How Cones And Rods Function In The Eye Oxford Vision Care

How Cones And Rods Function In The Eye Oxford Vision Care Rods are the reason we can see in the dark. they detect low levels of light and makeup what is called our scotopic vision (cones make up our photopic vision). while cones give us more detailed information, rods are by far more sensitive. rods are the reason you can see shapes in low levels of light and are responsible for our peripheral vision. Implications for vision and eye care. understanding the functions of cones and rods is essential for diagnosing and addressing vision related disorders. certain conditions, such as color blindness, can arise from abnormalities in cone function. rod dysfunction, on the other hand, can result in night blindness or reduced peripheral vision.

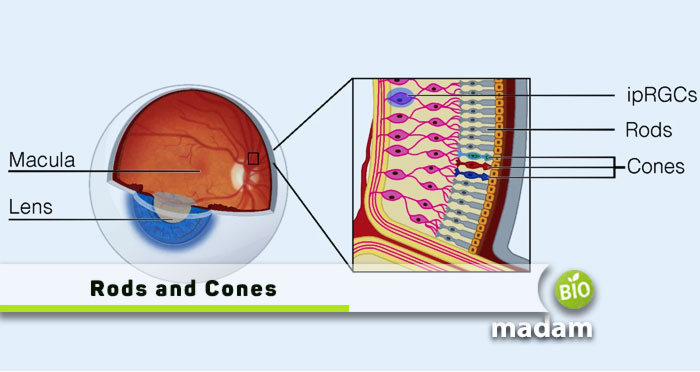
Rods And Cones In The Eye Diagram At Jerome Kilgore Blog Lining your retinas are millions of special cells called photoreceptors. these cells are the key to turning light that enters your eyes into a form your brain can use for your sense of vision. photoreceptors can be rod or cone shaped, and those shapes are part of how you can see in dim and bright conditions, and how you can see colors. The retina is the light sensitive part at the back of the eye. there are two photoreceptor types: rods and cones. signals from these photoreceptors are sent to the brain for processing via the optic nerve. the optic nerve is a bundle of nerve fibers that connects each eye’s retina to the brain. 1. there are more rod photoreceptors than cone. Vision is made possible by nerve cells on the retina of your eye known as cones. about 6 million of these cones allow us to see the world in all its colorful hues. they work together with 120 million rods, which provide black and white vision. this article explains the types and structure of eye cones, how they function, and problems with your. Photoreceptors and their function in the eye. small cells called photoreceptors in the eye play a vital role in night vision and also affect how the eye sees color. photoreceptor cells are located in the retina, which is the light sensitive tissue that lines the back of the eye. there are two kinds of photoreceptor cells: cones and rods.

Cones In Eye Vision is made possible by nerve cells on the retina of your eye known as cones. about 6 million of these cones allow us to see the world in all its colorful hues. they work together with 120 million rods, which provide black and white vision. this article explains the types and structure of eye cones, how they function, and problems with your. Photoreceptors and their function in the eye. small cells called photoreceptors in the eye play a vital role in night vision and also affect how the eye sees color. photoreceptor cells are located in the retina, which is the light sensitive tissue that lines the back of the eye. there are two kinds of photoreceptor cells: cones and rods. Anatomy of the retina. the human retina consists of layers of neural tissue that line the entire back wall of the eye. it’s the only extension of the brain visible from outside the body (via a retinal exam). 1. the retina attaches to the optic nerve at the optic disc. the optic nerve is one of the main cranial nerves coming from the brain. Rods and cones are the receptors in the retina responsible for your sense of sight. they are the part of the eye responsible for converting the light that enters your eye into electrical signals that can be decoded by the vision processing center of the brain. cones are responsible for color vision. every green mark on this image is a specific.

Human Eye Diagram With Rods And Cones Anatomy of the retina. the human retina consists of layers of neural tissue that line the entire back wall of the eye. it’s the only extension of the brain visible from outside the body (via a retinal exam). 1. the retina attaches to the optic nerve at the optic disc. the optic nerve is one of the main cranial nerves coming from the brain. Rods and cones are the receptors in the retina responsible for your sense of sight. they are the part of the eye responsible for converting the light that enters your eye into electrical signals that can be decoded by the vision processing center of the brain. cones are responsible for color vision. every green mark on this image is a specific.
Eyesight Rods Cones

Comments are closed.