How To Construct A Grouped Frequency Distribution Frequency Distribution Table Definition

How To Construct A Grouped Frequency Distribution Frequency Distribution Table Definition Example 1: whole numbers. sort these 20 20 items into the grouped frequency table. using the set of data, account for each item with a tally mark in the table. 2 fill in the frequency column. add up the tally marks and fill in the frequency column. 3 find the cumulative frequency and the relative frequency, if needed. Starting at 0 and with a group size of 4 we get: 0, 4, 8, 12, 16. write down the groups. include the end value of each group that must be less than the next group: the last group goes to 19 which is greater than the largest value. that is ok: the main thing is that it must include the largest value.

How To Construct A Frequency Distribution Table The Simple Tricks For Both Grouped And Steps. to make the frequency distribution table, first write the categories in one column (number of pets): next, tally the numbers in each category (from the results above). for example, the number zero appears four times in the list, so put four tally marks “||||”: finally, count up the tally marks and write the frequency in the final column. To calculate the relative frequencies, divide each frequency by the sample size. the sample size is the sum of the frequencies. example: relative frequency distribution. from this table, the gardener can make observations, such as that 19% of the bird feeder visits were from chickadees and 25% were from finches. 2. 7. 1. a frequency is the number of times a value of the data occurs. according to table table 2.1.1 2.1. 1, there are three students who work two hours, five students who work three hours, and so on. the sum of the values in the frequency column, 20, represents the total number of students included in the sample. To better understand your data’s distribution, consider the following steps: find the cumulative frequency distribution. create a relative frequency distribution. find the central tendency of your data. understand the variability of your data. calculate the descriptive statistics for your sample.
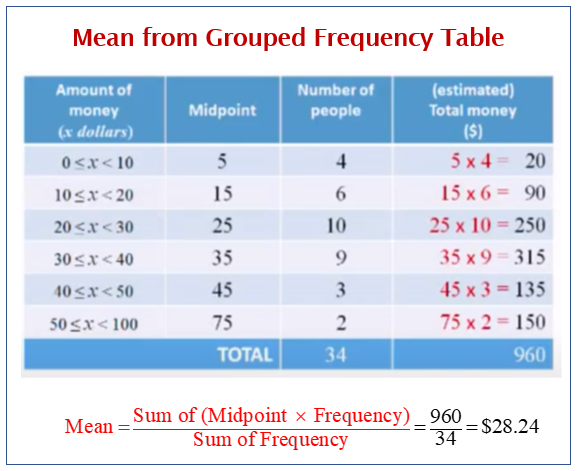
Grouped Frequency Tables Examples Solutions Videos Worksheets Activities 2. 7. 1. a frequency is the number of times a value of the data occurs. according to table table 2.1.1 2.1. 1, there are three students who work two hours, five students who work three hours, and so on. the sum of the values in the frequency column, 20, represents the total number of students included in the sample. To better understand your data’s distribution, consider the following steps: find the cumulative frequency distribution. create a relative frequency distribution. find the central tendency of your data. understand the variability of your data. calculate the descriptive statistics for your sample. A frequency distribution table for grouped data is known as a grouped frequency distribution table. it is based on the frequencies of class intervals. as it is already discussed above that in this table, all the categories of data are divided into different class intervals of the same width, for example, 0 10, 10 20, 20 30, etc. How to construct a frequency distribution. there are a number of types of frequency distributions. the table above is an example of a grouped frequency distribution, which is a frequency distribution with a large range of values such that the data is usually grouped into classes that are larger than one unit in width.

How To Construct A Frequency Distribution For Grouped Data Algebra Study A frequency distribution table for grouped data is known as a grouped frequency distribution table. it is based on the frequencies of class intervals. as it is already discussed above that in this table, all the categories of data are divided into different class intervals of the same width, for example, 0 10, 10 20, 20 30, etc. How to construct a frequency distribution. there are a number of types of frequency distributions. the table above is an example of a grouped frequency distribution, which is a frequency distribution with a large range of values such that the data is usually grouped into classes that are larger than one unit in width.

Comments are closed.