Cooling Curve Spm Chemistry

Cooling Curve Spm Chemistry Cooling curve. the graph above shows the cooling curve of a substance. the substance exists in gaseous state. the particles have very high energy and are moving randomly. the intermolecular forces between the particles are very weak and can be ignored. A cooling curve for a sample that begins at the temperature and composition given by point a is shown in figure 8.10.1b 8.10. 1 b. figure 8.10.1 8.10. 1: (a) cooling of a two component system from liquid to solid. (b) cooresponding cooling curve for this process. as the sample cools from point a, the temperature will decrease at a rate.
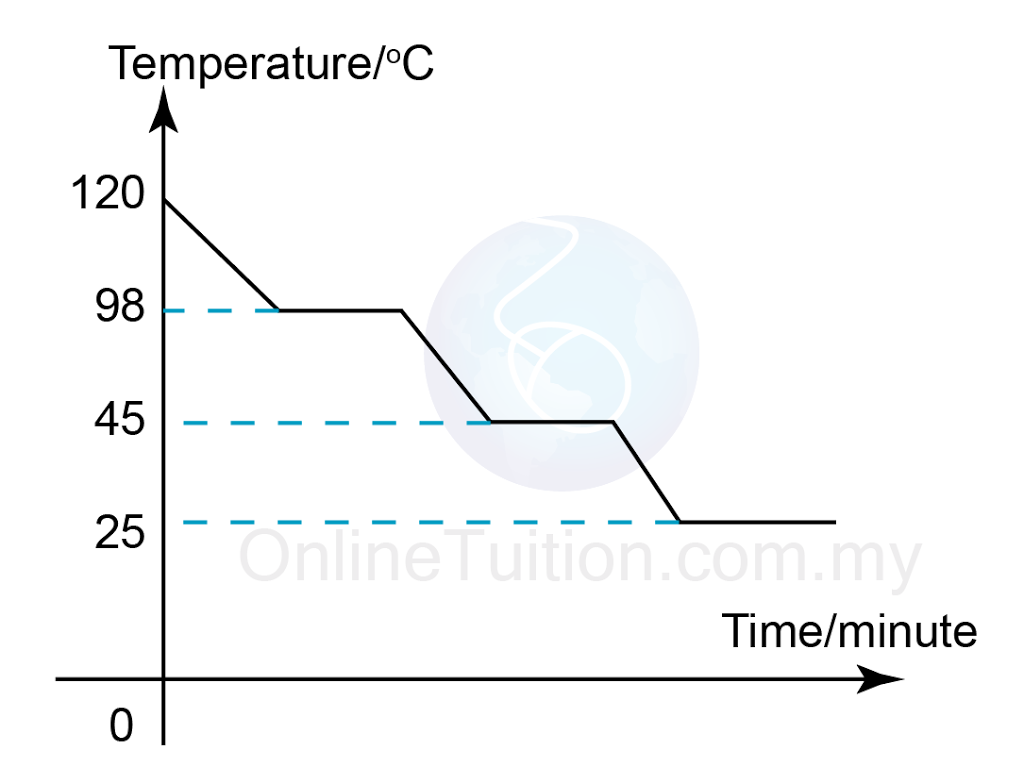
Three States Of Matter Structured Question 3 Spm Chemistry Figure 13.18.1 13.18. 1: in the heating curve of water, the temperature is shown as heat is continually added. changes of state occur during plateaus, because the temperature is constant. the change of state behavior of all substances can be represented with a heating curve of this type. Figure 2.5.3 2.5. 3: a heating curve for water. this plot of temperature shows what happens to a 75 g sample of ice initially at 1 atm and −23°c as heat is added at a constant rate: a–b: heating solid ice; b–c: melting ice; c–d: heating liquid water; d–e: vaporizing water; e–f: heating steam. thus the temperature of a system does. Spm physics form 4chapter 4: heat4.3 specific latent heat. Heating curve and cooling curve of naphthalene.

Heating And Cooling Curve Explanation Spm physics form 4chapter 4: heat4.3 specific latent heat. Heating curve and cooling curve of naphthalene. Oxidation and reduction – loss or gain of oxygen or hydrogen. redox reaction – oxidation of iron (ii) to iron (iii) redox reaction – reduction of iron (iii) to iron (ii) reaction between chlorine water and potassium bromide solution | oxidation and reduction. reaction between potassium dichromate (vi) and potassium iodide – part 1. A quick note about cooling curves. let's say we wanted to go from steam to ice. we would use a cooling curve. the cooling curve is a mirror image of the heating curve. so, it will start at a high temperature and have downward diagonals. the diagonals alternate with plateaus. the flat lines are the enthalpy of condensation and freezing. remember.

The Cooling Curve Spm Physics Form 4 Form 5 Revision Notes Oxidation and reduction – loss or gain of oxygen or hydrogen. redox reaction – oxidation of iron (ii) to iron (iii) redox reaction – reduction of iron (iii) to iron (ii) reaction between chlorine water and potassium bromide solution | oxidation and reduction. reaction between potassium dichromate (vi) and potassium iodide – part 1. A quick note about cooling curves. let's say we wanted to go from steam to ice. we would use a cooling curve. the cooling curve is a mirror image of the heating curve. so, it will start at a high temperature and have downward diagonals. the diagonals alternate with plateaus. the flat lines are the enthalpy of condensation and freezing. remember.

Comments are closed.