Thermal Conductivity Values

Thermal Conductivity Values Download Table These are not measured values. very high thermal conductivity measurements up to 22,600 w m −1 k −1 were reported by fenton, e.w., rogers, j.s. and woods, s.d. in reference 570 on page 1458, 41, 2026–33, 1963. the data is listed on pages 6 through 8 and graphed on page 1 where fenton and company are on curves 63 and 64. Thermal conductivity can be defined as. "the quantity of heat transmitted through a unit thickness of a material in a direction normal to a surface of unit area due to a unit temperature gradient under steady state conditions". thermal conductivity units are [w (m k)] in the si system and [btu (hr ft °f)] in the imperial system.
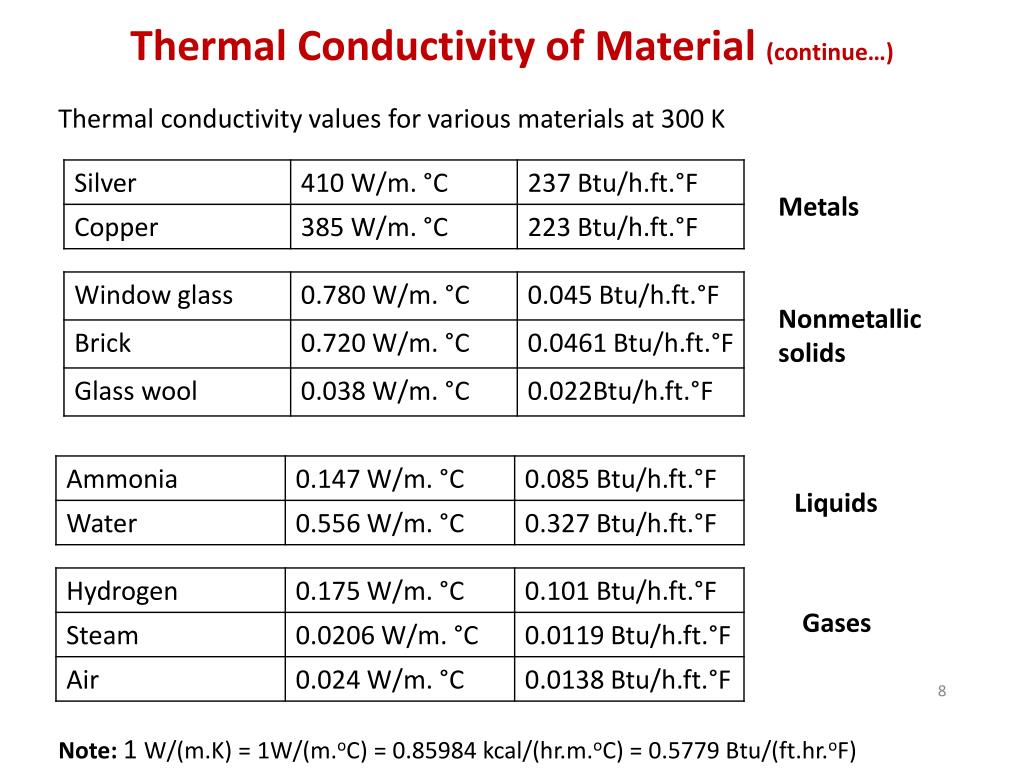
Thermal Conductivity Values Thermal conductivity and resistivity. the thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. it is commonly denoted by , , or and is measured in w·m −1 ·k −1. heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal conductivity. Thermal conductivity of materials. the heat transfer characteristics of a solid material are measured by a property called the thermal conductivity, k (or λ), measured in w m.k. it is a measure of a substance’s ability to transfer heat through a material by conduction. note that fourier’s law applies for all matter, regardless of its state. Thermal conductivity data tables & charts. explore a curated collection of tables and charts that provide thermal conductivity data for a wide range of materials including metals, polymers, ceramics, and fluids. what is thermal conductivity. Thermal conductivity, frequently represented by κ κ, is a property that relates the rate of heat loss per unit area of a material to its rate of change of temperature. [1] essentially, it is a value that accounts for any property of the material that could change the way it conducts heat. in si units, thermal conductivity is expressed in.

Comments are closed.