Consumers Decomposers And Producers

Components Of Ecosystem Biotic And Abiotic Teachoo Concepts Summary. ecosystems require constant inputs of energy from sunlight or chemicals. producers use energy and inorganic molecules to make food. consumers take in food by eating producers or other living things. decomposers break down dead organisms and other organic wastes and release inorganic molecules back to the environment. As shown in the infographic below, a basic food chain is composed of producers, consumers, and decomposers. the 4 levels of the food chain consist of: producers: at the bottom of the food chain, plants are natural producers and provide food and nutrients to consumers. herbivores: herbivores (primary consumers) nourish plants and insects.

Producers Consumers And Decomposers Science Quizizz Aquatic animal that strains nutrients from water. food chain. noun. group of organisms linked in order of the food they eat, from producers to consumers, and from prey, predators, scavengers, and decomposers. food web. noun. all related food chains in an ecosystem. also called a food cycle. Producers, consumers, and decomposers all interrelate in food chains and food webs and are dependent on one another for survival. producers they do not have to obtain energy from other organisms. Marine food webs. resource. add to collection. feeding relationships are often shown as simple food chains – in reality, these relationships are much more complex, and the term ‘food web’ more accurately shows the links between producers, consumers and decomposers. a food web diagram illustrates ‘what eats what’ in a particular habitat. Welcome to producers, consumers, and decomposers with mr. j! need help with what producers, consumers, and decomposers are? you're in the right place!whether.
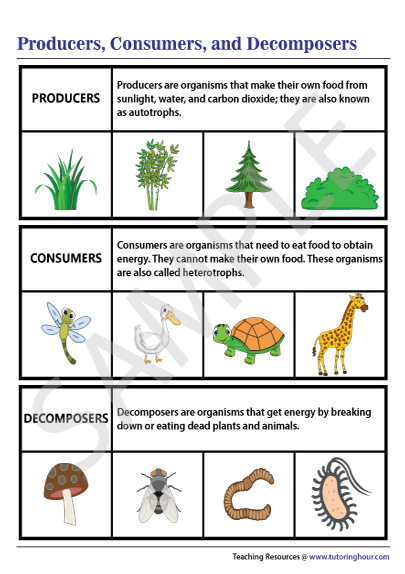
Producers Consumers And Decomposers Chart Marine food webs. resource. add to collection. feeding relationships are often shown as simple food chains – in reality, these relationships are much more complex, and the term ‘food web’ more accurately shows the links between producers, consumers and decomposers. a food web diagram illustrates ‘what eats what’ in a particular habitat. Welcome to producers, consumers, and decomposers with mr. j! need help with what producers, consumers, and decomposers are? you're in the right place!whether. The three basic ways in which organisms get food are as producers, consumers, and decomposers. producers (autotrophs) are typically plants or algae. plants and algae do not usually eat other organisms, but pull nutrients from the soil or the ocean and manufacture their own food using photosynthesis. for this reason, they are called primary. Roughly speaking, these levels are divided into producers (first trophic level), consumers (second, third, and fourth trophic levels), and decomposers. producers, also known as autotrophs, make their own food. they make up the first level of every food chain. autotrophs are usually plants or one celled organisms.

Comments are closed.