.

Secondary Consumer Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary Functions of secondary consumers. secondary consumers have an integral role to play in the food network. they are deeply involved in the regulation of the primary consumers’ populations in an ecosystem as they eat them for energy. moreover, secondary consumers also act as a source of nutrients and energy to the tertiary consumers. Definition of secondary consumers. secondary consumers are organisms that primarily feed on primary consumers, which are herbivores, in a food chain. they occupy the third trophic level and can be either carnivores, who eat only other animals, or omnivores, who consume both animal and plant matter. their role is vital in transferring energy. Tertiary consumers eat the secondary consumers. they are at the fourth trophic level. in the desert ecosystem, an owl or eagle may prey on a snake. there may be more levels of consumers before a chain finally reaches its top predator. top predators, also called apex predators, eat other consumers. they may be at the fourth or fifth trophic. Secondary consumers nearly always consume both producers and primary consumers and are therefore usually classed as omnivores. secondary consumers make up the third trophic level of the food chain and are – as are all consumers – heterotrophs. tertiary consumers. examples of tertiary consumers are hawks, snakes, crocodiles and some big cats.
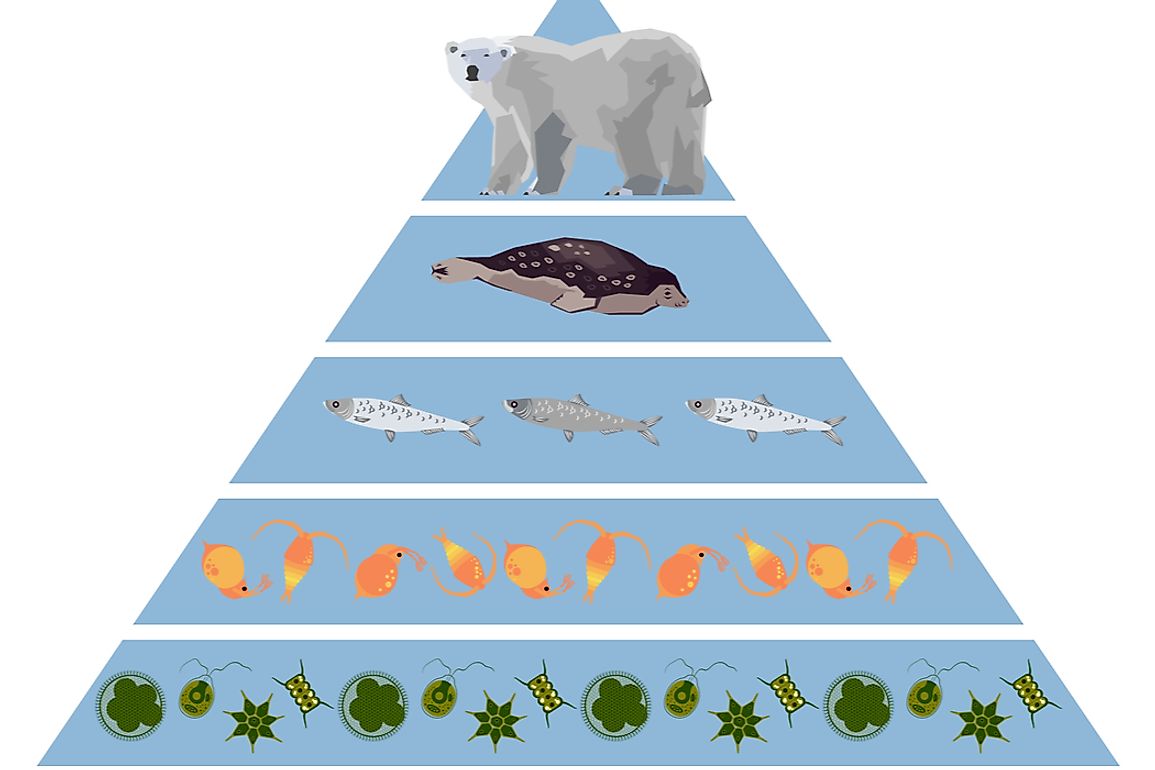
What Are Secondary Consumers Worldatlas Tertiary consumers eat the secondary consumers. they are at the fourth trophic level. in the desert ecosystem, an owl or eagle may prey on a snake. there may be more levels of consumers before a chain finally reaches its top predator. top predators, also called apex predators, eat other consumers. they may be at the fourth or fifth trophic. Secondary consumers nearly always consume both producers and primary consumers and are therefore usually classed as omnivores. secondary consumers make up the third trophic level of the food chain and are – as are all consumers – heterotrophs. tertiary consumers. examples of tertiary consumers are hawks, snakes, crocodiles and some big cats.

Comments are closed.