Non Performing Assets Npa Types Classification Of Npa For Banks
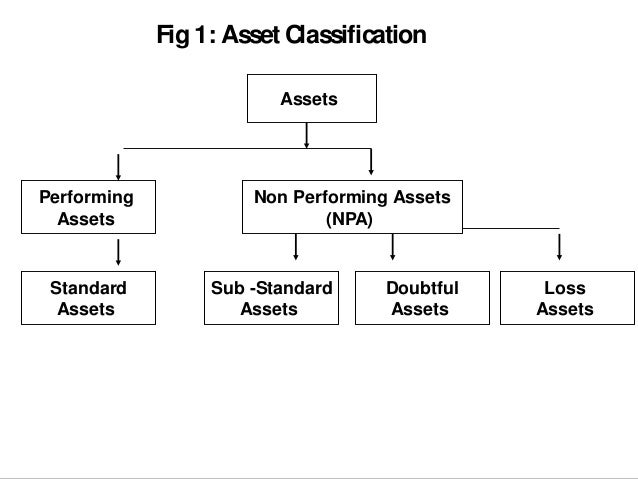
What Is Npa And How Do They Affect Banks A nonperforming asset (npa) refers to a classification of loans or advances that are in default or in arrears. a loan is in arrears when principal or interest payments are late or missed. a loan. Non performing assets (npa) refer to the classification of loans and advances in the books of a lender (usually banks) in which there is no payment of interest and principal has been received and is "past due." in most cases, debt has been classified as npas where the loan payments have been outstanding for more than 90 days.
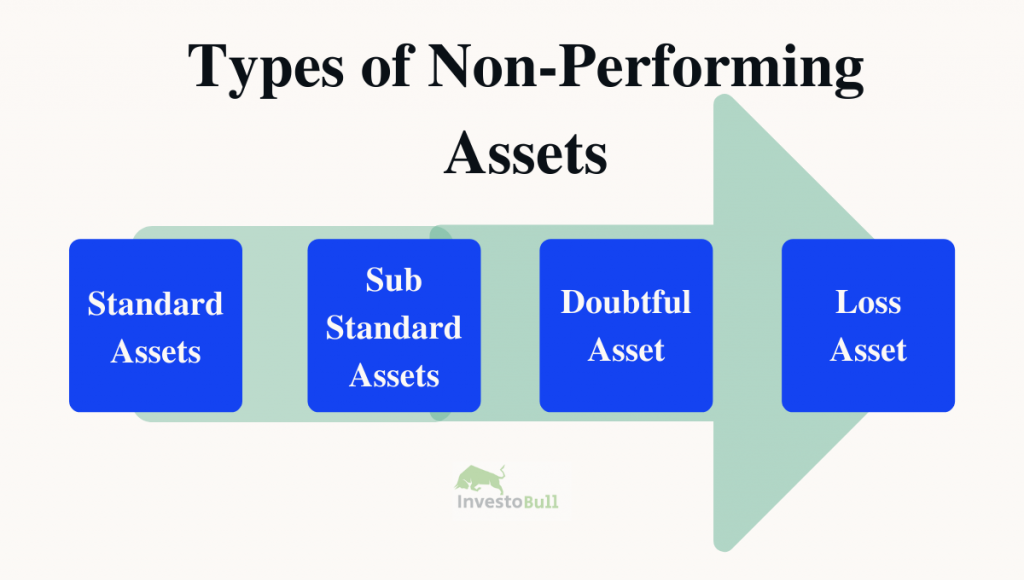
Non Performing Assets Of non performing assets, they include various asset classes such as foreclosed collateral. 3 npa identificatio n refers to the process used by banks and supervisors to classify an exposure as “non performing”, while npa measurement represents the level of provisions required to write down the npa exposure to its estimated recoverable amount. Impact of rising non performing assets. rising non performing assets has negative impact the overall growth of the economy as can be seen below. profitability: on an average, banks are providing around 25% to 30% additional provision on incremental non performing assets which has direct bearing on the banks’ profitability. Non performing assets in the doubtful debts category have been past due for at least 18 months. banks generally have serious doubts that the borrower will ever repay the full loan. this class of npa seriously affects the bank’s own risk profile. 4. loss assets. these are non performing assets with an extended period of non payment. An example of a non performing asset (npa) could be a home loan taken by an individual who has stopped paying the principal and interest for more than 90 days. if the borrower fails to make payments for three consecutive months, the loan account will be classified as an npa. non performing assets is an advance or a loan overdue for over 90 days.
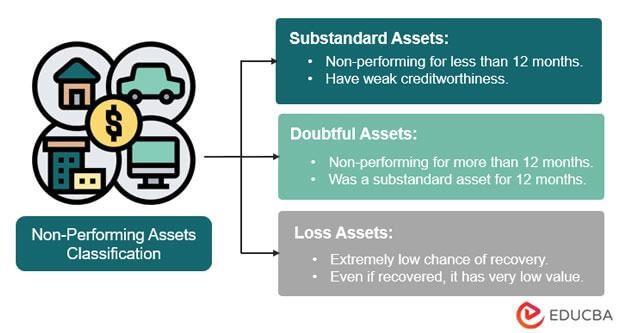
Non Performing Assets Npa Definition Examples Types 2023 Updated Non performing assets in the doubtful debts category have been past due for at least 18 months. banks generally have serious doubts that the borrower will ever repay the full loan. this class of npa seriously affects the bank’s own risk profile. 4. loss assets. these are non performing assets with an extended period of non payment. An example of a non performing asset (npa) could be a home loan taken by an individual who has stopped paying the principal and interest for more than 90 days. if the borrower fails to make payments for three consecutive months, the loan account will be classified as an npa. non performing assets is an advance or a loan overdue for over 90 days. They are also called ‘distressed assets’ or ‘bad assets’. for a bank, a loan is an asset as it generates income from the interest payments. however, it classifies the loan as a non performing asset when the borrower fails to repay the loan despite repeated attempts by the bank. typically, an asset is classified as an npa after 90 days. Non performing asset (npa) refers to a loan or advance that has stopped generating income for the lender, typically a bank. non performing asset, or npa, is a crucial concept in the field of finance and banking. when a borrower defaults on the principal amount or interest payment within a given period, it becomes a non performing asset.

Comments are closed.