Covalent Bonding In An Oxygen Molecule

Covalent Bonding In An Oxygen Molecule An oxygen atom has 6 electrons in its outer shell. oxygen is in group 6 of the periodic table. two oxygen atoms will each share two electrons to form two covalent bonds and make an oxygen molecule (o 2). this is a picture of an oxygen molecule. by sharing the four electrons where the shells touch each oxygen atom can count 8 electrons in its. How many covalent bonds hold the water molecule together? a: the oxygen atom shares one pair of valence electrons with each hydrogen atom. each pair of shared electrons represents one covalent bond, so two covalent bonds hold the water molecule together. the diagram in the figure below shows an example of covalent bonds between two atoms of the.
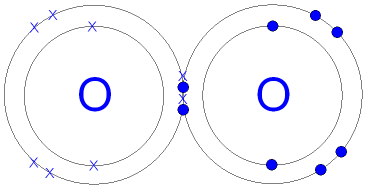
Gcse Chemistry Covalent Bonding In An Oxygen Molecule What Is The Structure Of An Oxygen Oxygen and other atoms in group 6a (16) obtain an octet by forming two covalent bonds. fluorine and the other halogens in group 7a (17) have seven valence electrons and can obtain an octet by forming one covalent bond. typically, the atoms of group 4a form 4 covalent bonds; group 5a form 3 bonds; group 6a form 2 bonds; and group 7a form one bond. The simplest compound of nitrogen is molecular nitrogen, n2. the two nitrogen atoms are bonded together by a triple bond, consisting of a σ and two π bonds. molecular nitrogen, n2[8] a common nitrogen containing molecule is ammonia (nh3), which is analogous to methane (ch3). in ammonia the nitrogen atom is bonded to three hydrogen atoms. Chapter 4 – covalent bonds and molecular compounds. chemical bonds are generally divided into two fundamentally different types: ionic and covalent. in reality, however, the bonds in most substances are neither purely ionic nor purely covalent, but lie on a spectrum between these extremes. although purely ionic and purely covalent bonds. The water molecule (h 2 o) is an example of compound with covalent bonds. the oxygen atom shares one electron with each of the two hydrogen atoms, forming two covalent bonds. octet rule and covalent bonding. the concept of covalent bonding ties in with the octet rule.
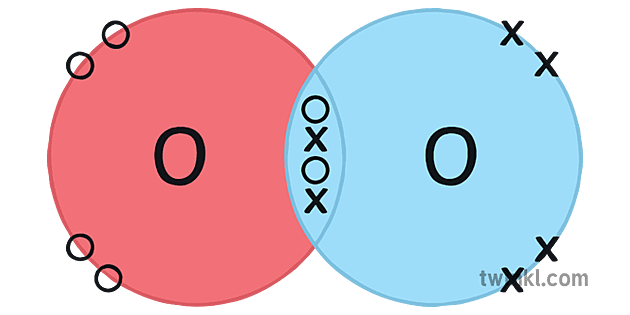
O2 Oksijeni Covalent Bonding Dot Cross Diagram Science Ks4 Ilustración Chapter 4 – covalent bonds and molecular compounds. chemical bonds are generally divided into two fundamentally different types: ionic and covalent. in reality, however, the bonds in most substances are neither purely ionic nor purely covalent, but lie on a spectrum between these extremes. although purely ionic and purely covalent bonds. The water molecule (h 2 o) is an example of compound with covalent bonds. the oxygen atom shares one electron with each of the two hydrogen atoms, forming two covalent bonds. octet rule and covalent bonding. the concept of covalent bonding ties in with the octet rule. The covalent bond. atoms can combine to achieve an octet of valence electrons by sharing electrons. two fluorine atoms, for example, can form a stable f 2 molecule in which each atom has an octet of valence electrons by sharing a pair of electrons. a pair of oxygen atoms can form an o 2 molecule in which each atom has a total of eight valence. Here is the dot and cross diagram for oxygen (o 2), a diatomic molecule. a single covalent bond is when two atoms share a single pair of electrons. represented by a single line (–).

Comments are closed.