Human Eye Anatomy Parts And Structure Online Biology Notes
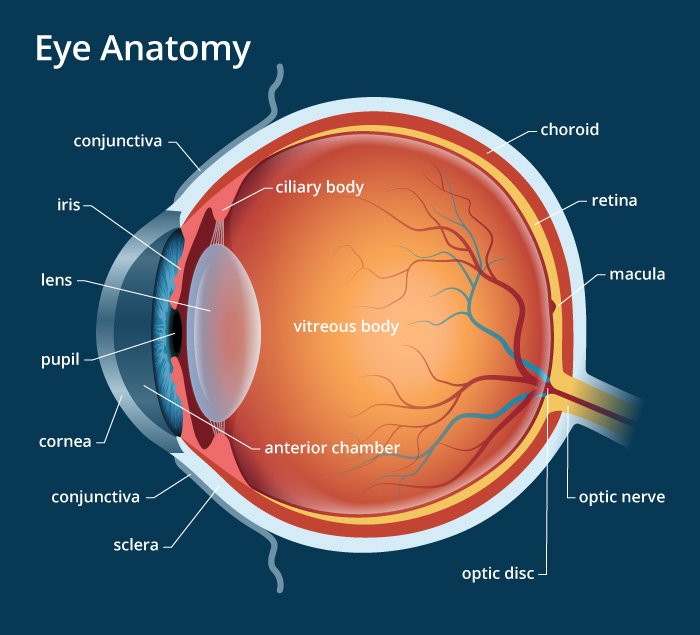
Human Eye Anatomy Parts And Structure Online Biology Notes Human eye: anatomy, parts and structure. the eye is the photo receptor organ. size and shape: human eye is spherical about 2.5 cm in diameter. location: it is situated on an orbit of skull and is supplied by optic nerve. there are 6 sets of muscles attached to outer surface of eye ball which helps to rotate it in different direction. Anatomy of the eye. the eye is a globe shaped organ nestled within the eye socket (orbit) of the skull. it consists of several layers that work together to capture and process light. sclera: the outermost layer is the sclera, commonly known as the “white of the eye.”. it’s a tough and protective layer that maintains the eye’s shape.
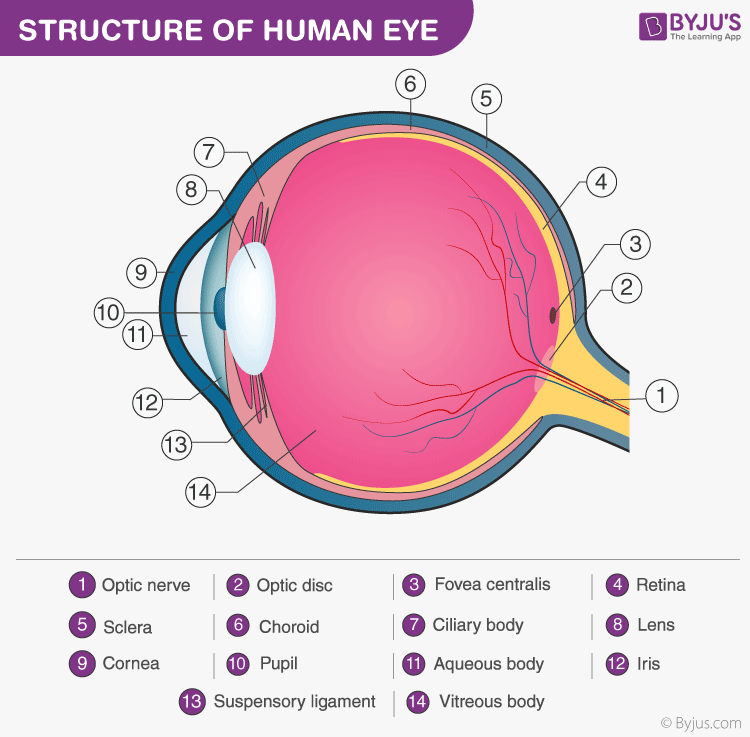
Structure And Functions Of Human Eye With Labelled Diagram Eye parts and functions. the eye has many parts which work together to accomplish vision, and to keep the structures required for vision safe from infection and injury. these parts include: the conjunctiva. the surface of the eye and of the inner eyelids is covered by a clear, protective membrane called the “conjunctiva.”. Now that you know the names of the parts of the eye, it’s easy to follow the steps leading to vision. cornea: light enters the eye through the cornea. because of the shape of the cornea, it exits pre focused. aqueous humor pupil: from the cornea, light passes through the aqueous humor and through the pupil. Figure 36.13.1 36.13. 1: rods and cones: rods and cones are photoreceptors in the retina. rods respond in low light and can detect only shades of gray. cones respond in intense light and are responsible for color vision. the fovea is the region in the center back of the eye that is responsible for acute (central) vision. Briefly explain the structure of the human eye. the human eye is a roughly spherical organ, responsible for perceiving visual stimuli. it is enclosed within the eye sockets in the skull and is anchored down by muscles within the sockets. anatomically, the eye comprises two components fused into one; hence, it does not possess a perfect.
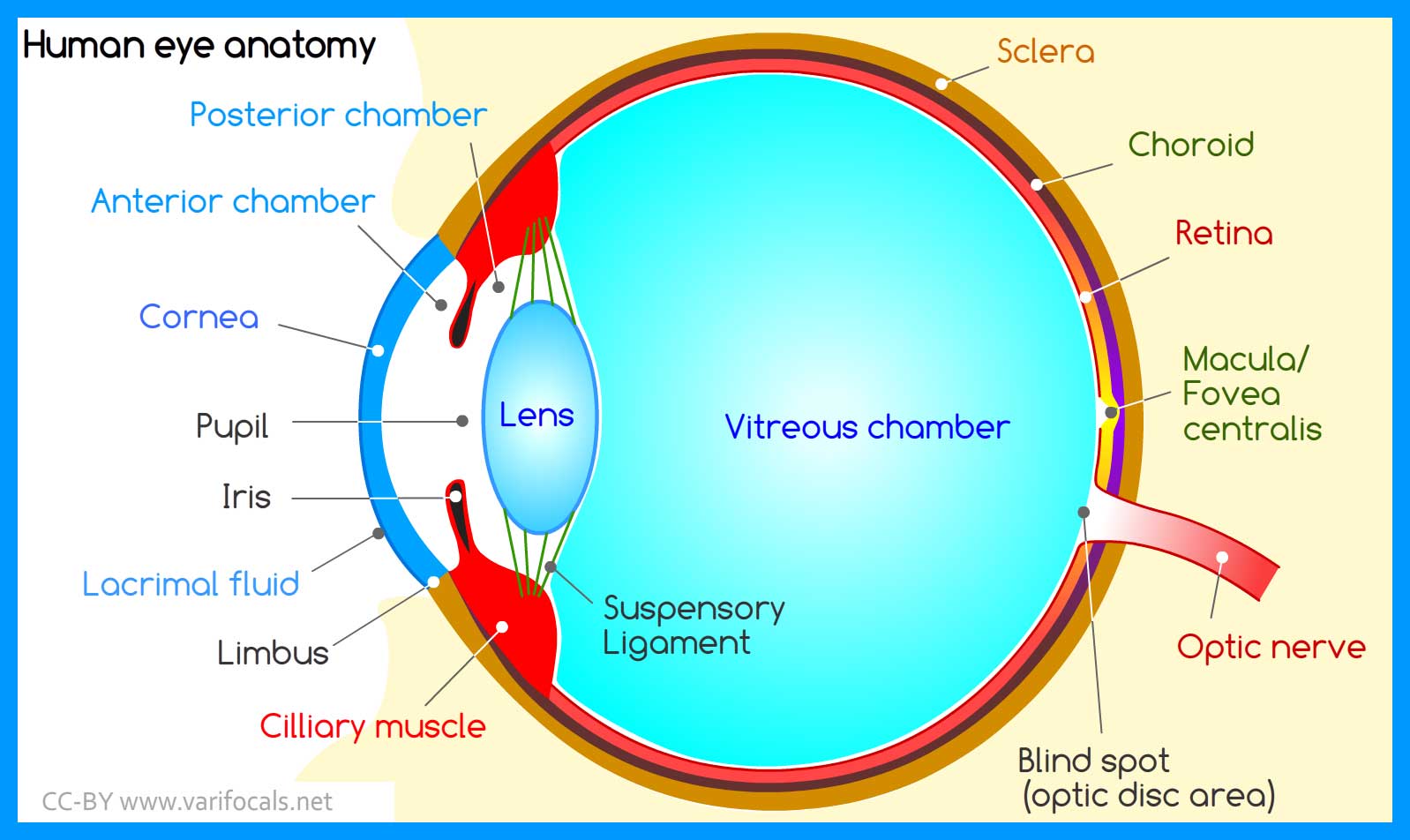
Human Eye Anatomy Structure And Function Figure 36.13.1 36.13. 1: rods and cones: rods and cones are photoreceptors in the retina. rods respond in low light and can detect only shades of gray. cones respond in intense light and are responsible for color vision. the fovea is the region in the center back of the eye that is responsible for acute (central) vision. Briefly explain the structure of the human eye. the human eye is a roughly spherical organ, responsible for perceiving visual stimuli. it is enclosed within the eye sockets in the skull and is anchored down by muscles within the sockets. anatomically, the eye comprises two components fused into one; hence, it does not possess a perfect. Introduction. the human eye is a complex organ that allows us to perceive the world around us. it plays a critical role in our daily lives, allowing us to see and interpret visual information. in this chapter, we will explore the anatomy and physiology of the human eye, including its structure, function, and clinical significance. Human eye, specialized sense organ in humans that is capable of receiving visual images, which are relayed to the brain. the anatomy of the eye includes auxiliary structures, such as the bony eye socket and extraocular muscles, as well as the structures of the eye itself, such as the lens and the retina.
/GettyImages-695204442-b9320f82932c49bcac765167b95f4af6.jpg)
Structure And Function Of The Human Eye Introduction. the human eye is a complex organ that allows us to perceive the world around us. it plays a critical role in our daily lives, allowing us to see and interpret visual information. in this chapter, we will explore the anatomy and physiology of the human eye, including its structure, function, and clinical significance. Human eye, specialized sense organ in humans that is capable of receiving visual images, which are relayed to the brain. the anatomy of the eye includes auxiliary structures, such as the bony eye socket and extraocular muscles, as well as the structures of the eye itself, such as the lens and the retina.
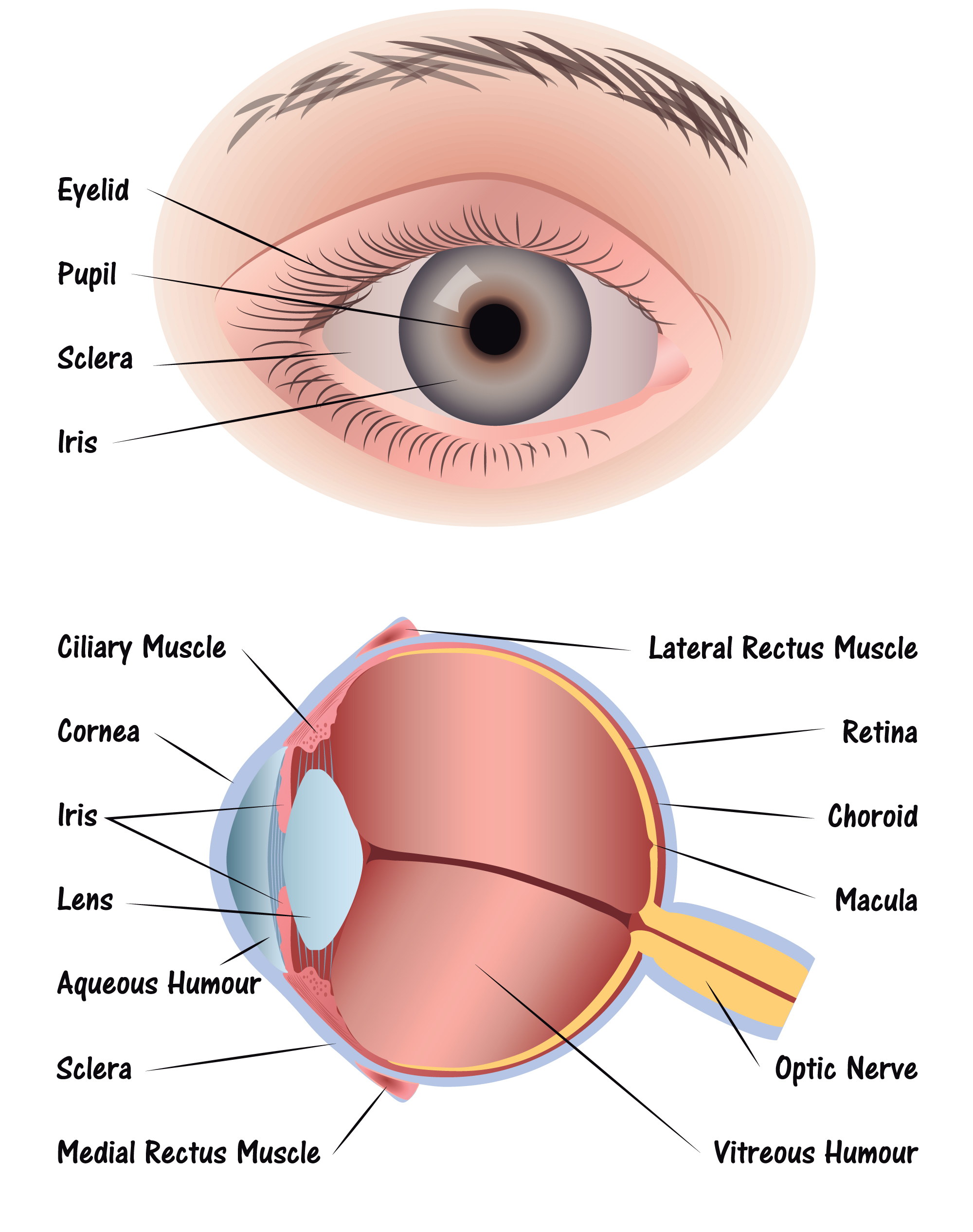
Eye Diagram Discovery Eye Foundation

Comments are closed.