Muscle Tissue Human Physiology And Anatomy Lecture Slides Docsity

Muscle Tissue Anatomy Lecture Slides Docsity These are the important key points of lecture slides of human physiology and anatomy are: muscle tissue, introduction to muscle, characteristics of muscle, skeletal muscle, connective tissue elements, muscle fiber, multiple flattened nuclei, sarcoplasmic reticulum, thick filaments, thin filaments. This lecture is taken from slides of physiology and anatomy. key important points are: muscle tissue, walls of hollow visceral organs, intercalcated disks, muscle function, functional characteristics, skeletal muscle tissue, cardiac muscle tissue, calcium ion present. show more. preview the document. uploaded on 01 26 2013.

Types Of Muscle Tissue Introduction To Human Physiology Lecture Slides Docsity Human anatomy course teaches a student the structural nature and significance of each of the major organ systems, and how each system carries out its unique role in the living organism. key points in this lecture are:muscle tissue, skeletal, cardiac, smooth, reticular fiber matrix, skeletal muscle cells, require neural stimulation, voluntary, voluntary movement, forms some sphincters. This document provides an overview of muscle anatomy. it begins by defining muscle tissue and its basic properties, including excitability, contractility, extensibility, and elasticity. the three main types of muscle are then described: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. skeletal muscle makes up the majority of muscle in the body and is. Figure 4.4.1 – muscle tissue: (a) skeletal muscle cells have prominent striation and nuclei on their periphery. (b) smooth muscle cells have a single nucleus and no visible striations. (c) cardiac muscle cells appear striated and have a single nucleus. from top, lm × 1600, lm × 1600, lm × 1600. Facial muscles. found in voluntary sphincters lips, urethra, and anus. table 10.1: muscle type – structure, function, location. figure 10.2 the three types of muscle tissue the body contains three types of muscle tissue: (a) skeletal muscle, (b) smooth muscle, and (c) cardiac muscle.

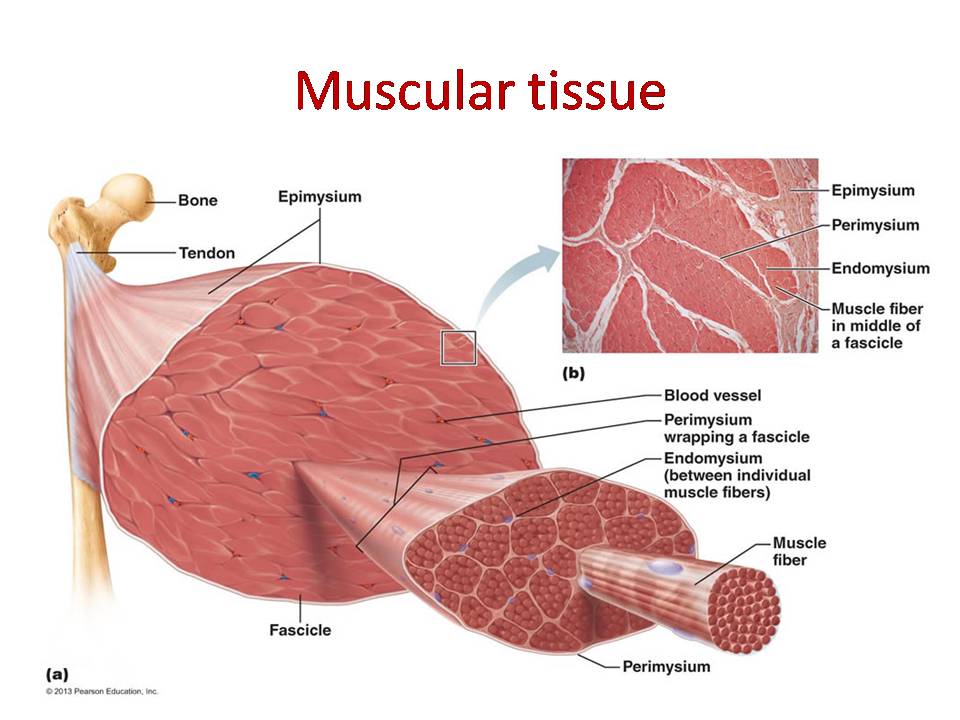
Types Of Muscle Tissue Physiology And Anatomy Lecture Slides Docsity Figure 4.4.1 – muscle tissue: (a) skeletal muscle cells have prominent striation and nuclei on their periphery. (b) smooth muscle cells have a single nucleus and no visible striations. (c) cardiac muscle cells appear striated and have a single nucleus. from top, lm × 1600, lm × 1600, lm × 1600. Facial muscles. found in voluntary sphincters lips, urethra, and anus. table 10.1: muscle type – structure, function, location. figure 10.2 the three types of muscle tissue the body contains three types of muscle tissue: (a) skeletal muscle, (b) smooth muscle, and (c) cardiac muscle. Tissue is group of cells, which have similar in origin, structure and function are called as “tissues”. 1. muscle tissue is one of four primary tissue types and is divided into three main categories: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. skeletal muscle is attached to bones and allows voluntary movement. 2. General anatomy of muscles. this document provides an overview of muscle anatomy and physiology. it discusses the three types of muscles skeletal, smooth and cardiac and their microscopic structures. skeletal muscle is composed of fascicles containing bundles of striated muscle fibers. each fiber contains myofibrils made up of actin and.

Muscle Tissue Physiology And Anatomy Lecture Slides Slides Physiology Docsity Tissue is group of cells, which have similar in origin, structure and function are called as “tissues”. 1. muscle tissue is one of four primary tissue types and is divided into three main categories: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. skeletal muscle is attached to bones and allows voluntary movement. 2. General anatomy of muscles. this document provides an overview of muscle anatomy and physiology. it discusses the three types of muscles skeletal, smooth and cardiac and their microscopic structures. skeletal muscle is composed of fascicles containing bundles of striated muscle fibers. each fiber contains myofibrils made up of actin and.
Muscular Tissue Skeletal Smooth And Cardiac Muscle Online Biology Notes

Comments are closed.