Construct Frequency Distribution Table Histogram And Frequency Polygon For The Following Data

Histogram And Frequency Polygon Youtube Table 2.2.2: frequency distribution for monthly rent. make sure the total of the frequencies is the same as the number of data points. it is difficult to determine the basic shape of the distribution by looking at the frequency distribution. it would be easier to look at a graph. the graph of a frequency distribution for quantitative data is. Therefore, bars = 6. the following histogram displays the number of books on the x axis and the frequency on the y axis. figure 2.3.2 2.3. 2: histogram consists of 6 bars with the y axis in increments of 2 from 0 16 and the x axis in intervals of 1 from 0.5 6.5.
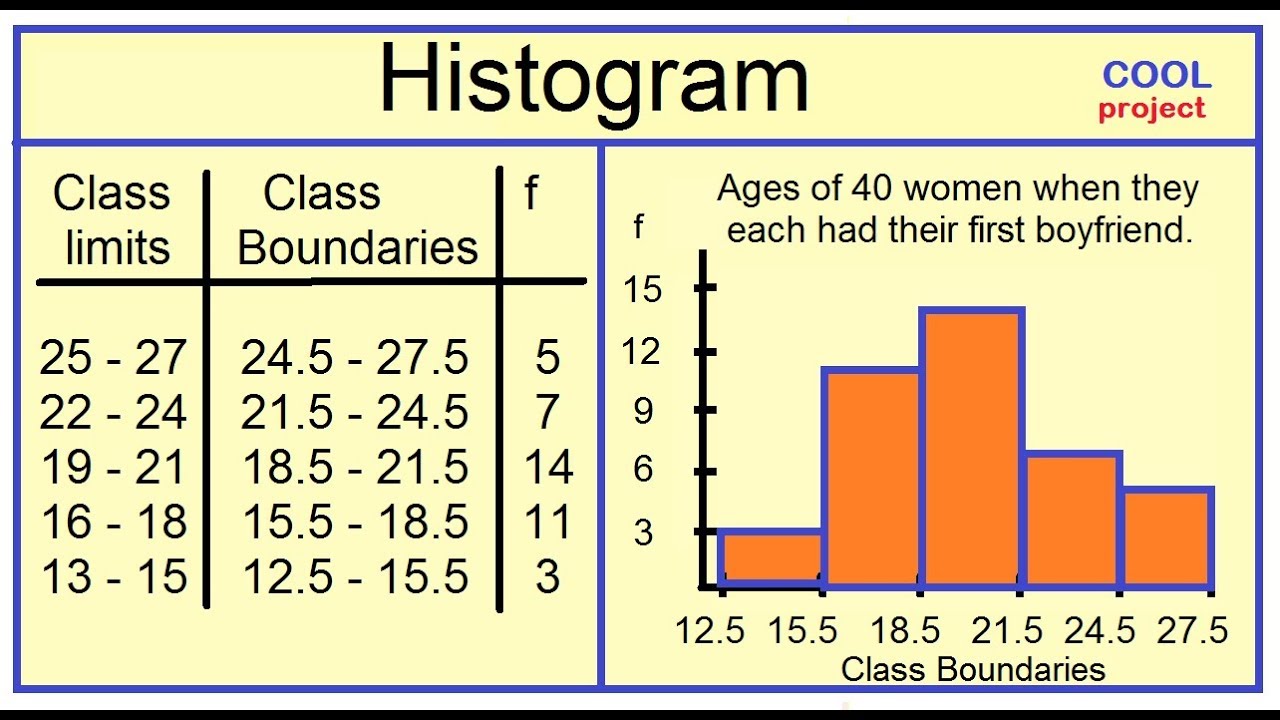
Histogram And Frequency Polygon Youtube Frequency polygons are used to display a set of data and show the frequency distribution over a continuous scale. to construct a frequency polygon, you need to know the value for the frequency of each group. for example, below is an example of a frequency polygon, with the associated frequency distribution table. Frequency and frequency distributions. frequency is the number of times a data value or groups of data values (called classes) occur in a data set. a frequency distribution is a listing of each data value or class of data values along with their frequencies. relative frequency is the frequency divided by n n, the size of the sample. A histogram is a type of chart that allows us to visualize the values in a frequency table. the following step by step example shows how to make a histogram from a frequency table. step 1: create the frequency table. suppose we collect the following data that shows the exam scores of 20 students in some class:. Part 2: sorting the data. step 2: subtract the minimum data value from the maximum data value. for example, our iq list above had a minimum value of 118 and a maximum value of 154, so: 154 – 118 = 36. step 3: divide your answer in step 2 by the number of classes you chose in step 1.
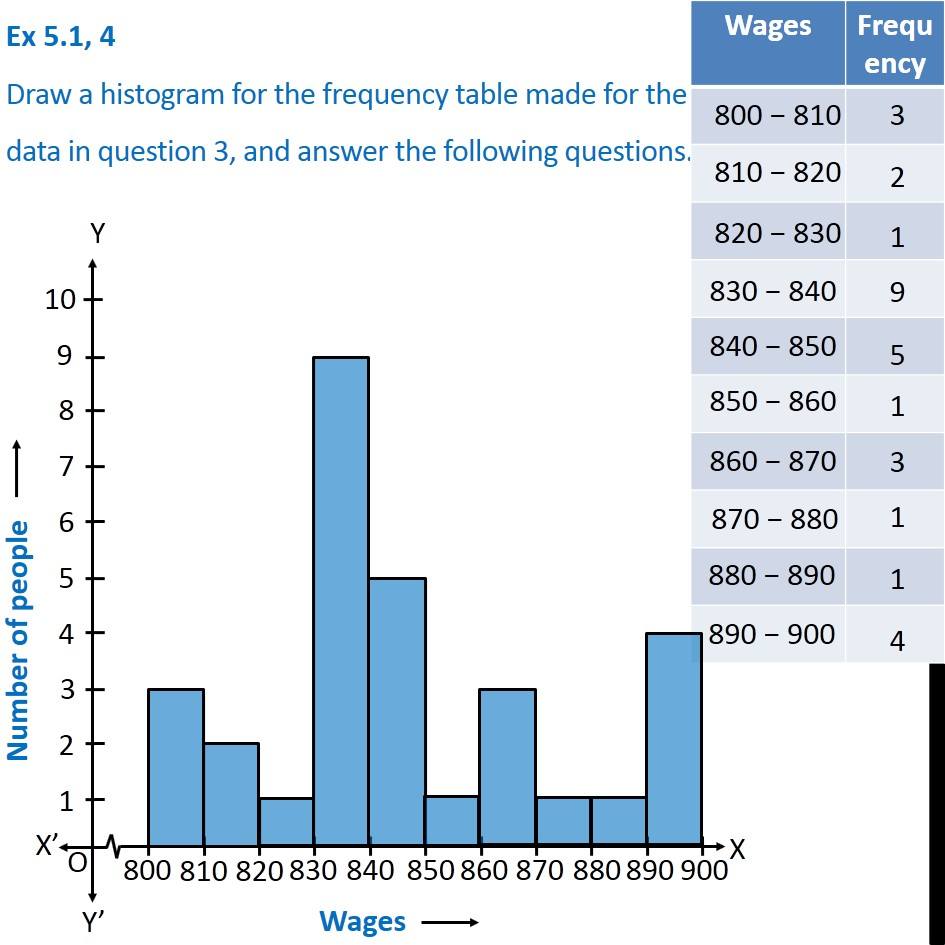
Question 4 Draw A Histogram For The Frequency Table Made For The Dat A histogram is a type of chart that allows us to visualize the values in a frequency table. the following step by step example shows how to make a histogram from a frequency table. step 1: create the frequency table. suppose we collect the following data that shows the exam scores of 20 students in some class:. Part 2: sorting the data. step 2: subtract the minimum data value from the maximum data value. for example, our iq list above had a minimum value of 118 and a maximum value of 154, so: 154 – 118 = 36. step 3: divide your answer in step 2 by the number of classes you chose in step 1. Figure 2.5.1 2.5. 1: overlaid cumulative frequency polygons. it is also possible to plot two cumulative frequency distributions in the same graph. this is illustrated in figure 2.5.4 2.5. 4 using the same data from the cursor task. the difference in distributions for the two targets is again evident. 2. using this table, construct a frequency polygon. step 1: calculate the midpoint of each bin by adding the 2 numbers of the interval and dividing the sum by 2. step 2: plot the midpoints on a grid, making sure to number the x axis with a scale that will include the bin sizes. join the plotted midpoints with lines.

From The Following Data Construct Frequency Histogram Frequency Polygon And Frequency Curve Figure 2.5.1 2.5. 1: overlaid cumulative frequency polygons. it is also possible to plot two cumulative frequency distributions in the same graph. this is illustrated in figure 2.5.4 2.5. 4 using the same data from the cursor task. the difference in distributions for the two targets is again evident. 2. using this table, construct a frequency polygon. step 1: calculate the midpoint of each bin by adding the 2 numbers of the interval and dividing the sum by 2. step 2: plot the midpoints on a grid, making sure to number the x axis with a scale that will include the bin sizes. join the plotted midpoints with lines.

Draw A Histogram For The Frequency Distribution Of The Following Data Class Interval 20 25 25

Comments are closed.