Nutrients Free Full Text Maternal Vegetable And Fruit Consumption During Pregnancy And Its

Nutrients Free Full Text Maternal Vegetable And Fruit Consumption During Pregnancy And Its Maternal nutrition intake during pregnancy may affect the mother to child transmission of bacteria, resulting in gut microflora changes in the offspring, with long term health consequences in later life. longitudinal human studies are lacking, as only a small amount of studies showing the effect of nutrition intake during pregnancy on the gut microbiome of infants have been performed, and. Role of high energy breakfast “big breakfast diet” in clock gene regulation of postprandial hyperglycemia and weight loss in type 2 diabetes.
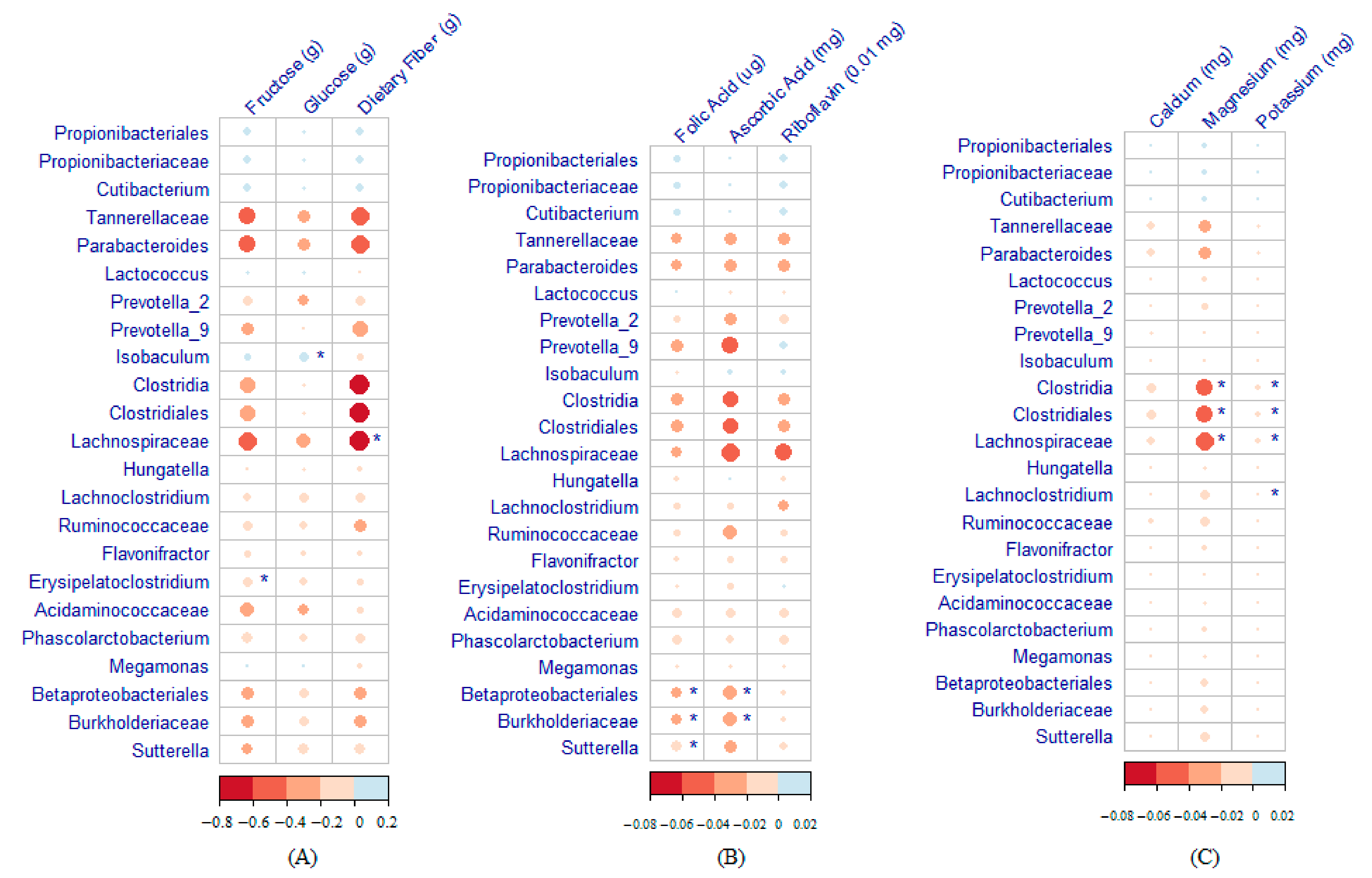
Nutrients Free Full Text Maternal Vegetable And Fruit Consumption During Pregnancy And Its Characteristics of groups with high and low maternal consumption of fruits and vegetables during pregnancy. figures available via license: creative commons attribution 4.0 international content. Eleven studies of the association between maternal fruits and vegetables consumption during pregnancy and infant birth weight or risk for sga birth were identified. 14 – 16, 28 – 35 pregnant women residing in countries within europe or australasia ranking very high on metrics of human development as defined by the human development index. Overall, the women consumed an average of 243.5 g day of fruit, 188.8 g day of cereal and grain based foods, and 165.5 g day of vegetables. the women consumed limited intakes of legumes (14.3 g day) and nuts (4.1 g day). figure 2. fiber rich foods (grams day) consumed by women during late pregnancy. Most women in the united states do not meet the recommendations for healthful nutrition and weight before and during pregnancy. women and providers often ask what a healthy diet for a pregnant woman should look like. the message should be “eat better, not more.” this can be achieved by basing diet on a variety of nutrient dense, whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole.

Comments are closed.