Frequency Distribution Table Meaning Examples
Frequency Distribution Definition Facts Examples Cuemath A frequency distribution table for grouped data is known as a grouped frequency distribution table. it is based on the frequencies of class intervals. as it is already discussed above that in this table, all the categories of data are divided into different class intervals of the same width, for example, 0 10, 10 20, 20 30, etc. To better understand your data’s distribution, consider the following steps: find the cumulative frequency distribution. create a relative frequency distribution. find the central tendency of your data. understand the variability of your data. calculate the descriptive statistics for your sample.

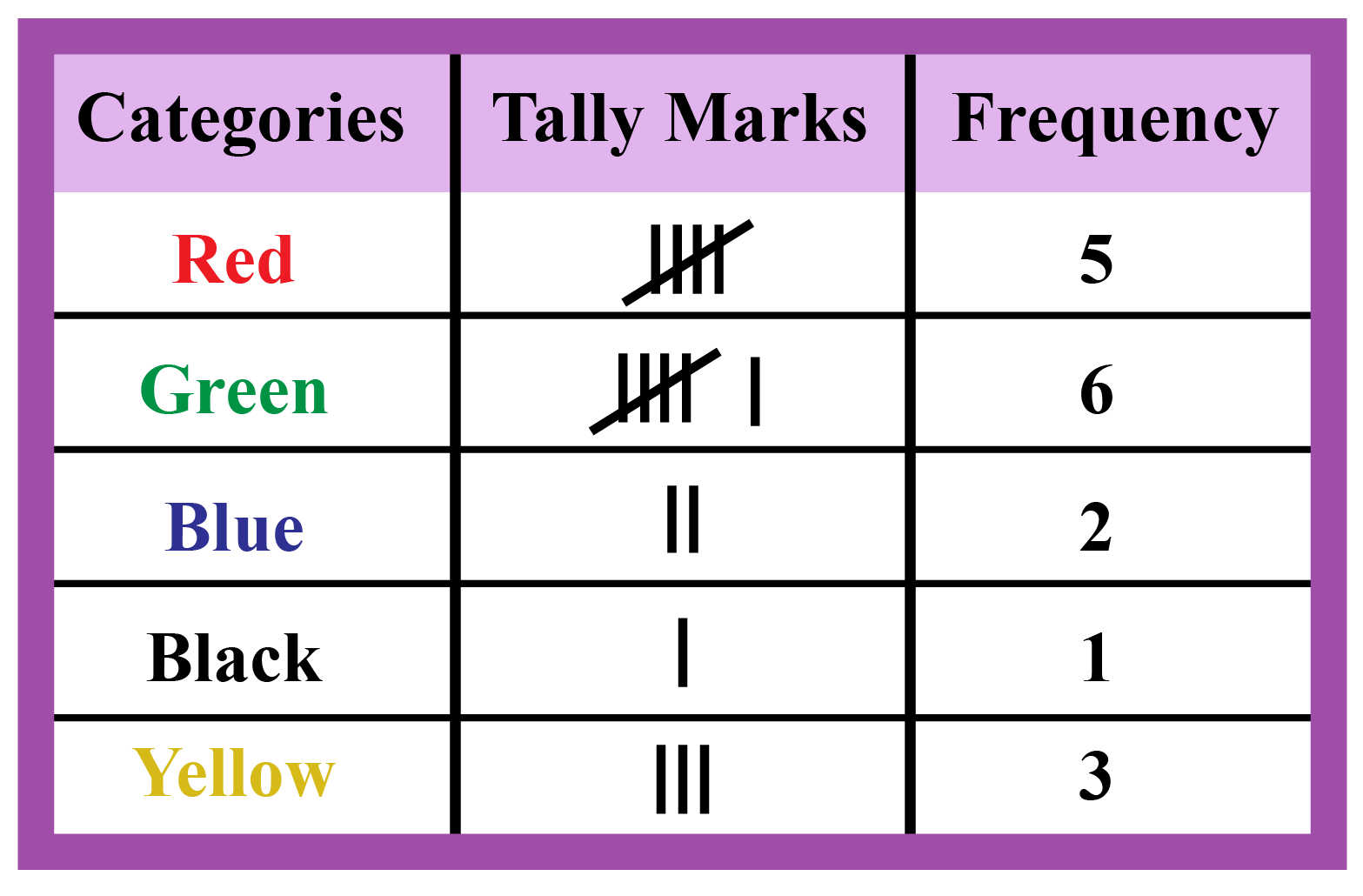
Frequency Distribution Definition Facts Examples Cuemath Steps. to make the frequency distribution table, first write the categories in one column (number of pets): next, tally the numbers in each category (from the results above). for example, the number zero appears four times in the list, so put four tally marks “||||”: finally, count up the tally marks and write the frequency in the final column. A frequency distribution describes the number of observations for each possible value of a variable. frequency distributions are depicted using graphs and frequency tables. example: frequency distribution. in the 2022 winter olympics, team usa won 25 medals. this frequency table gives the medals’ values (gold, silver, and bronze) and frequencies:. Step 1: to make a frequency chart, first, write the categories in the first column. step 2: in the next step, tally the score in the second column. step 3: and finally, count the tally to write the frequency of each category in the third column. thus, in this way, we can find the frequency distribution of an event. Frequency distribution examples. example 1: suppose we have a series, with a mean of 20 and a variance is 100. find out the coefficient of variation. solution: we know the formula for coefficient of variation, \frac {\sigma} {\bar {x}} \times 100 xˉσ ×100. given mean \bar {x} xˉ = 20 and variance \sigma^2 σ2 = 100.

Frequency Distribution Definition Facts Examples Cuemath Step 1: to make a frequency chart, first, write the categories in the first column. step 2: in the next step, tally the score in the second column. step 3: and finally, count the tally to write the frequency of each category in the third column. thus, in this way, we can find the frequency distribution of an event. Frequency distribution examples. example 1: suppose we have a series, with a mean of 20 and a variance is 100. find out the coefficient of variation. solution: we know the formula for coefficient of variation, \frac {\sigma} {\bar {x}} \times 100 xˉσ ×100. given mean \bar {x} xˉ = 20 and variance \sigma^2 σ2 = 100. The cumulative relative frequency is the sum of the relative frequencies. how to create a frequency table. let's take a look at an example. a biology teacher gave a quiz to the 20 students in her class. each of the students received a score out of 10, and she wants to show them how well they performed overall, as a group. here are the steps to. For example, using this frequency table, you can calculate the cumulative frequency distribution. to find the cumulative frequency, start with the first data point, 18, 18, 18, which has the frequency of 5. 5. 5. then add the frequency of the next age group, which is 6; 5 6 = 11. 6; 5 6 = 11. 6;5 6 = 11.

Frequency Distribution Definition Facts Examples Cuemath The cumulative relative frequency is the sum of the relative frequencies. how to create a frequency table. let's take a look at an example. a biology teacher gave a quiz to the 20 students in her class. each of the students received a score out of 10, and she wants to show them how well they performed overall, as a group. here are the steps to. For example, using this frequency table, you can calculate the cumulative frequency distribution. to find the cumulative frequency, start with the first data point, 18, 18, 18, which has the frequency of 5. 5. 5. then add the frequency of the next age group, which is 6; 5 6 = 11. 6; 5 6 = 11. 6;5 6 = 11.
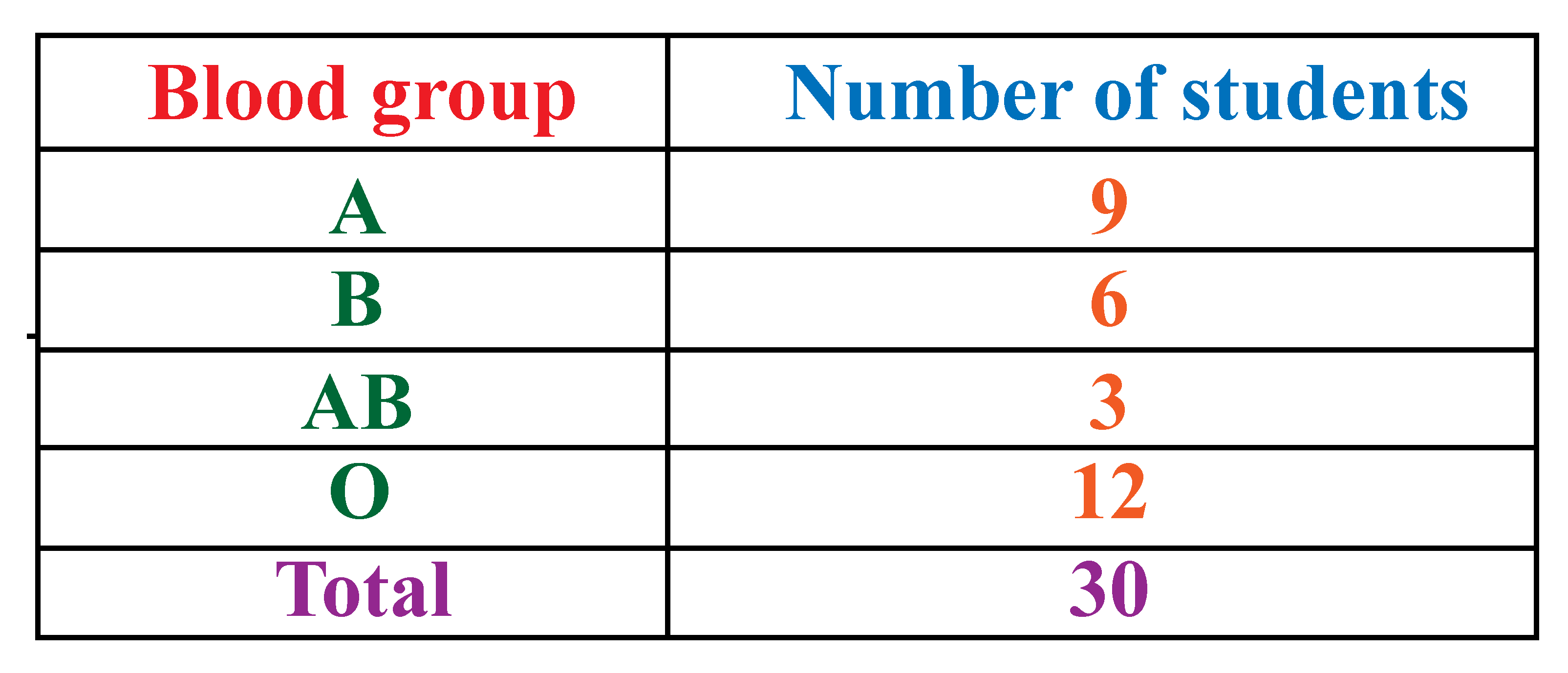
Frequency Distribution Definition Facts Examples Cuemath

Comments are closed.