Muscle Tissue Skeletal Smooth And Cardiac Stock Vector Illustration Of Heart Normal 138153915

Muscle Tissue Skeletal Smooth And Cardiac Stock Vector Illustration Of Heart Normal 138153915 Muscle tissue: skeletal, smooth and cardiac. illustration about heart, normal, anatomy, muscular, cardiac, care, disease, musculoskeletal, fiber, healthy, anatomical. List the major structural and functional differences among the three types of muscle tissue. skeletal muscle tissue is primarily attached to bones. it is striated and voluntary. cardiac muscle tissue forms the wall of the heart. it is striated and involuntary. smooth (visceral) muscle tissue is located in the viscera.
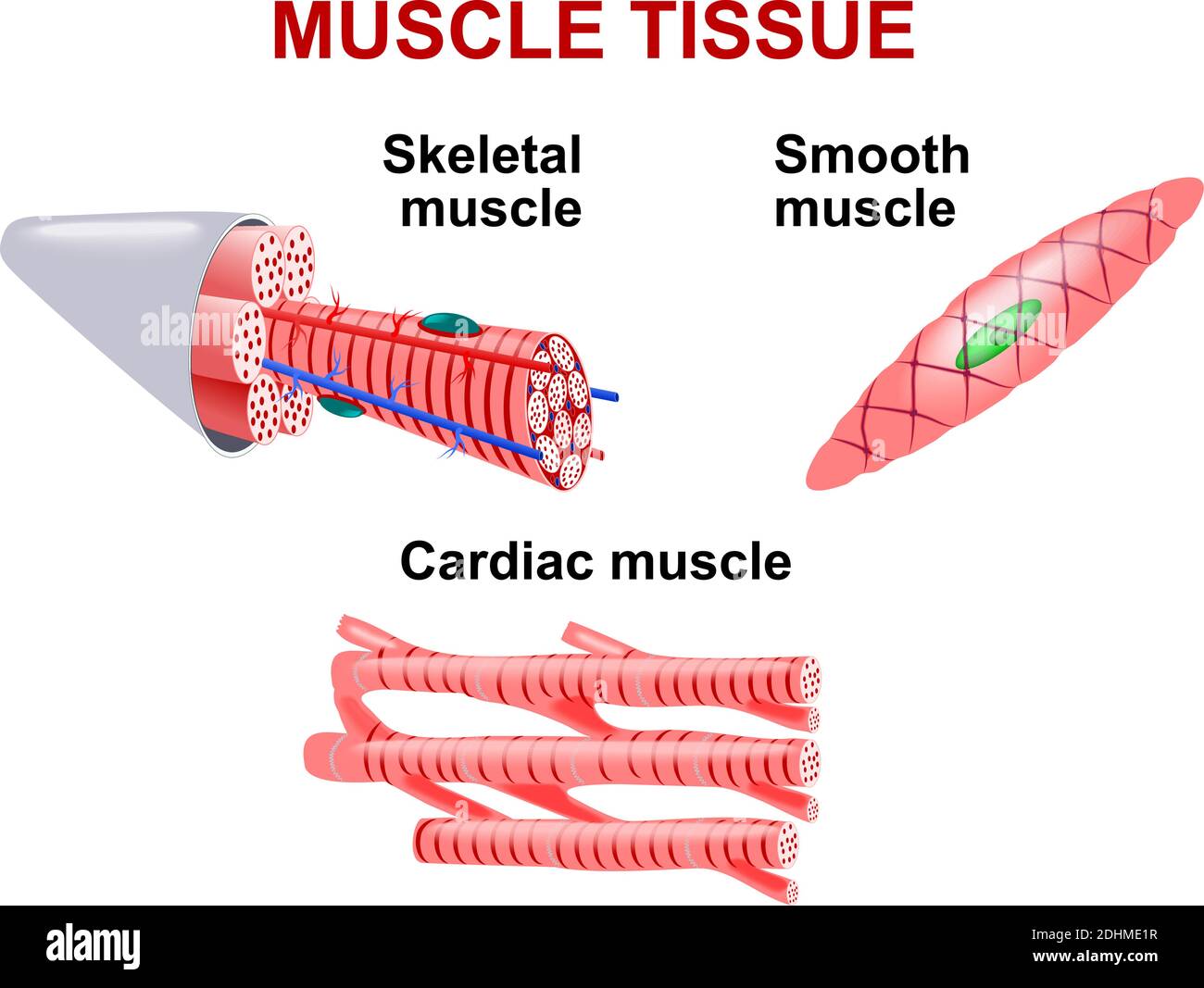
Types Of Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle Smooth Muscle Cardiac Muscle Stock Vector Image Art Characteristics. cardiac muscle tissue, also known as myocardium, is a structurally and functionally unique subtype of muscle tissue located in the heart, that actually has characteristics from both skeletal and muscle tissues. it is capable of strong, continuous, and rhythmic contractions that are automatically generated. Tiny doctors at huge board with infographics presenting skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscles muscular health concept. tiny doctors characters at huge board with infographics presenting skeletal, cardiac and smooth musculature. medicine, muscles anatomy. cartoon people vector illustration cardiac muscle tissue stock illustrations. Different types of muscle tissue vector illustration different types of muscle tissue vector illustration. smooth, skeletal and cardiac muscles of human body. can be used for anatomy, biology, education, science concept cardiac tissue stock illustrations. Muscle tissue is classified into striated (skeletal and cardiac) vs smooth muscle tissue according to the arrangement of the contractile proteins, or lack thereof. striated muscle organises actin and myosin into sarcomeres where these proteins are regularly spaced, whereas in smooth muscle these elements are organised into a more flexible arrangement that favours a larger range of possible.
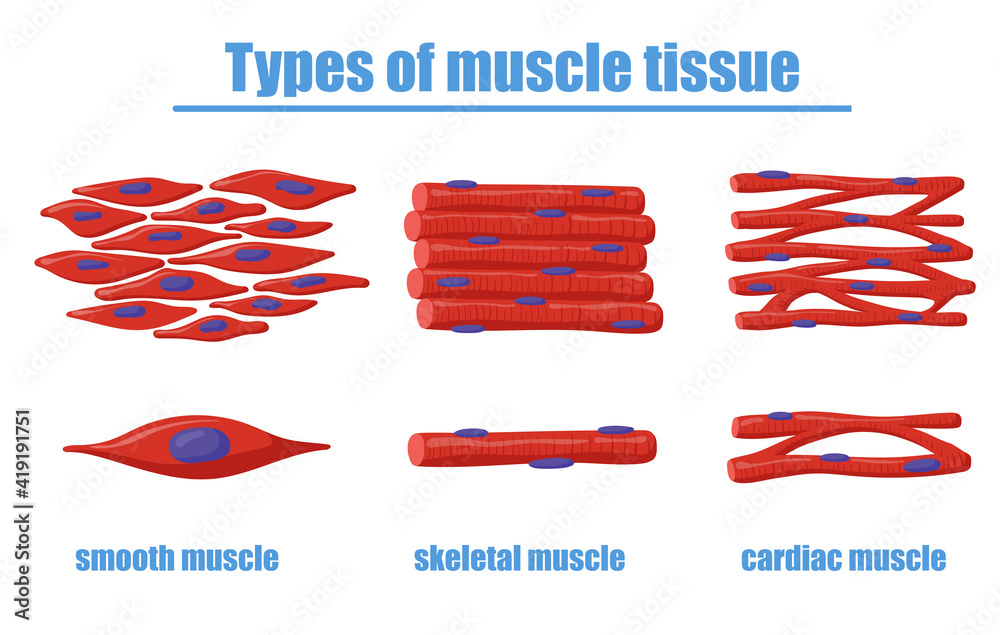
Different Types Of Muscle Tissue Vector Illustration Smooth Skeletal And Cardiac Muscles Of Different types of muscle tissue vector illustration different types of muscle tissue vector illustration. smooth, skeletal and cardiac muscles of human body. can be used for anatomy, biology, education, science concept cardiac tissue stock illustrations. Muscle tissue is classified into striated (skeletal and cardiac) vs smooth muscle tissue according to the arrangement of the contractile proteins, or lack thereof. striated muscle organises actin and myosin into sarcomeres where these proteins are regularly spaced, whereas in smooth muscle these elements are organised into a more flexible arrangement that favours a larger range of possible. Figure 3.5.2 3.5. 2: histology of muscle tissue types at 400x. (a) skeletal muscle cells have prominent striations and nuclei on their periphery. (b) smooth muscle cells have a single nucleus and no visible striations. (c) cardiac muscle cells appear faintly striated and have a single nucleus. Muscle cells, commonly known as myocytes, are the cells that make up muscle tissue. there are 3 types of muscle cells in the human body; cardiac, skeletal, and smooth. skeletal muscle cells are long, cylindrical, multi nucleated and striated. each nucleus regulates the metabolic requirements of the sarcoplasm around it.

Types Muscle Tissue Skeletal Smooth Cardiac Stock Illustration 435097303 Shutterstock Figure 3.5.2 3.5. 2: histology of muscle tissue types at 400x. (a) skeletal muscle cells have prominent striations and nuclei on their periphery. (b) smooth muscle cells have a single nucleus and no visible striations. (c) cardiac muscle cells appear faintly striated and have a single nucleus. Muscle cells, commonly known as myocytes, are the cells that make up muscle tissue. there are 3 types of muscle cells in the human body; cardiac, skeletal, and smooth. skeletal muscle cells are long, cylindrical, multi nucleated and striated. each nucleus regulates the metabolic requirements of the sarcoplasm around it.

Comments are closed.