The Effects Of Opioids On The Brain The Best Treatment
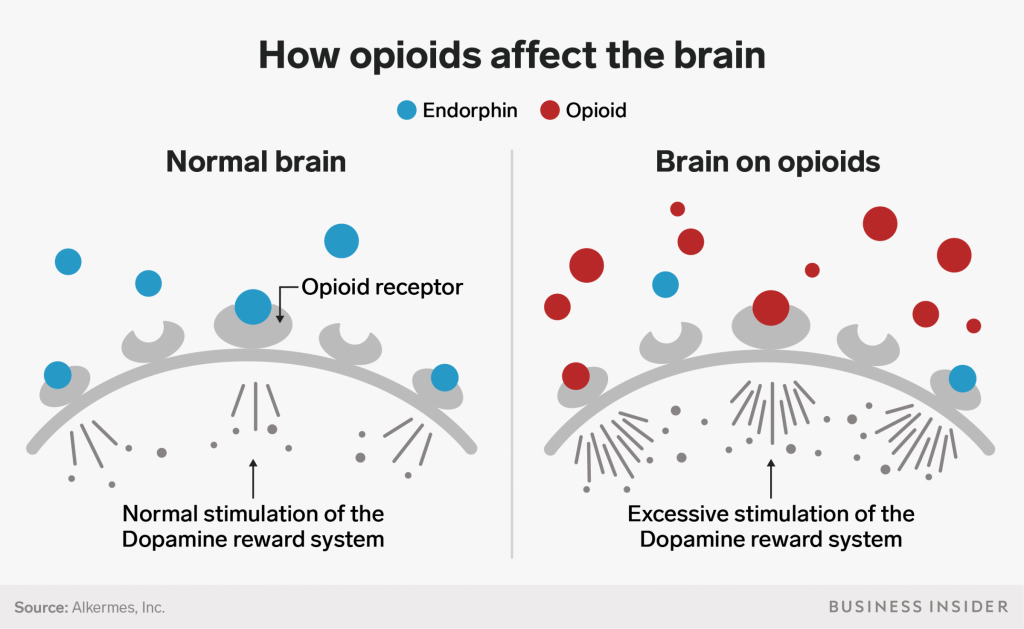
What Are Opioids Opioid Addiction Pursuecare In addition, whereas dor agonism in humans produces anxiolytic effects, kor agonism produces dysphoria (16, 27) thus, current neurobiological models of addictions emphasize the role of mors during the consummatory phase of addiction (e.g., binge intoxication), but the role of kors and dors during withdrawal and negative affective states (16). The immediate effect of opioids on the brain can cause: opioids can also cause accidental overdose and death. overdoses are unpredictable and can occur regardless of how long you’ve been taking.

Opioid Facts Vaccination against opioids to prevent oud and its consequences is a relatively new avenue of research. such vaccines work by causing a person's body to create its own antibody response to a specific opioid, thus blocking the psychoactive effects of that opioid in the brain if it is ingested (bremer et al., 2017). because mu opioid receptors. While opioids are not themselves acutely neurotoxic, the chronic relapsing and remitting nature of this disorder means that individuals are often exposed to exogenous opioids for lengthy periods of time (either illicit or prescribed as treatment). we are increasingly characterizing the effect of such long term opioid exposure on the brain. Heroin is an illegal opioid that people high, often with a needle. it can be a white or brown powder, sticky substance called black tar heroin. sometimes people call heroin names. horse, brown sugar, hell dust, and. another illegal opioid is fentanyl, a many times more powerful than heroin. sometimes street heroin is laced (mixed) fentanyl, and. Introduction. opioid use disorder (oud) is a chronic and relapsing disorder of the brain caused by repeated exposure to exogenous opioids. clinically, individuals present with a compulsion or craving to consume opioids, prioritizing the use of opioids at the expense of other activities or responsibilities, and a physiological dependence on opioids which manifests as increased tolerance and an.
The Effects Of Opioids On The Brain The Best Treatment Heroin is an illegal opioid that people high, often with a needle. it can be a white or brown powder, sticky substance called black tar heroin. sometimes people call heroin names. horse, brown sugar, hell dust, and. another illegal opioid is fentanyl, a many times more powerful than heroin. sometimes street heroin is laced (mixed) fentanyl, and. Introduction. opioid use disorder (oud) is a chronic and relapsing disorder of the brain caused by repeated exposure to exogenous opioids. clinically, individuals present with a compulsion or craving to consume opioids, prioritizing the use of opioids at the expense of other activities or responsibilities, and a physiological dependence on opioids which manifests as increased tolerance and an. 00:45 the neuroscience of fentanyl addiction. research in mice has shown that fentanyl addiction is the result of two brain circuits working in tandem, rather than a single neural pathway as had. Abstract. the number of people diagnosed with opioid use disorder has skyrocketed as a consequence of the opioid epidemic and the increased prescribing of opioid drugs for chronic pain relief. opioid use disorder is characterized by loss of control of drug taking, continued drug use in the presence of adverse consequences, and repeated relapses.

Comments are closed.