Muscle Tissue Basicmedical Key

Muscle Tissue Basicmedical Key Characteristics of the skeletal muscle cell or fiber. skeletal muscle cells are formed in the embryo by the fusion of myoblasts that produce a postmitotic, multinucleated myotube. the myotube matures into the long muscle cell with a diameter of 10 to 100 μm and a length of up to several centimeters. the plasma membrane (called the sarcolemma. Muscle tissue in the body is classified into one of three major categories according to structure, function, and location. skeletal muscle is the most common and characteristic type; the other two kinds are cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. skeletal muscle produces purposeful movements of the skeleton. cardiac muscle forms the myocardium and is.
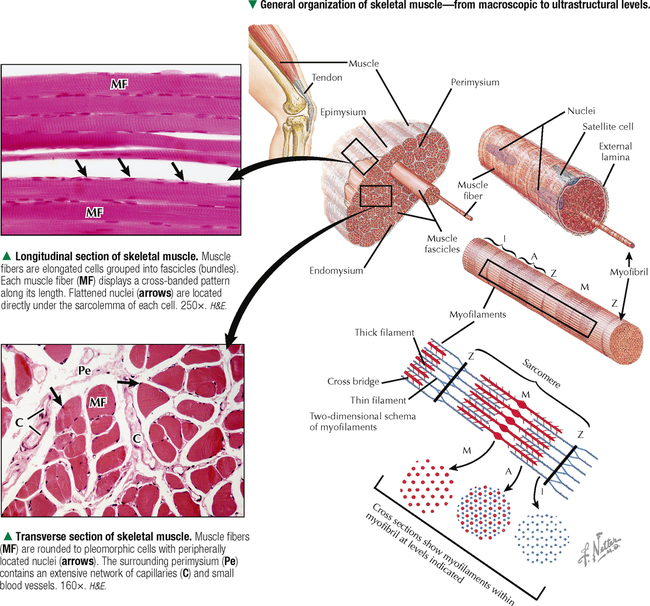
Muscle Tissue Basicmedical Key The twitch starts about 2 ms after the start of depolarization of the membrane, before repolarization is complete. the duration of the twitch varies with the type of muscle being tested. “fast” muscle fibers, primarily those concerned with fine, rapid, precise movement, have twitch durations as short as 7.5 ms. Muscle is a soft tissue that is highly specialized for the production of tension which results in the generation of force. muscle cells, or myocytes, contain myofibrils comprised of actin and myosin myofilaments which slide past each other producing tension that changes the shape of the myocyte. numerous myocytes make up muscle tissue and the. Muscle ultrasound is a reliable method to measure muscle thickness and cross sectional areas, 15–17 with a test retest correlation of 0.98 to 0.99 15,18 and a 0.99 correlation mri. 15 several studies have used ultrasound to establish muscle thickness in healthy subjects. during childhood, muscle thickness increases rapidly. Muscular system. • the muscular system comprises striated or skeletal muscle, i.e. muscle which is attached to the skeleton and brings about movement of a region. • each striated muscle fibre is filled with myofibrils made of two contractile proteins, actin and myosin. at the cellular level, muscle contraction results from the formation of.
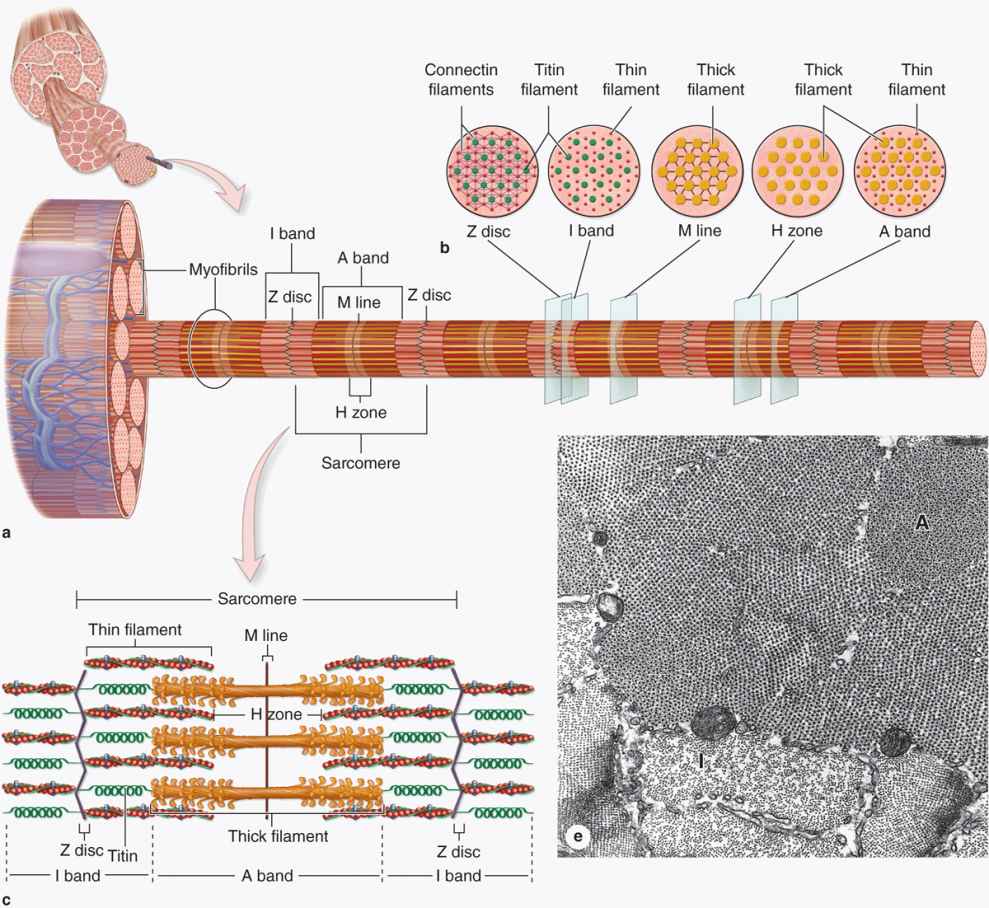
Muscle Tissue Basicmedical Key Muscle ultrasound is a reliable method to measure muscle thickness and cross sectional areas, 15–17 with a test retest correlation of 0.98 to 0.99 15,18 and a 0.99 correlation mri. 15 several studies have used ultrasound to establish muscle thickness in healthy subjects. during childhood, muscle thickness increases rapidly. Muscular system. • the muscular system comprises striated or skeletal muscle, i.e. muscle which is attached to the skeleton and brings about movement of a region. • each striated muscle fibre is filled with myofibrils made of two contractile proteins, actin and myosin. at the cellular level, muscle contraction results from the formation of. Scar formation may inhibit innervation of regenerating muscle tissue and reduce muscle contractility and range of motion (quintero et al. 2009). the developing scar is the weakest point for recurrent tears up to 12 days post injury. after this time, re tears occur in the adjacent myofibrils at the margins of the scar (järvinen et al. 2000). Key facts. muscle is a dynamic tissue that can be subject to direct and indirect traumatic injuries. type 1 muscle fibers contain more numerous mitochondria, enabling longer, sustained contractions that are more resistant to fatigue (e.g., soleus). type 2 fibers elicit faster, shorter, more powerful contractions, which are optimal for short.
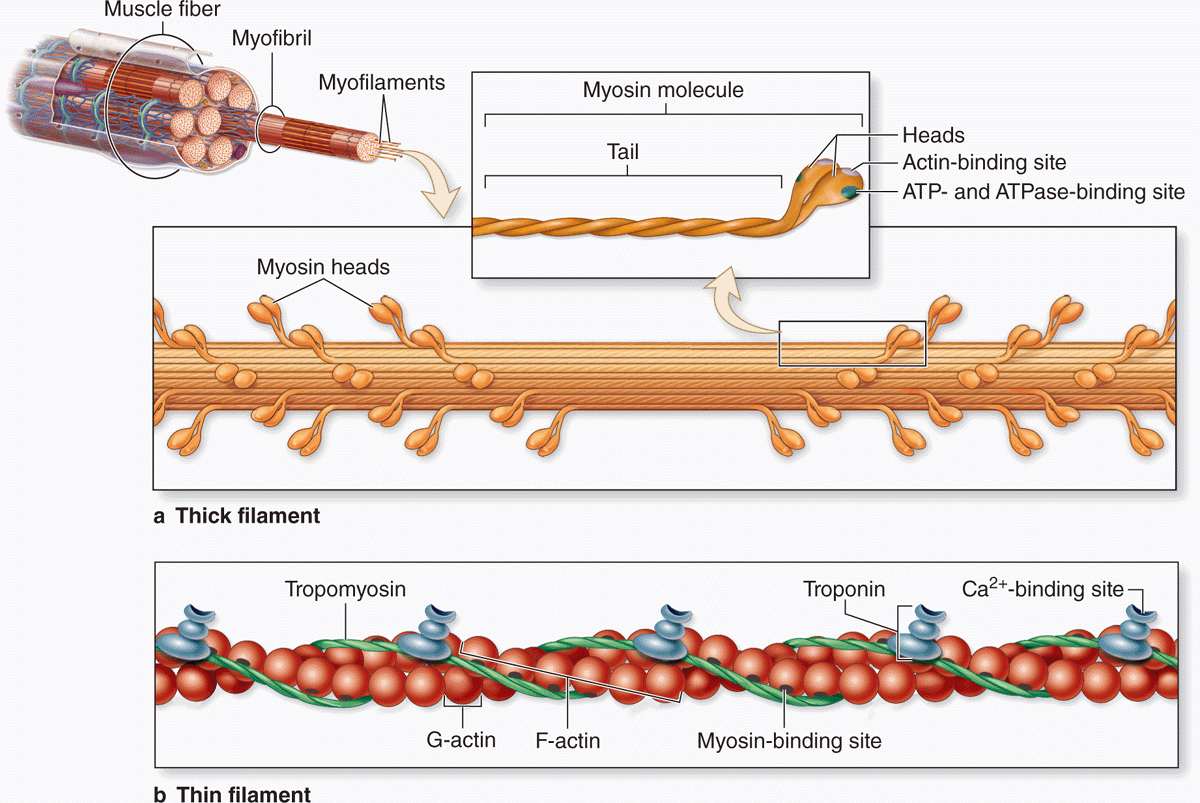
Muscle Tissue Basicmedical Key Scar formation may inhibit innervation of regenerating muscle tissue and reduce muscle contractility and range of motion (quintero et al. 2009). the developing scar is the weakest point for recurrent tears up to 12 days post injury. after this time, re tears occur in the adjacent myofibrils at the margins of the scar (järvinen et al. 2000). Key facts. muscle is a dynamic tissue that can be subject to direct and indirect traumatic injuries. type 1 muscle fibers contain more numerous mitochondria, enabling longer, sustained contractions that are more resistant to fatigue (e.g., soleus). type 2 fibers elicit faster, shorter, more powerful contractions, which are optimal for short.

Comments are closed.