The Eye And Its Functions In 2022 The Retina Cone Cell Gcse Revision

The Eye And Its Functions In 2022 The Retina Cone Cell Gcse Revision The eye is a sense organ containing receptor cells which are sensitive to light intensity and colour. the purpose of the eye is to receive light and focus it onto the retina at the back of the eye. there are two main functions of the eye: accommodation to focus on near or distant objects. adaptation to dim light. Light passes through the eyeball to the retina. there are two main types of light receptors rods and cones . rods are more sensitive to light than cones so they are useful for seeing in dim light.

The Eye And Its Structure Revise Gcse Biology With Albert Teen The iris is a muscle which controls the size of the pupil by contracting or relaxing. this allows the eye to adjust to bright and dim lighting. describe the structure and function of the ciliary muscles and suspensory ligaments. the ciliary muscles and suspensory ligaments hold the lens in place and control its shape. Rods and cones are the two types of receptor cell present in the retina of the eye. rod cells and cone cells have different roles in detecting light stimuli: rods can detect light at low levels, so play an important role in night vision. three different types of cones can detect light at three different wavelengths, enabling colour vision. rods. The eye is a sense organ containing receptors sensitive to light intensity and colour. receptors are groups of specialised cells that can generate an electrical impulse in a sensory neurone. the eye contains two types of receptor cell: rod cells which are sensitive to light intensity and cone cells which are sensitive to different wavelengths. Light sensitive cell layer made of rod (light intensity) and cone (red, green, blue colour perception) cells. what does the optic nerve do? carries impulses from the receptors to the brain. what is the cornea? outer transparent layer, bends refracts light into the eye, covers the pupil and iris. what does the iris do? controls how much light.
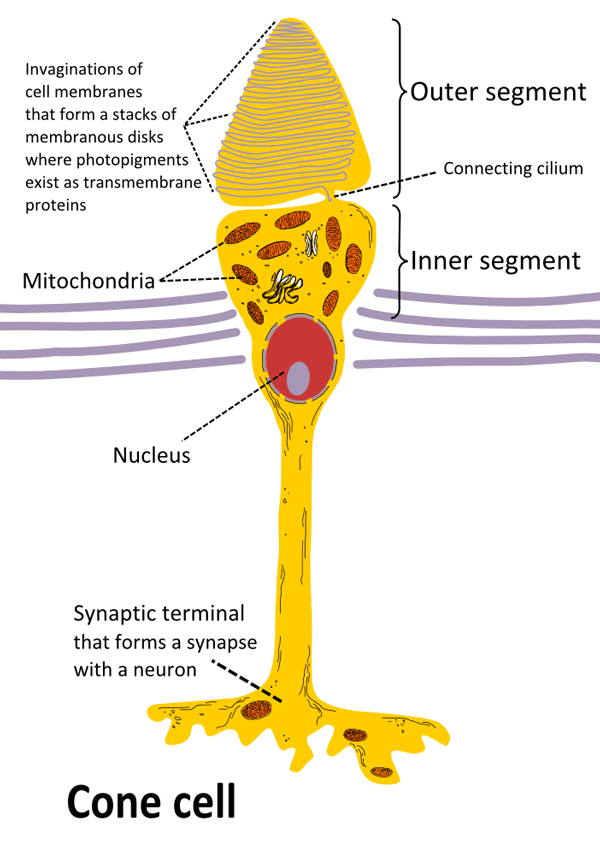
Inside The Eye On The Retina You Will Find Rod And Cone Cells The eye is a sense organ containing receptors sensitive to light intensity and colour. receptors are groups of specialised cells that can generate an electrical impulse in a sensory neurone. the eye contains two types of receptor cell: rod cells which are sensitive to light intensity and cone cells which are sensitive to different wavelengths. Light sensitive cell layer made of rod (light intensity) and cone (red, green, blue colour perception) cells. what does the optic nerve do? carries impulses from the receptors to the brain. what is the cornea? outer transparent layer, bends refracts light into the eye, covers the pupil and iris. what does the iris do? controls how much light. This is everything you need to know about the eye, including the parts of the eye and their functions explained by real teachers! 📚 get your free gcse & i. Question 1: describe how light enters the eye. [4 marks] question 2: explain how the eye responds to dim light. [3 marks] question 3: a person struggles to read small text in a book when it is close to their face. explain what can you conclude about their vision and the structure of their eyes. [3 marks].

The Eye An Introduction Gcse Biology Study Mind This is everything you need to know about the eye, including the parts of the eye and their functions explained by real teachers! 📚 get your free gcse & i. Question 1: describe how light enters the eye. [4 marks] question 2: explain how the eye responds to dim light. [3 marks] question 3: a person struggles to read small text in a book when it is close to their face. explain what can you conclude about their vision and the structure of their eyes. [3 marks].

Comments are closed.