Structure And Function Of The Human Eye Riset

Structure And Function Of The Human Eye Riset The main parts of the human eye are the cornea, iris, pupil, aqueous humor, lens, vitreous humor, retina, and optic nerve. the iris controls the size of the pupil, which is the opening that allows light to enter the lens. light enters the eye by passing through the cornea and aqueous humor. then, the lens focuses the light, which travels. The structures and functions of the eyes are complex. each eye constantly adjusts the amount of light it lets in, focuses on objects near and far, and produces continuous images that are instantly transmitted to the brain. the orbit is the bony cavity that contains the eyeball, muscles, nerves, and blood vessels, as well as the structures that.
/GettyImages-695204442-b9320f82932c49bcac765167b95f4af6.jpg)
Structure And Function Of The Human Eye Learn about an ophthalmologist's role in eye care. get ophthalmologist reviewed tips and information about eye health and preserving your vision. learn about eye anatomy and learn how your eyes work with ophthalmologist approved facts. The surface of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelids are covered with a clear membrane called the conjunctiva. the layers of the tear film keep the front of the eye lubricated. tears lubricate the eye and are made up of three layers. these three layers together are called the tear film. the mucous layer is made by the conjunctiva. Humans eyes work much like cameras. here is a simple step by step explanation of how the human eye works and a look at the structure and function of the parts of the eye. parts of the eye and their functions. to understand how the human eye works, you need to know the names and functions of its structures. Human eye, specialized sense organ in humans that is capable of receiving visual images, which are relayed to the brain. the anatomy of the eye includes auxiliary structures, such as the bony eye socket and extraocular muscles, as well as the structures of the eye itself, such as the lens and the retina.
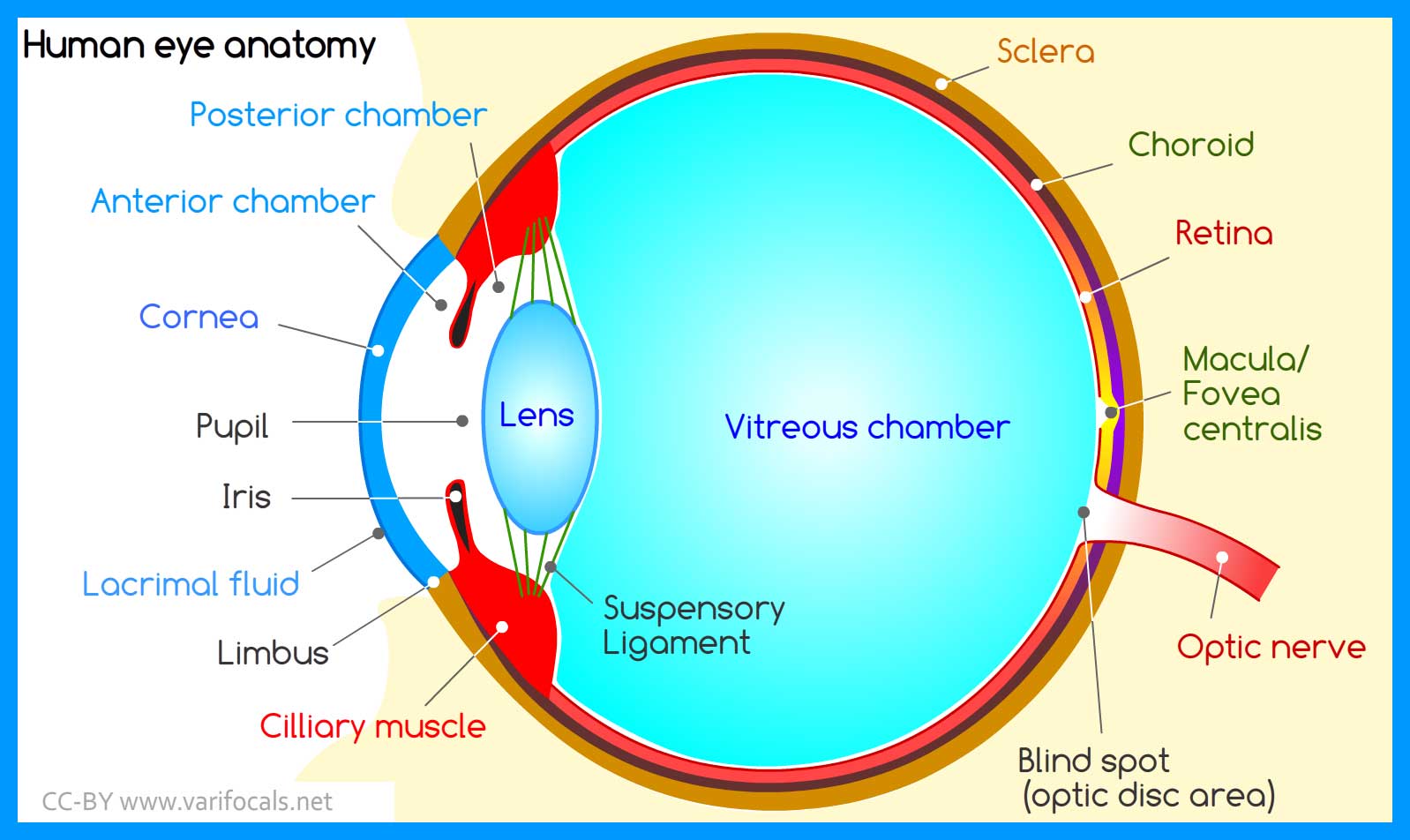
Human Eye Anatomy Structure And Function Humans eyes work much like cameras. here is a simple step by step explanation of how the human eye works and a look at the structure and function of the parts of the eye. parts of the eye and their functions. to understand how the human eye works, you need to know the names and functions of its structures. Human eye, specialized sense organ in humans that is capable of receiving visual images, which are relayed to the brain. the anatomy of the eye includes auxiliary structures, such as the bony eye socket and extraocular muscles, as well as the structures of the eye itself, such as the lens and the retina. The average human eye can see around 100 different shades of color and has a resolution that equals 576 gigapixels. these remarkable features of our eye are enabled by the complex structure of the eyeball. the eyeball consists of three layers; fibrous, vascular and nervous . functionally, the most important layer is the retina, which receives. The iris is a flat, thin, ring shaped structure sticking into the anterior chamber. this is the part that identifies a person’s eye colour. the iris contains both circular muscles going around the pupil and radial muscles radiating toward the pupil. when the circular muscles contract, they make the pupil smaller.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/eye-conjunctiva-871453538-5a26c6ad22fa3a0037d5edad.jpg)
How The Human Eye Works Structure And Function The average human eye can see around 100 different shades of color and has a resolution that equals 576 gigapixels. these remarkable features of our eye are enabled by the complex structure of the eyeball. the eyeball consists of three layers; fibrous, vascular and nervous . functionally, the most important layer is the retina, which receives. The iris is a flat, thin, ring shaped structure sticking into the anterior chamber. this is the part that identifies a person’s eye colour. the iris contains both circular muscles going around the pupil and radial muscles radiating toward the pupil. when the circular muscles contract, they make the pupil smaller.

Comments are closed.