The Eye Gcse Biology Revision
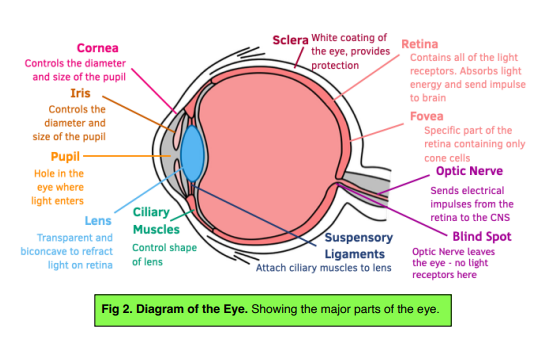
The Eye An Introduction Gcse Biology Study Mind The eye is a sense organ containing receptor cells which are sensitive to light intensity and colour. the purpose of the eye is to receive light and focus it onto the retina at the back of the eye. there are two main functions of the eye: accommodation to focus on near or distant objects. adaptation to dim light. Gcse; aqa; coordination and control the nervous system aqa the eye. the nervous system enables humans to react to their surroundings and to coordinate their behaviour.

Component Parts Of The Eye Gcse Biology Revision Science Revision Biology The iris is a muscle which controls the size of the pupil by contracting or relaxing. this allows the eye to adjust to bright and dim lighting. describe the structure and function of the ciliary muscles and suspensory ligaments. the ciliary muscles and suspensory ligaments hold the lens in place and control its shape. The eyes example questions. question 1: describe how light enters the eye. [4 marks] gcse biology foundation biology higher aqa. show answer. question 2: explain how the eye responds to dim light. [3 marks] gcse biology foundation biology higher aqa. show answer. The eye is a sense organ containing receptors close receptors organs which recognise and respond to stimuli. sensitive to light intensity and colour. figure caption, the structure of the human eye. Learn about and revise the nervous system, reflex actions, the brain and the eye with gcse bitesize biology.

The Brain And The Eye Gcse Biology Edexcel Revision Study Rocket The eye is a sense organ containing receptors close receptors organs which recognise and respond to stimuli. sensitive to light intensity and colour. figure caption, the structure of the human eye. Learn about and revise the nervous system, reflex actions, the brain and the eye with gcse bitesize biology. The eye is a sensory organ, and therefore it follows similar principles to what we learnt about earlier – i.e. it has receptors to detect a stimulus, and then transmits information via an electrical impulse to a coordinator, the brain, before initiating a response via effectors. the eye is also involved in reflexes, which we learn about below. Iris. controls the amount of light that can enter the eye. it does this by altering the diameter of the pupil. this is why your pupil sometimes appears larger or smaller, especially in very bright or pitch black environments. the iris is also the coloured part of the eye. ciliary muscles.
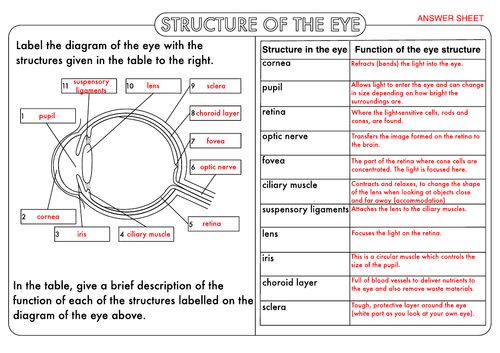
Gcse Biology The Eye Teaching Resources The eye is a sensory organ, and therefore it follows similar principles to what we learnt about earlier – i.e. it has receptors to detect a stimulus, and then transmits information via an electrical impulse to a coordinator, the brain, before initiating a response via effectors. the eye is also involved in reflexes, which we learn about below. Iris. controls the amount of light that can enter the eye. it does this by altering the diameter of the pupil. this is why your pupil sometimes appears larger or smaller, especially in very bright or pitch black environments. the iris is also the coloured part of the eye. ciliary muscles.

The Structure Of The Eye Gcse Revision Eyes Aqa

Comments are closed.