Parts Of The Human Eye And Their Functions
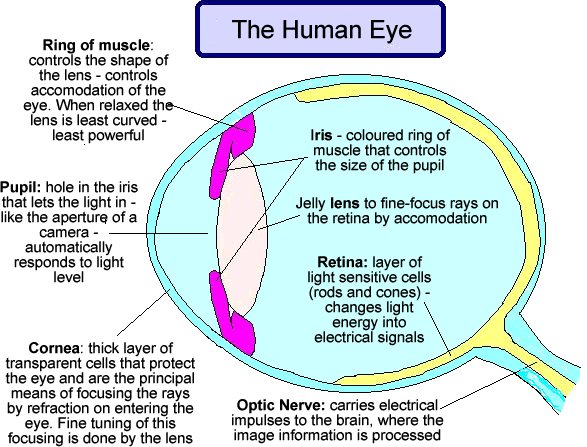
The Human Eye And Its Function Science Hub 4 Kids Learn about the basic structure and function of the eye, from the outside to the inside. find out how the cornea, lens, iris, pupil, retina, optic nerve, and tear film work together to produce vision. The following are parts of the human eyes and their functions: 1. conjunctiva. the conjunctiva is the membrane covering the sclera (white portion of your eye). the conjunctiva also covers the interior of your eyelids. the conjunctiva helps lubricate the eyes by generating mucus and tears. it also aids in immunological monitoring and prevents.
/GettyImages-695204442-b9320f82932c49bcac765167b95f4af6.jpg)
Structure And Function Of The Human Eye These glands are located on the outer corner of each eye. they produce tears which help moisten the eye when it becomes dry, and flush out particles which irritate the eye. as tears flush out potentially dangerous irritants, it becomes easier to focus properly. lens. the lens sits directly behind the pupil. The structures and functions of the eyes are complex. each eye constantly adjusts the amount of light it lets in, focuses on objects near and far, and produces continuous images that are instantly transmitted to the brain. the orbit is the bony cavity that contains the eyeball, muscles, nerves, and blood vessels, as well as the structures that. Eye anatomy. the parts of your eye include the: cornea. this protects the inside of your eye like a windshield. your tear fluid lubricates your corneas. the corneas also do part of the work bending light as it enters your eyes. sclera. this is the white part of your eye that forms the general shape and structure of your eyeball. conjunctiva. The colored part of the eye. the iris is partly responsible for regulating the amount of light permitted to enter the eye. lens (also called crystalline lens). the transparent structure inside the eye that focuses light rays onto the retina. lower eyelid. skin that covers the lower part of the eyeball, including the cornea, when closed. macula.

Eye Anatomy And Function Anatomical Charts Posters Eye anatomy. the parts of your eye include the: cornea. this protects the inside of your eye like a windshield. your tear fluid lubricates your corneas. the corneas also do part of the work bending light as it enters your eyes. sclera. this is the white part of your eye that forms the general shape and structure of your eyeball. conjunctiva. The colored part of the eye. the iris is partly responsible for regulating the amount of light permitted to enter the eye. lens (also called crystalline lens). the transparent structure inside the eye that focuses light rays onto the retina. lower eyelid. skin that covers the lower part of the eyeball, including the cornea, when closed. macula. The main parts of the human eye are the cornea, iris, pupil, aqueous humor, lens, vitreous humor, retina, and optic nerve. the iris controls the size of the pupil, which is the opening that allows light to enter the lens. light enters the eye by passing through the cornea and aqueous humor. then, the lens focuses the light, which travels. The eye is kept moist by secretions of the lacrimal glands (tear glands). these almond shaped glands under the upper lids extend inward from the outer corner of each eye. each gland has two portions. one portion is in a shallow depression in the part of the eye socket formed by the frontal bone.
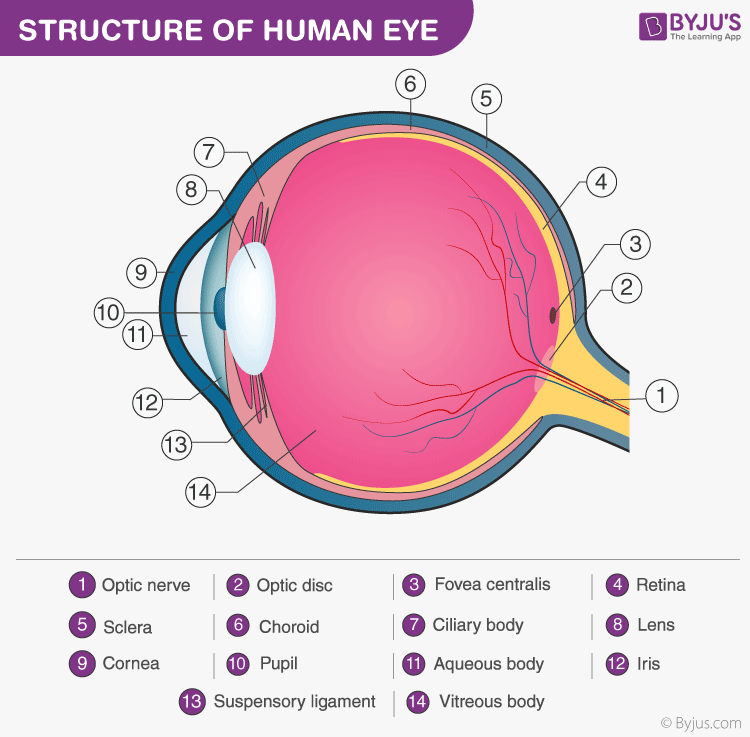
Human Eye Definition Structure Function Parts Diagram The main parts of the human eye are the cornea, iris, pupil, aqueous humor, lens, vitreous humor, retina, and optic nerve. the iris controls the size of the pupil, which is the opening that allows light to enter the lens. light enters the eye by passing through the cornea and aqueous humor. then, the lens focuses the light, which travels. The eye is kept moist by secretions of the lacrimal glands (tear glands). these almond shaped glands under the upper lids extend inward from the outer corner of each eye. each gland has two portions. one portion is in a shallow depression in the part of the eye socket formed by the frontal bone.

Human Eye Different Parts And Their Functions Class 10 Teachoo

Comments are closed.