Muscle Tissues Biology Anatomy Physiology Anatomyandphysiology Study Premed Stem Muscle
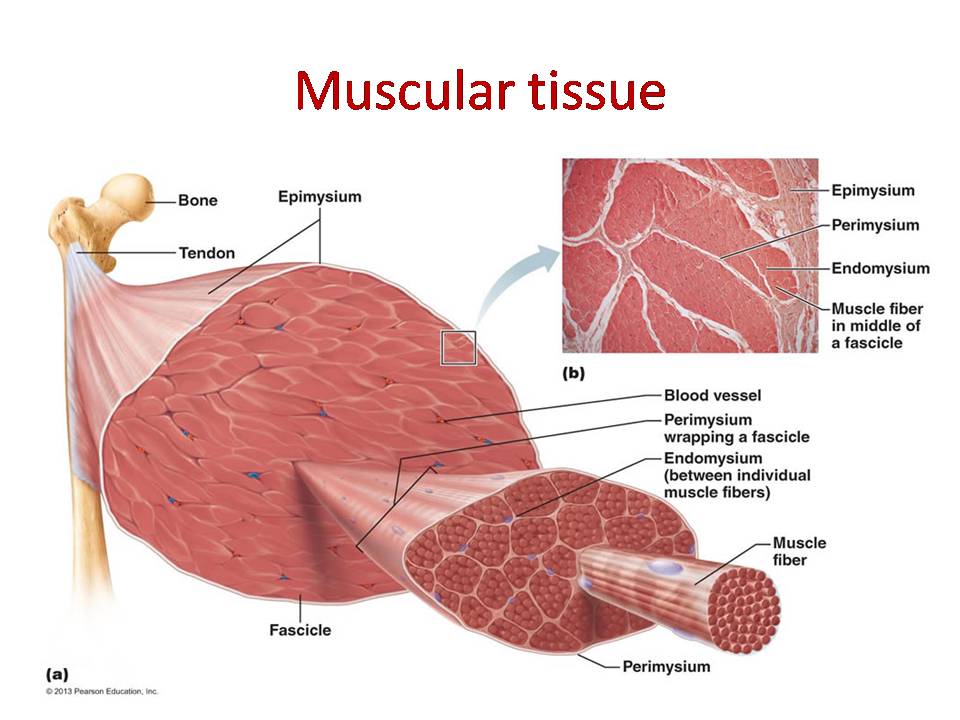
Muscular System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs Muscle tissue located on the heart wall, its contraction propels blood through circulatory system. it is adjusted by autonomic ns and hormones. involuntary control. has intercolated discs. smooth muscle. muscle tissue that surrounds hollow organs and tubes, it is found as single cells or in small groups. Skeletal muscles. muscle tissue, connective tissue, nerves, blood vessels. connective tissues. epimysium, perimysium, endomysium. epimysium. exterior collagen layer, connected to deep fascia, separates muscle from surrounding tissues. perimysium. surrounds muscles fiber bundles (fascicles), contains blood vessel and nerve supply to fascicles.
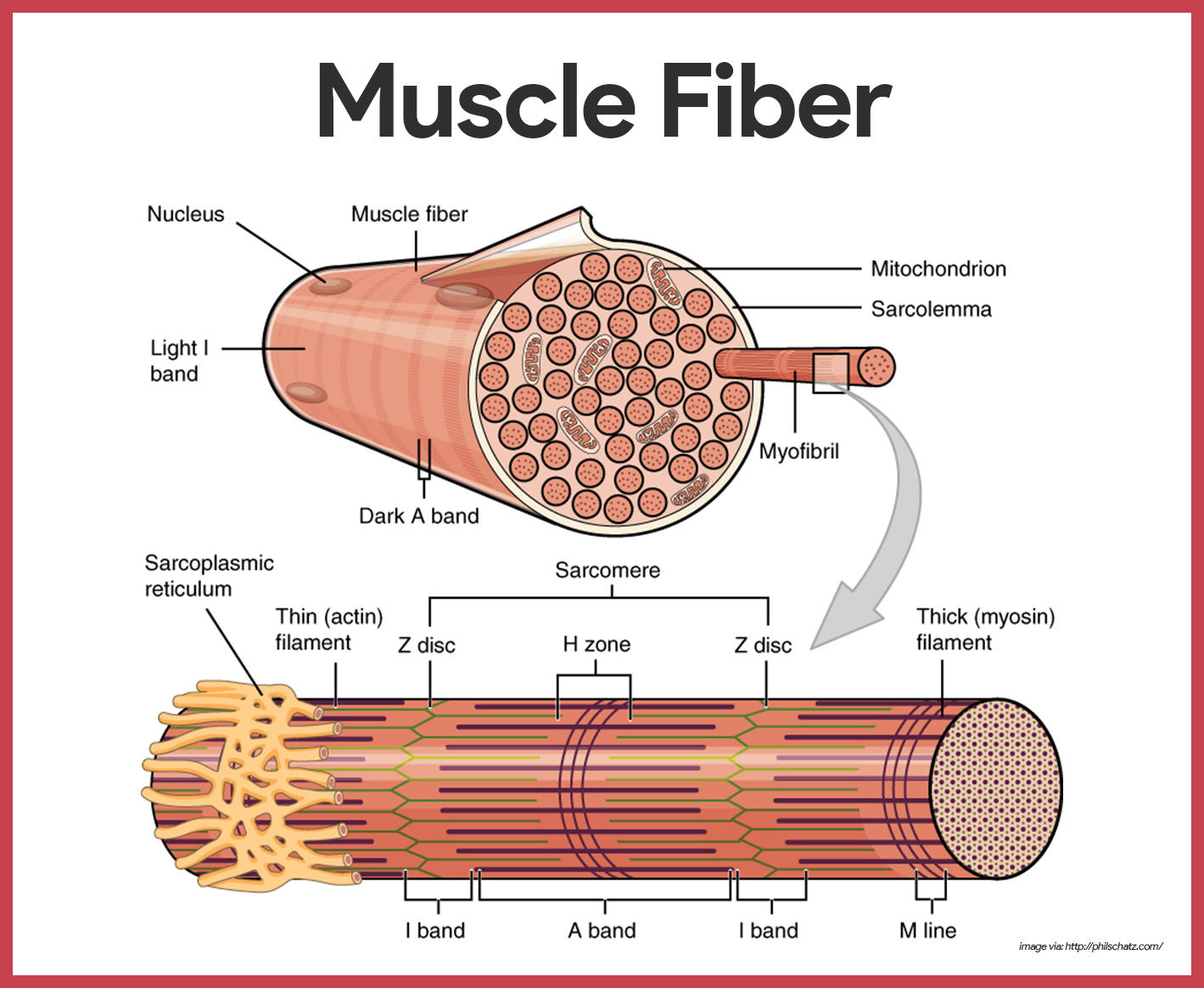
Muscle Tissue Diagram Labeled There are six functions of skeletal muscle, they are: 1) produce skeletal movement. 2) maintain body position. 3) support soft tissues. 4) guard openings. 5) maintain body temperature. 6) store nutrient reserves. muscle: group of individual muscle cells with the same attachments and functions. Summary. the muscular system is composed of specialized cells called muscle fibers, which contain contractile proteins that enable them to contract and relax. the main types of muscle tissue are: skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscles. skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles attached to bones, which enable movement of the skeleton, and maintain. Cardiac muscle. striated muscle; formed of short, uninucleate, branching myocytes which connected at intercalated discs. specialized muscle of the heart → myocardium. smooth muscle. non striated muscle; formed of short, uninucleate, spindle shaped myocytes. located in the walls of internal organs, blood vessels etc. Learn anatomy faster andremember everything you learn. a free website study guide review that uses interactive animations to help you learn online about anatomy and physiology, human anatomy, and the human body systems. start learning now!.

Comments are closed.