Development Of A Cellular Therapy For Age Related Macular Degeneration
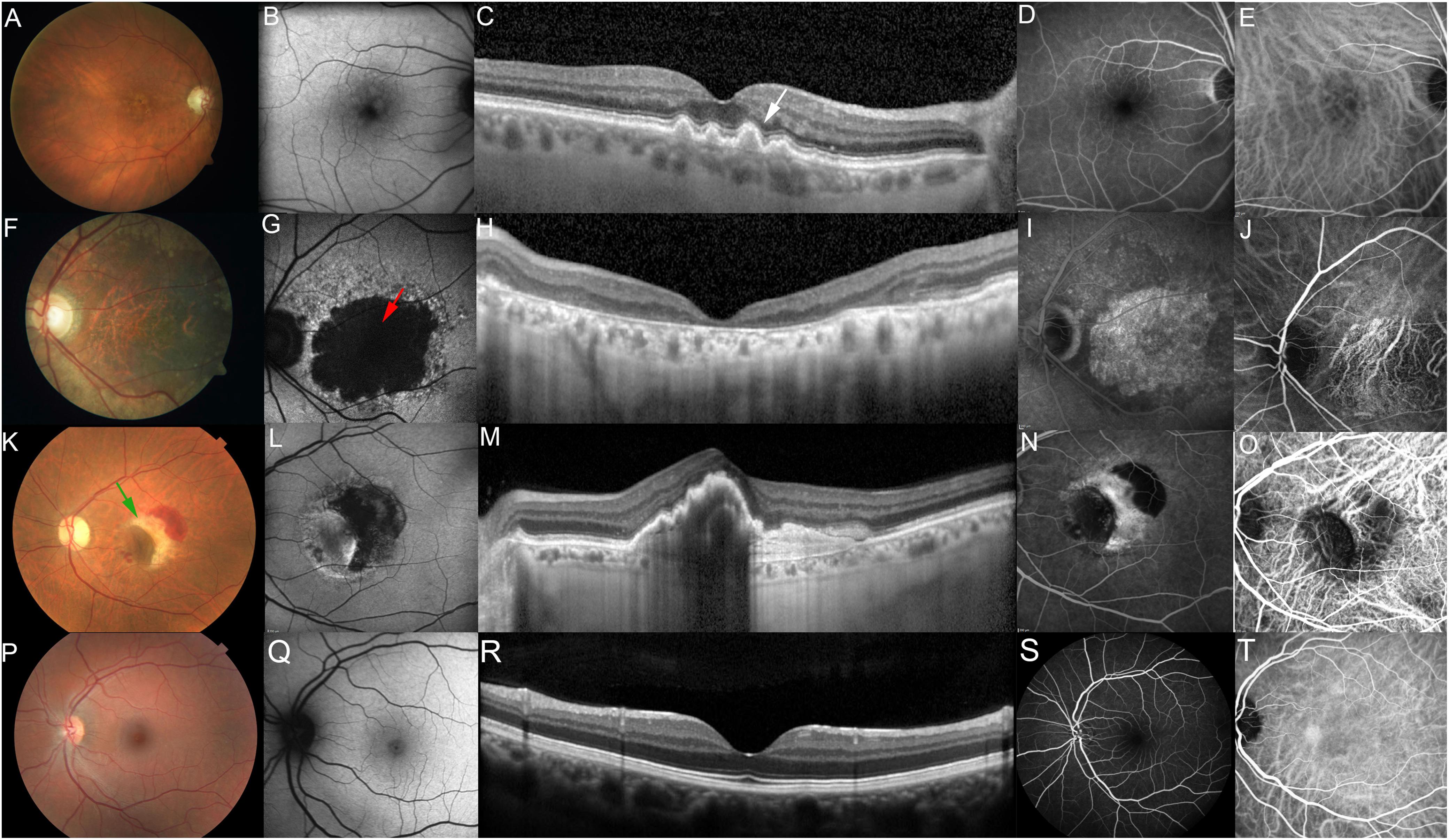
Frontiers Age Related Macular Degeneration Revisited From Pathology And Cellular Stress To Age related macular degeneration (amd) is the most common cause of irreversible vision loss among the elderly in western communities, with an estimated global prevalence of 10 – 20% in people older than 65 years. amd leads to central vision loss due to degeneration of the photoreceptors, retinal pigment epithelium and the choriocapillaris. Age related macular degeneration (amd) is a complex neurodegenerative visual disorder that causes profound physical and psychosocial effects. visual impairment in amd is caused by the loss of retinal pigmented epithelium (rpe) cells and the light sensitive photoreceptor cells that they support. there is currently no effective treatment for the.
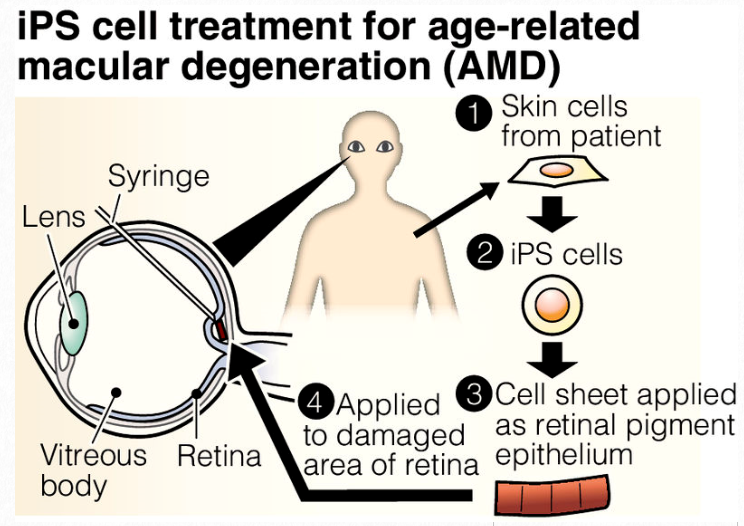
Ips Cell Treatment For Age Related Macular Degeneration Amd We present the available data of current clinical trials for the treatment of neovascular and dry age related macular degeneration with different aav based gene therapies. Joo seok han and colleagues report ng101, a recombinant aav vector encoding aflibercept, as a promising gene therapy candidate for wet age related macular degeneration. in non human primates, a single subretinal injection of ng101 effectively reduced choroidal neovascularization at very low doses, with sustained aflibercept expression and a favorable safety profile. Age related macular degeneration (amd) is a leading cause of blindness worldwide. the pathogenesis of amd involves dysfunction and loss of the retinal pigment epithelium (rpe), a monolayer of cells that provide nourishment and functional support for the overlying photoreceptors. rpe cells in mammals are not known to divide, renew or regenerate. Macular degeneration, age related, 2. age related macular degeneration (amd) is a complex neurodegenerative visual disorder that causes profound physical and psychosocial effects. visual impairment in amd is caused by the loss of retinal pigmented epithelium (rpe) cells and the light sensitive photoreceptor cells that they support.

Antioxidants Free Full Text Oxidative Stress Induced Cellular Senescence In Aging Retina And Age related macular degeneration (amd) is a leading cause of blindness worldwide. the pathogenesis of amd involves dysfunction and loss of the retinal pigment epithelium (rpe), a monolayer of cells that provide nourishment and functional support for the overlying photoreceptors. rpe cells in mammals are not known to divide, renew or regenerate. Macular degeneration, age related, 2. age related macular degeneration (amd) is a complex neurodegenerative visual disorder that causes profound physical and psychosocial effects. visual impairment in amd is caused by the loss of retinal pigmented epithelium (rpe) cells and the light sensitive photoreceptor cells that they support. Age related macular degeneration (amd) is a blinding disease triggered by degeneration of the retinal pigment epithelium (rpe), a monolayer tissue that functionally supports retinal photoreceptors. several recently published clinical and preclinical studies have tested psc derived rpe as a potential treatment for amd. Keywords: age related macular degeneration, cellular senescence, immune homeostasis dysregulation. introduction. age related macular degeneration (amd) is a major cause of blindness among the elderly in developed countries, and its prevalence is escalating due to an aging global population.

Comments are closed.