Understanding The Food Chain Tertiary Consumers Explained
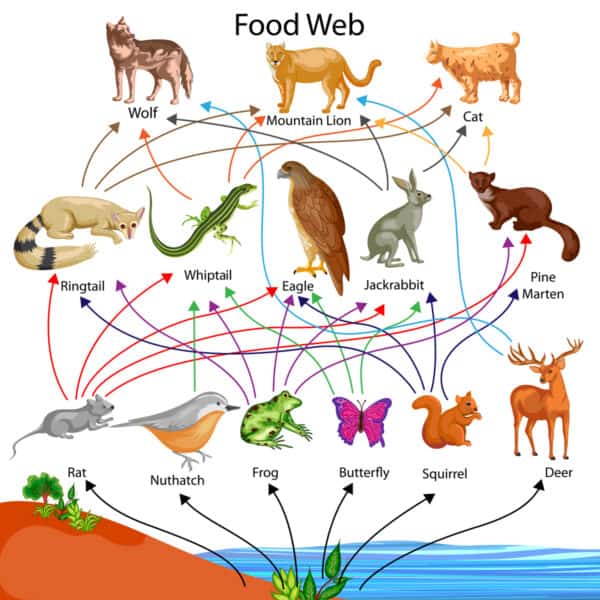
Food Chain 4 Tertiary Consumer A Z Animals Primary consumers are the second step, and secondary consumers are the third. this makes a tertiary consumer the fourth step in the food chain because they consume secondary consumers for energy. tertiary consumers can be: herbivores — organisms that eat plants. carnivores — organisms that eat meat. omnivores — organisms that eat plants. Higher level consumers include secondary consumers (third trophic level), which are usually carnivores that eat the primary consumers, and tertiary consumers (fourth trophic level), which are carnivores that eat other carnivores. in the lake ontario food chain, shown in figure \(\pageindex{g}\), the chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the.
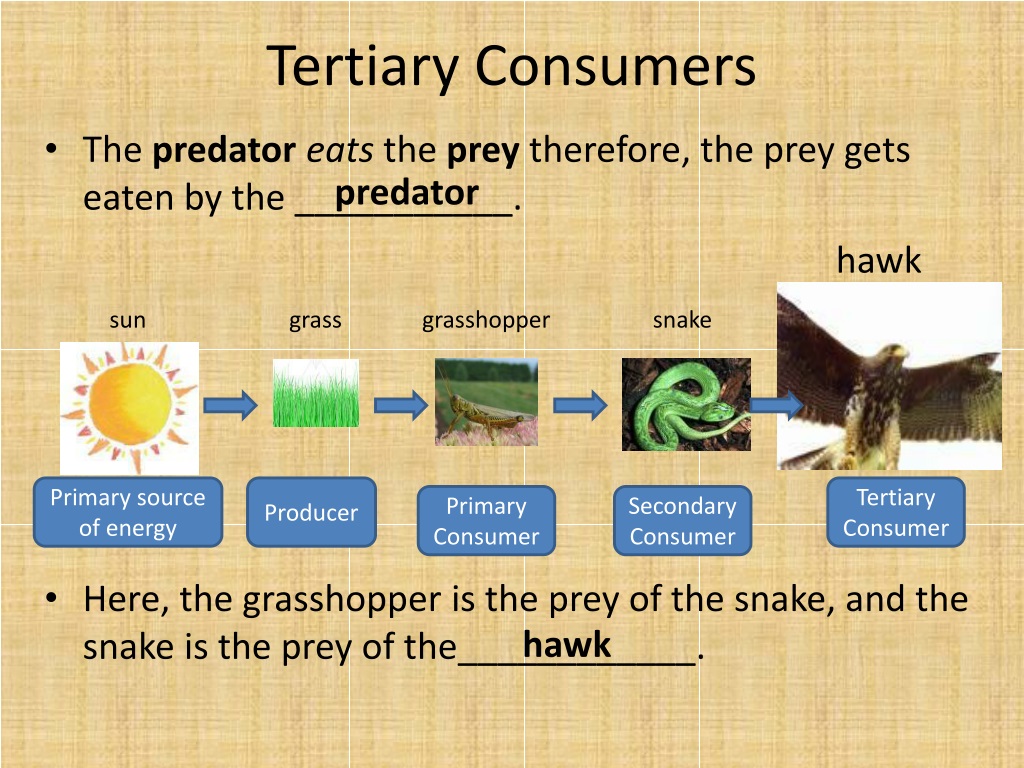
Ppt Food Chains Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 9522090 Tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower trophic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the apex consumers. in the lake ontario food chain, shown in figure \(\pageindex{2}\), the chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the top of this food chain. The hawk swooping down to snatch a mouse, the spider trapping an unwary fly—these are examples of secondary consumers. level 4: tertiary consumers – the top predators. on the fourth level, we find the “tertiary consumers,” also known as apex predators. they’re the top dogs in the food chain with no predators of their own. Tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower tropic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the apex consumers. in the lake ontario food chain shown in figure 1, the chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the top of this food chain. Tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower tropic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the apex consumers. in the lake ontario food chain shown in figure 1, the chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the top of this food chain.

Trophic Pyramid Definition Examples Britannica Tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower tropic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the apex consumers. in the lake ontario food chain shown in figure 1, the chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the top of this food chain. Tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower tropic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the apex consumers. in the lake ontario food chain shown in figure 1, the chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the top of this food chain. The 10% energy rule. one of the key principles governing energy flow in food chains is the ‘10% rule.’. this rule states that, on average, only about 10% of the energy from one trophic level is transferred to the next. the remaining 90% is expended as heat, used in metabolic processes, or unassimilated. Following the primary consumer are one or more additional consumers, called the secondary (2nd) consumer, tertiary (3rd) consumer, quaternary (4th) consumer, etc… secondary and higher consumers will always be omnivores or carnivores. the final consumer on any food chain is also known as a top predator because it has no predators of its own.

Comments are closed.