How Do Opiates Work In The Brain
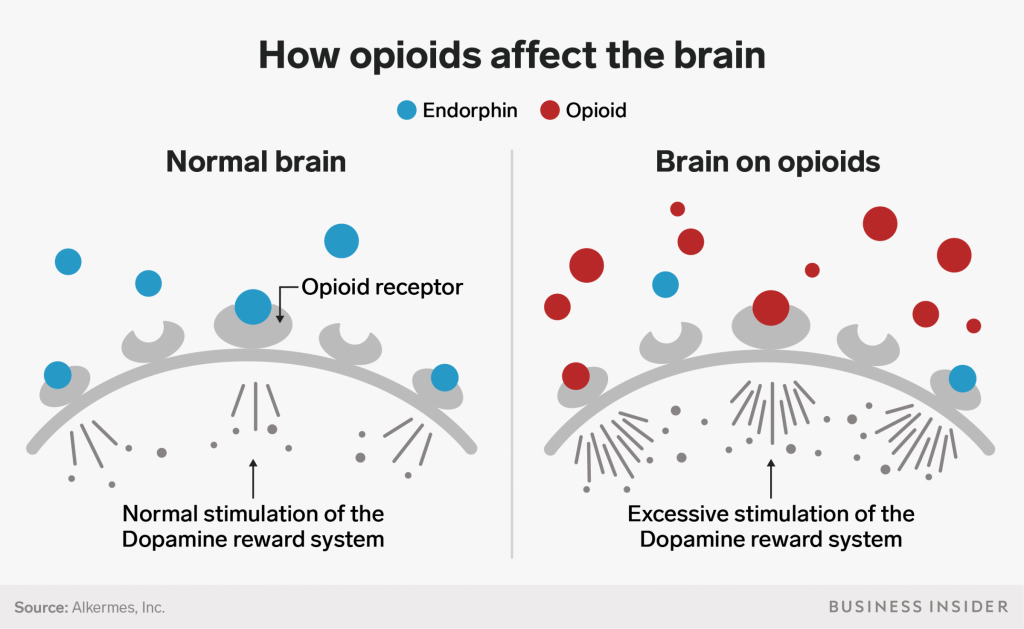
How Do Opiates Work In The Brain Opioids work by activating opioid receptors on nerve cells. these receptors belong to a family of proteins known as g protein coupled receptors (gpcrs). scientists have always assumed that all opioids—whether produced by the body (endogenously) or taken as a drug—interact in the same way with opioid receptors. Current neurobiological theories of addiction and relevance to oud. prevailing neurobiological theories conceptualize addiction as a chronic, relapsing brain disorder in which initial, voluntary drug use progresses into compulsive, uncontrolled drug seeking and taking (50).

Opioids Rewire The Brain Ohsu Scientist Says Oregonlive The spinal cord: opioids may also affect the spinal cord, which is like a central highway for nerve cells traveling throughout your body. these effects may play a role in pain relief. the. When opioid drugs infiltrate a part of the brain stem called the locus ceruleus, their receptors slow respiration, cause constipation, lower blood pressure and decrease alertness. addiction begins. The effects of opioids on the brain result in euphoria, reduced pain, and suppressed breathing. these symptoms occur as opioids attach to and activate opioid receptors in brain nerve cells. long. The brain is made up of many parts with interconnected circuits that all work together as a team. different brain circuits are responsible for coordinating and performing specific functions. networks of neurons send signals back and forth to each other and among different parts of the brain, the spinal cord, and nerves in the rest of the body.
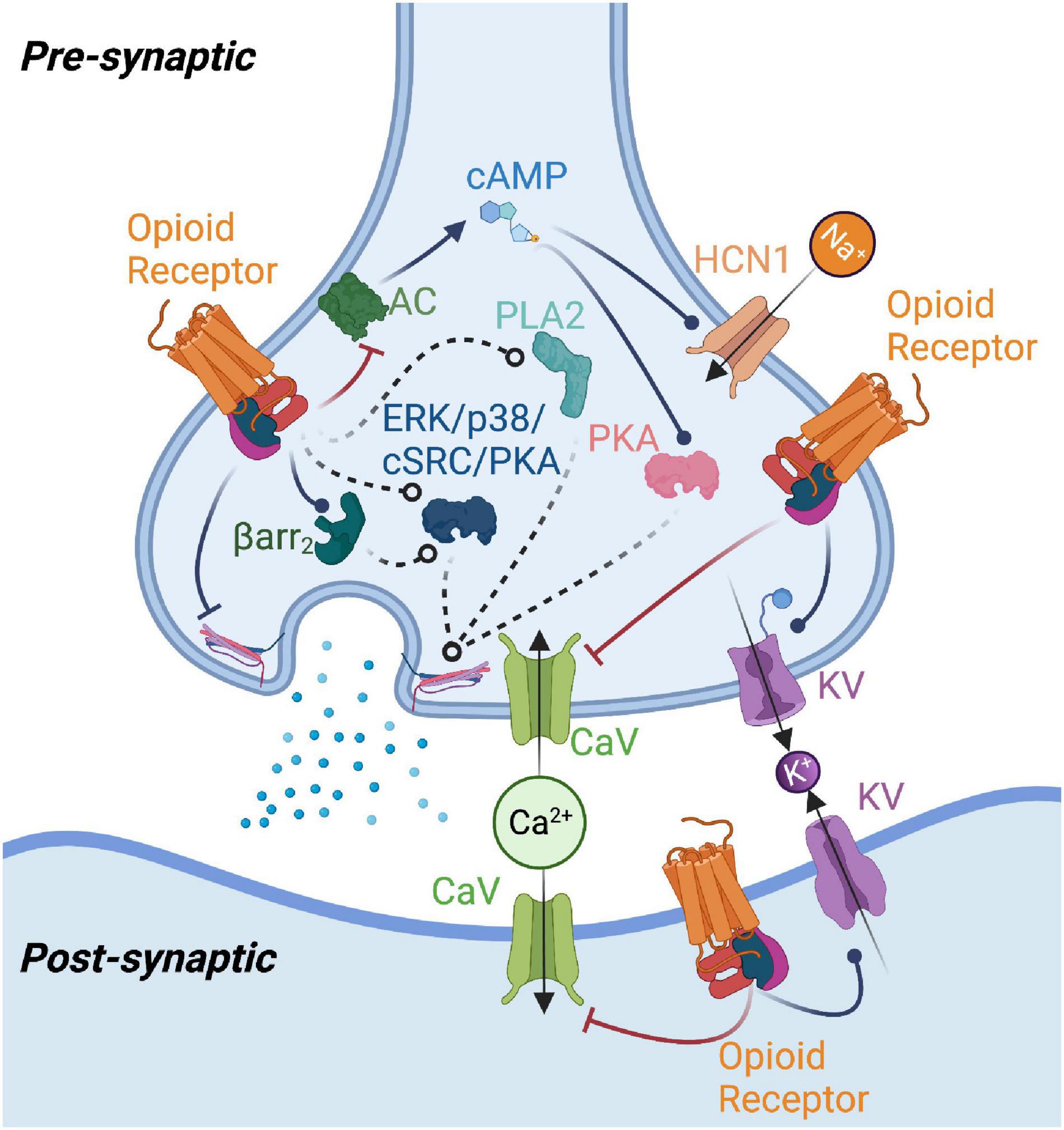
Frontiers Opioid Receptor Mediated Regulation Of Neurotransmission In The Brain The effects of opioids on the brain result in euphoria, reduced pain, and suppressed breathing. these symptoms occur as opioids attach to and activate opioid receptors in brain nerve cells. long. The brain is made up of many parts with interconnected circuits that all work together as a team. different brain circuits are responsible for coordinating and performing specific functions. networks of neurons send signals back and forth to each other and among different parts of the brain, the spinal cord, and nerves in the rest of the body. Opioids. hi there! mind matters is a series that explores the ways that different drugs affect your brain, body, and life. in this issue we are going to talk about opioids. you may have heard a lot about opioids lately. it’s possible you know them as drugs called oxy or vikes. opioids have been used for thousands of years. 00:45 the neuroscience of fentanyl addiction. research in mice has shown that fentanyl addiction is the result of two brain circuits working in tandem, rather than a single neural pathway as had.

Comments are closed.