Histology Of Muscle Tissue Cardiac Muscle Skeletal Muscle Smooth Muscle Anatomy Youtube

Histology Of Muscle Tissue Cardiac Muscle Skeletal Muscle Smooth Muscle Anatomy Youtube What’s the difference between skeletal muscle, cardiac, and smooth muscle? and how can we tell them apart under a microscope? in this video, we’ll also go ov. Three types of muscle tissue (smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscle tissue) are found in the human body. in this anatomy review compilation, i cover some of t.

Muscle Histology Lab Skeletal Vs Cardiac Vs Smooth Muscle Youtube This video is about the histology of muscular tissue, types and functions with clinical correlations in detail.follow me @ human anatomylessons.blogs. Muscle cells, commonly known as myocytes, are the cells that make up muscle tissue. there are 3 types of muscle cells in the human body; cardiac, skeletal, and smooth. skeletal muscle cells are long, cylindrical, multi nucleated and striated. each nucleus regulates the metabolic requirements of the sarcoplasm around it. Smooth muscle is a type of tissue found in the walls of hollow organs, such as the intestines, uterus and stomach. you can also find smooth muscle in the walls of passageways, including arteries and veins of the cardiovascular system. this type of involuntary non striated muscle is also found in the tracts of the urinary, respiratory and. Skeletal muscle histology. this type of tissue is found in skeletal muscles and is responsible for the voluntary movements of bones. skeletal muscle is an excitable, contractile tissue responsible for maintaining posture and moving the orbits, together with the appendicular and axial skeletons. it attaches to bones and the orbits through tendons.
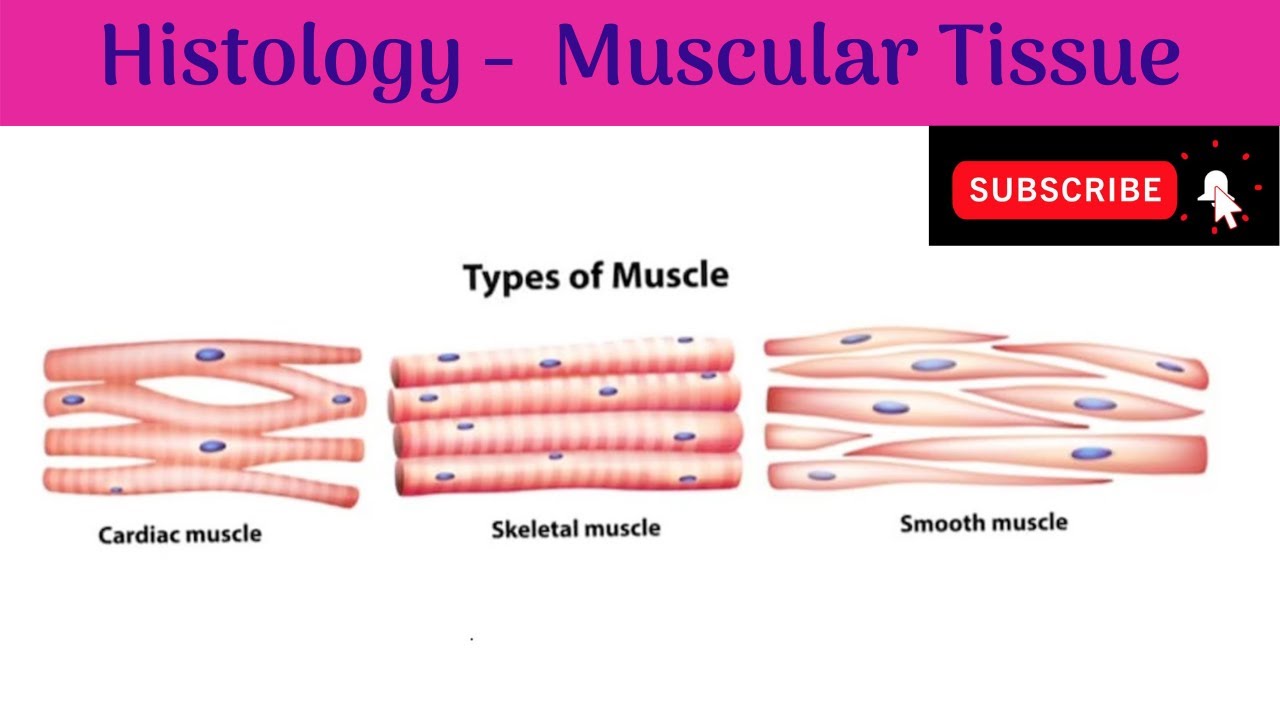
Histology Of Muscular Tissue Skeletal Cardiac Smooth Muscles Clinical Correlations Youtube Smooth muscle is a type of tissue found in the walls of hollow organs, such as the intestines, uterus and stomach. you can also find smooth muscle in the walls of passageways, including arteries and veins of the cardiovascular system. this type of involuntary non striated muscle is also found in the tracts of the urinary, respiratory and. Skeletal muscle histology. this type of tissue is found in skeletal muscles and is responsible for the voluntary movements of bones. skeletal muscle is an excitable, contractile tissue responsible for maintaining posture and moving the orbits, together with the appendicular and axial skeletons. it attaches to bones and the orbits through tendons. Muscle tissue is composed of cells specialized for contraction. muscle is classified into three types according to their structure and function: skeletal and cardiac muscle cells are called striated because they show an alternating series of bands. the repeating arrangement of their basic contractile unit, the sarcomere, produces these striations. There are three varieties of human of muscles: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. skeletal striated muscle is the most abundant type (over 400 distinct muscles), is the only muscle under voluntary control, and in individuals with normal body mass index, represents approximately 40% of their body weight.[1] smooth muscle manages contraction of non voluntary muscles. the role of smooth muscle in.

Comments are closed.