Eye Diagram Discovery Eye Foundation
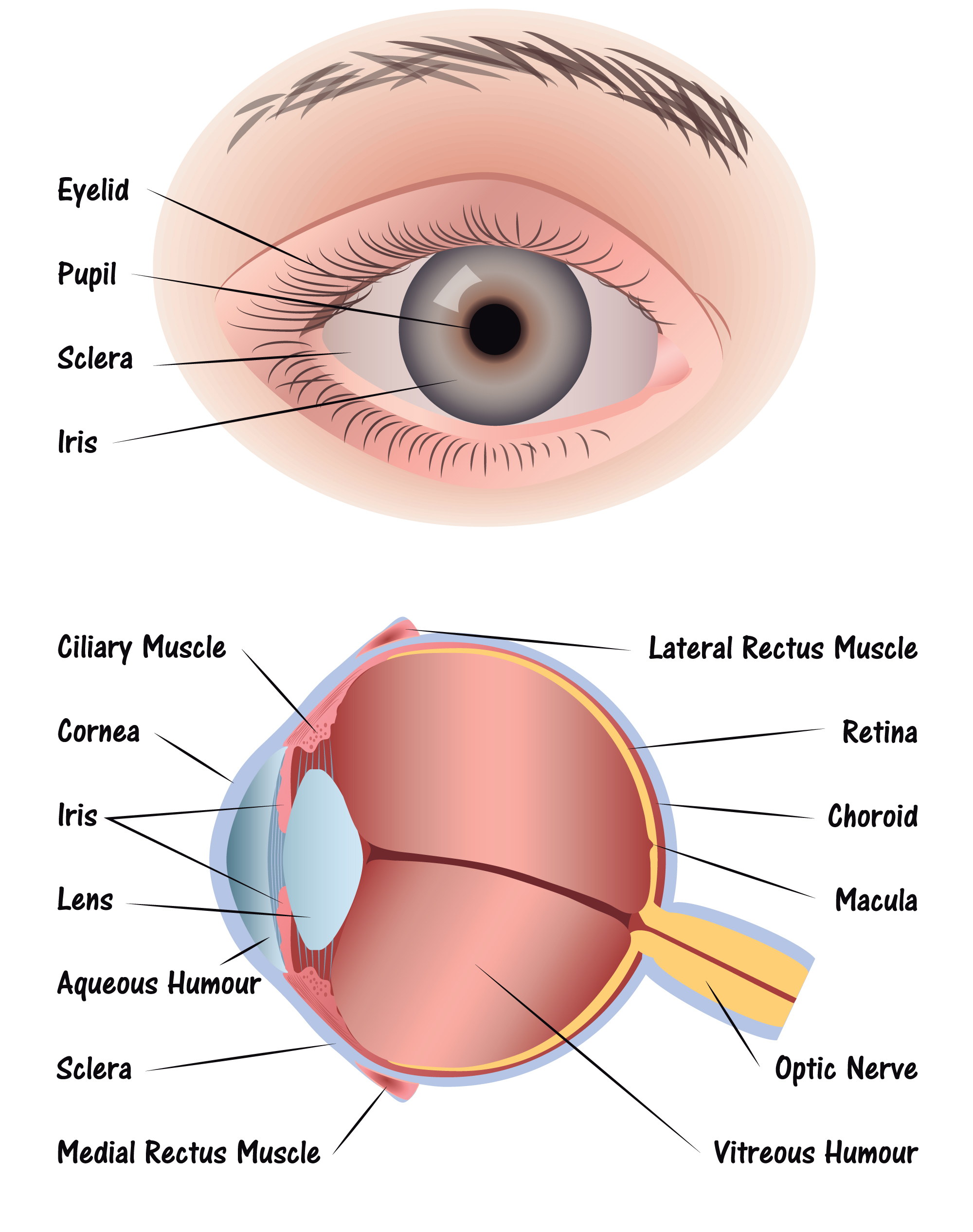
Eye Diagram Discovery Eye Foundation Help def unlock $100,000 matching gift. 100000. donate now. Discovery eye foundation march 12, 2015 anatomy of the eye, eye health, glaucoma. the optic nerve, a cable–like grouping of nerve fibers, connects and transmits visual information from the eye to the brain. the optic nerve is mainly composed of retinal ganglion cell (rgc) axons. in the human eye, the optic nerve receives light signals from.
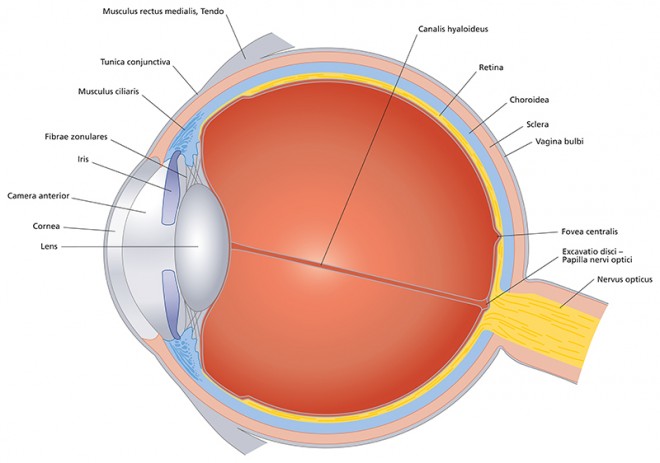
Eye Cross Section Discovery Eye Foundation Diagram of the eye. study the diagram below or click here for an interactive study guide and game! cornea: curved to bend light into your eye, its tough and clear like a windshield to protect your eye from dust. pupil: a hole in the middle of the iris that changes size to let in more or less light. iris: the colored part of the eye with two. These original videos discuss a variety of eye diseases, genetic factors, potential treatments and the researchers working to save vision. eye disease topics include age related macular. Behind the anterior chamber is the eye’s iris (the colored part of the eye) and the dark hole in the middle called the pupil. muscles in the iris dilate (widen) or constrict (narrow) the pupil to control the amount of light reaching the back of the eye. directly behind the pupil sits the lens. the lens focuses light toward the back of the eye. The following are parts of the human eyes and their functions: 1. conjunctiva. the conjunctiva is the membrane covering the sclera (white portion of your eye). the conjunctiva also covers the interior of your eyelids. the conjunctiva helps lubricate the eyes by generating mucus and tears. it also aids in immunological monitoring and prevents.
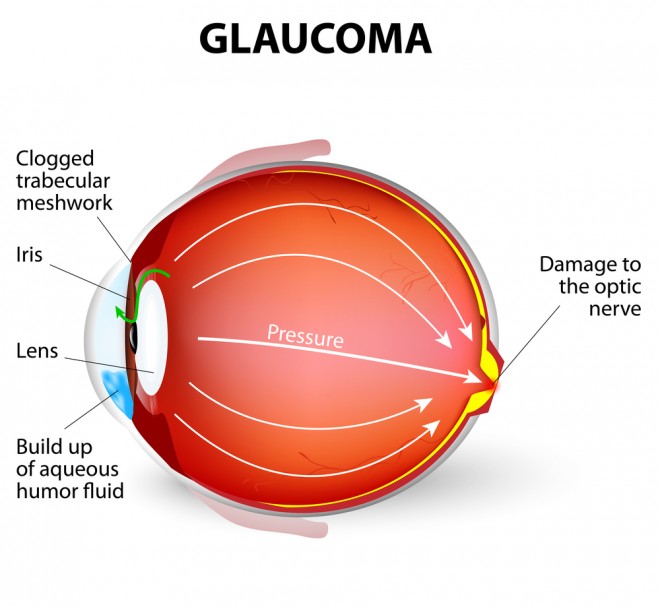
Glaucoma Diagram Discovery Eye Foundation Behind the anterior chamber is the eye’s iris (the colored part of the eye) and the dark hole in the middle called the pupil. muscles in the iris dilate (widen) or constrict (narrow) the pupil to control the amount of light reaching the back of the eye. directly behind the pupil sits the lens. the lens focuses light toward the back of the eye. The following are parts of the human eyes and their functions: 1. conjunctiva. the conjunctiva is the membrane covering the sclera (white portion of your eye). the conjunctiva also covers the interior of your eyelids. the conjunctiva helps lubricate the eyes by generating mucus and tears. it also aids in immunological monitoring and prevents. Choroid – this is made up of a layer of blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the retina. defect in the chm gene can cause choroideremia, leaky blood vessels can expand in the retina causing wet age related macular degeneration (amd) and diabetic retinopathy. retinal pigment epithelium – this is a single layer of cells that. The eye is a sense organ containing receptor cells which are sensitive to light intensity and colour. the purpose of the eye is to receive light and focus it onto the retina at the back of the eye. there are two main functions of the eye: accommodation to focus on near or distant objects. adaptation to dim light.

Comments are closed.