Thermal Conductivity Stefan Boltzmann Law Heat Transfer Conduction Convecton Radiation Physics

Thermal Conductivity Stefan Boltzmann Law Heat Transfer Conduction Convecton Radiation This physics video tutorial explains the concept of the different forms of heat transfer such as conduction, convection and radiation. it also shows how to. The rate of heat transfer by emitted radiation is described by the stefan boltzmann law of radiation: p = σ a e t 4 , p = σ a e t 4 , where σ = 5.67 × 10 −8 j s · m 2 · k 4 σ = 5.67 × 10 −8 j s · m 2 · k 4 is the stefan boltzmann constant, a combination of fundamental constants of nature; a is the surface area of the object; and t.
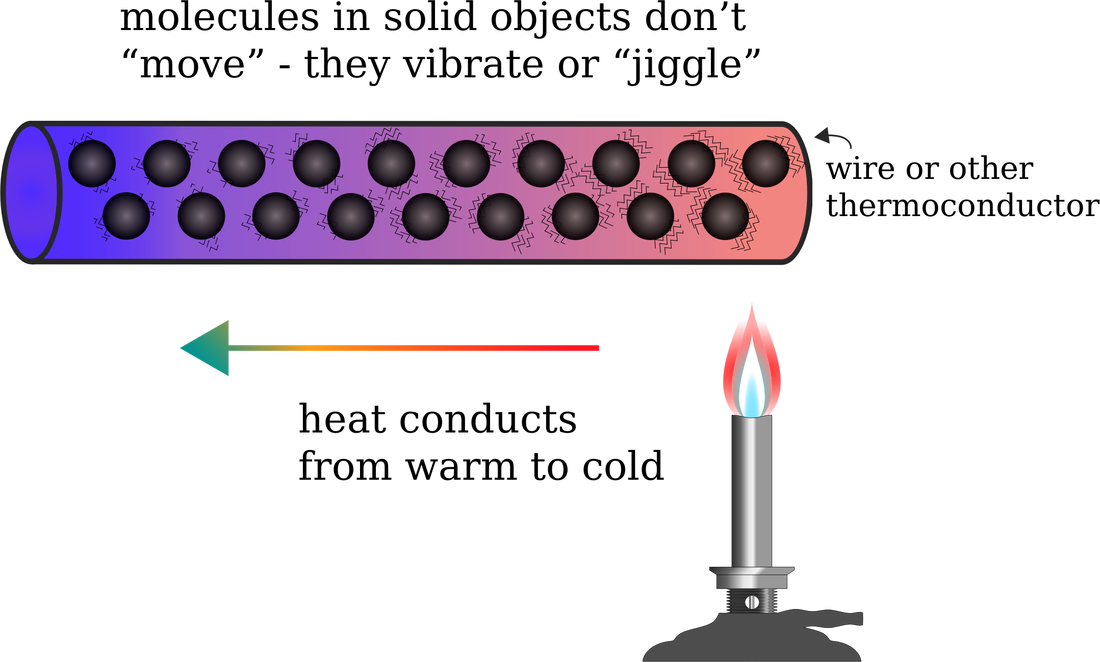
Heat Transfer Conduction Convection Radiation Flashcards The rate of heat transfer by emitted radiation is described by the stefan boltzmann law of radiation: \[p = \sigma aet^4,\] where \(\sigma = 5.67 \times 10^{ 8} \, j s \cdot m^2 \cdot k^4\) is the stefan boltzmann constant, a combination of fundamental constants of nature; a is the surface area of the object; and t is its temperature in kelvins. The three types of heat transfer differ according to the nature of the medium that transmits heat: conduction requires contact. convection requires fluid flow. radiation does not require any medium. conduction is heat transfer directly between neighboring atoms or molecules. usually, it is heat transfer through a solid. Example 13.4.1 13.4. 1: calculating heat transfer by convection: convection of air through the walls of a house. most houses are not airtight: air goes in and out around doors and windows, through cracks and crevices, following wiring to switches and outlets, and so on. the air in a typical house is completely replaced in less than an hour. 5.2. stefan boltzmann law. the stefan boltzmann law states that the total radiant heat energy emitted per unit surface area of a black body is directly proportional to the fourth power of its absolute temperature. this law is crucial in understanding thermal radiation and heat transfer. e = σ t 4. e is the radiant heat energy per unit area,.

Comments are closed.