Glial Cells Astrocytes Microglia Oligodendrocytes Schwann Cells Ependymal Cells

Types Of Neuroglia Classification Of Glial Cells Microglia Astrocytes Oligodendrocytes And Many glial cells provide support for an essential nervous system function. in addition to providing support for neurons, glial cells aid in the maintenance of homeostasis, and form myelin. as a whole, glial cells are the most abundant cells in the central nervous system. the most notable glial cells include oligodendrocytes, schwann cells, astrocytes, microglia, and ependymal cells. most glial. These cells have an important role in supporting the brain. glial cells are a type of cell that provides physical and chemical support to neurons and maintain their environment. located in the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system, glial cells are sometimes called the "glue" of the nervous system, as well as neuroglia or just glia.
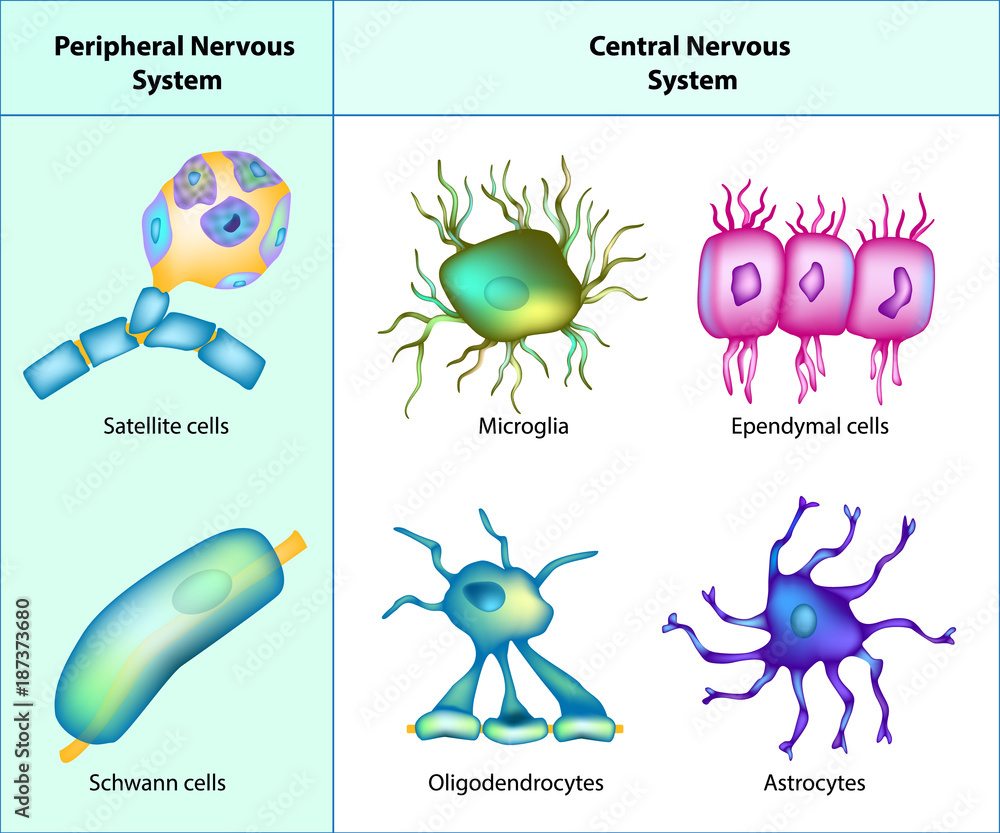
Types Of Neuroglia Oligodendrocytes Astrocytes Microglia Schwann Cells Satellite Cells The microglial cell population accounts for roughly 5% of the glial population. these cells are small, their nuclei are elongated and their cytoplasm is sparse. the cells are found in both white and grey matter. they originate from the monocyte cell line (specialized macrophage derived from myeloid precursor cells) and act as the immune. Neuroglia in the cns include astrocytes, microglial cells, ependymal cells, and oligodendrocytes. in the human brain, it is estimated that the total number of glia roughly equals the number of neurons, although the proportions vary in different brain areas. astrocytes are delicate, star shaped branching glial cells. In the central nervous system, glia develop from the ventricular zone of the neural tube. these glia include the oligodendrocytes, ependymal cells, and astrocytes. in the peripheral nervous system, glia derive from the neural crest. these pns glia include schwann cells in nerves and satellite glial cells in ganglia. There are three types of glial cells in the mature central nervous system: astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglial cells (figure 1.4a — c).astrocytes, which are restricted to the brain and spinal cord, have elaborate local processes that give these cells a starlike appearance (hence the prefix “astro”).
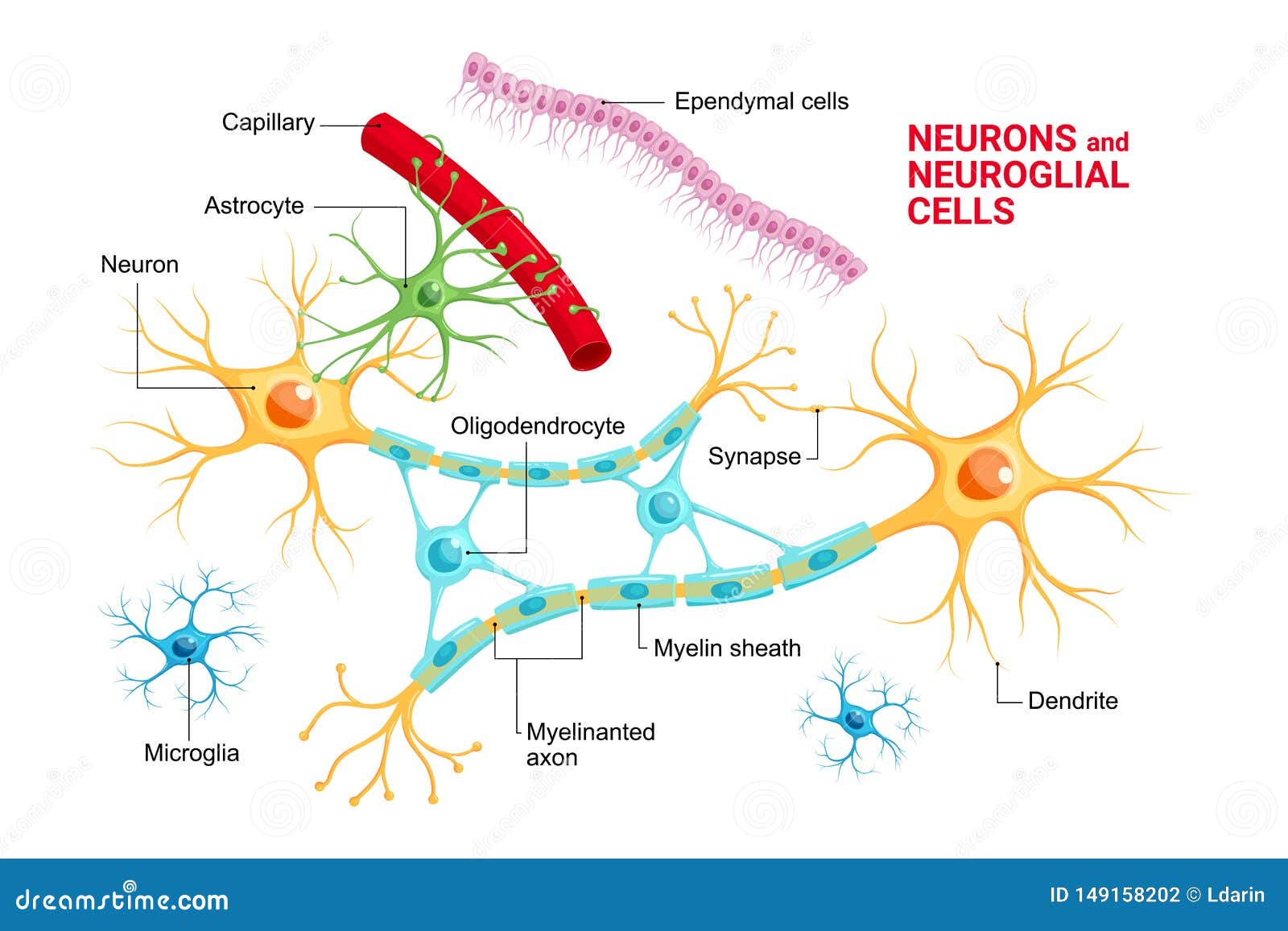
Vector Infographic Of Neuron And Glial Cells Neuroglia Astrocyte Microglia And Oligodendrocyte In the central nervous system, glia develop from the ventricular zone of the neural tube. these glia include the oligodendrocytes, ependymal cells, and astrocytes. in the peripheral nervous system, glia derive from the neural crest. these pns glia include schwann cells in nerves and satellite glial cells in ganglia. There are three types of glial cells in the mature central nervous system: astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglial cells (figure 1.4a — c).astrocytes, which are restricted to the brain and spinal cord, have elaborate local processes that give these cells a starlike appearance (hence the prefix “astro”). Other types of macroglia. ependymal cells: ependymal cells line the spinal cord and ventricles of the brain. they are involved in creating cerebrospinal fluid (csf). radial glia: radial glial cells are progenitor cells that can generate neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. schwann cells: similar to oligodendrocytes in the central nervous. The main types of cns glia include astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, ependymal cells, radial glia, and microglia. in the pns, the main glial cells are schwann cells, satellite cells, and enteric glia. these cells differ and are classified according to their morphologies, distinct anatomical locations in the nervous system, functions, developmental.
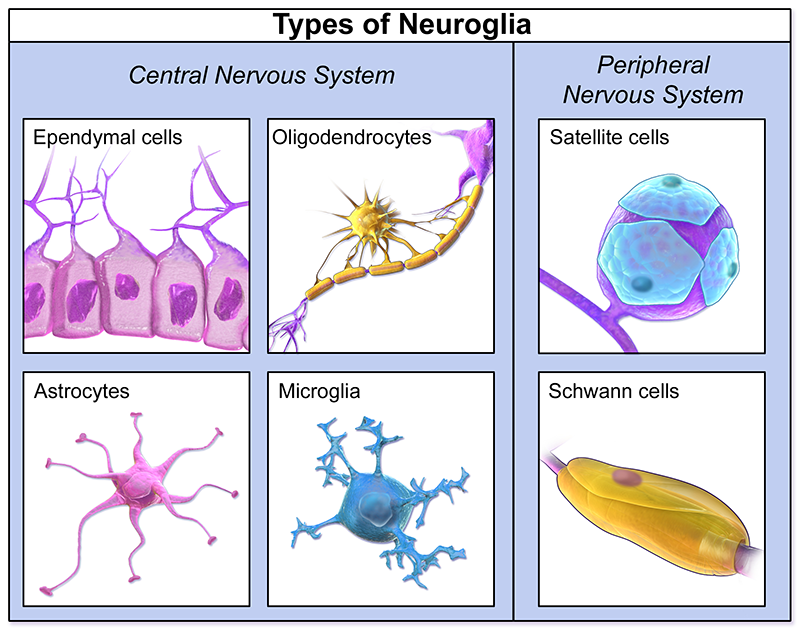
Satellite Cells And Schwann Cells Other types of macroglia. ependymal cells: ependymal cells line the spinal cord and ventricles of the brain. they are involved in creating cerebrospinal fluid (csf). radial glia: radial glial cells are progenitor cells that can generate neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. schwann cells: similar to oligodendrocytes in the central nervous. The main types of cns glia include astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, ependymal cells, radial glia, and microglia. in the pns, the main glial cells are schwann cells, satellite cells, and enteric glia. these cells differ and are classified according to their morphologies, distinct anatomical locations in the nervous system, functions, developmental.

Comments are closed.