Is Congenital Cataract Reversible They Can Be Treated

Treatment For Congenital Cataracts Kids Eye Gear Key takeaways. congenital cataract is a clouding of the lens in the eye that is present at birth. causes of congenital cataract can include genetic factors, infections during pregnancy, and metabolic disorders. risk factors for congenital cataract include family history of cataracts, maternal age, and certain medical conditions like diabetes. Congenital cataracts also can occur when, during pregnancy, the mother develops infections such as measles or rubella (the most common cause), rubeola, chicken pox, cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex, herpes zoster, poliomyelitis, influenza, epstein barr virus, syphilis and toxoplasmosis. older babies and children also can be diagnosed with.
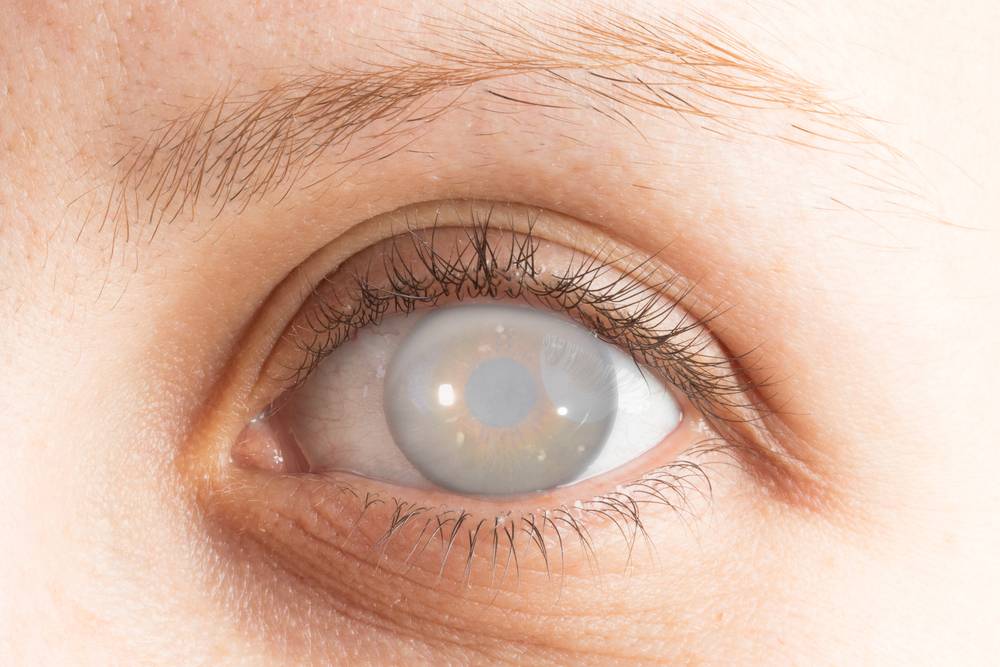
Congenital Cataract Treatment Some Options And Tips Introduction and epidemiology. in children, cataract causes more visual disability than any other form of treatable blindness. children with untreated, visually significant cataracts face a lifetime of blindness at tremendous quality of life and socioeconomic costs to the child, the family, and the society. more than 200,000 children are blind. A congenital cataract causes the same symptoms as adult cataracts—a clouding in the lens of the eye that can cause blurry vision or blindness. located behind the iris of the eye, the lens is normally clear and allows incoming light to clearly focus an image on the retina. if a cataract develops, the lens becomes cloudy, causing images to. A cataract is any light scattering opacity of the lens. it is estimated that congenital cataracts are responsible for 5% to 20% of blindness in children worldwide. incidence varies from country to country. one retrospective study of the prevalence of infantile cataracts in the u.s. showed a rate of 3 4 visually significant cataracts per 10,000. 2. cortical cataracts: these form in the outer layer (cortex) of the lens and can cause visual disturbances such as glare or blurred vision. 3. posterior subcapsular cataracts: these develop at the back of the lens, just beneath the lens capsule. they can cause difficulty with near vision and sensitivity to light.

Comments are closed.