Values Of The Thermal Conductivity For Ferrous Oxides Obtained Using Download Scientific

Values Of The Thermal Conductivity For Ferrous Oxides Obtained Using Download Scientific Download scientific diagram | values of the thermal conductivity for ferrous oxides obtained using experimental data from publication: particularities regarding the thermal radiation inside the. Abstract. iron (iii) oxide is a compound that appears in at least four different polymorphs: α fe 2 o 3, β fe 2 o 3, γ fe 2 o 3, and ε fe 2 o 3. however, fe 3 ions are also present in another form of iron oxide: fe 3 o 4, which is an iron crystal structure with both fe 2 and fe 3 ions. and in its turn, fe 2 ions are also present in the.

Values Of The Thermal Conductivity For Ferrous Oxides Obtained Using Download Scientific The oxide layer is a porous layer whose porosity can be higher than 40% [9]. this results in a large dispersion of the thermal conductivity values of the scale reported in the literature [10]. the. For instance, the thermal conductivity of the m fe 3 o 4 ldpe composites is 0.461 w m −1 k −1 at 7.0 vol.% concentration, higher than that of the fe 3 o 4 ldpe composites (0.384 w m −1 k. Qasim et al. 17 investigated the relation of temperature and thermal conductivity of materials and found that the temperature is higher for higher values of thermal conductivity parameter ε. A maximum enhancement in the thermal conductivity of over 200% at 25 °c, under an applied magnetic field of 1000 g, was observed. it was seen that the maximum value of thermal conductivity increased nonlinearly with increasing magnetic field intensities (fig. 14 (b)). it is worth mentioning that at all intensities of applied magnetic field.

Thermal Capacity And Conductivity Of The Oxide Layer Using Theoretical Download Scientific Qasim et al. 17 investigated the relation of temperature and thermal conductivity of materials and found that the temperature is higher for higher values of thermal conductivity parameter ε. A maximum enhancement in the thermal conductivity of over 200% at 25 °c, under an applied magnetic field of 1000 g, was observed. it was seen that the maximum value of thermal conductivity increased nonlinearly with increasing magnetic field intensities (fig. 14 (b)). it is worth mentioning that at all intensities of applied magnetic field. The ratio of thermal memristance between its ‘on’ and ‘off’ states is determined by the emissivity contrast between the insulating and metallic phases of the used oxides 9. the analogy. High pressure temperature electrical conductivity of magnesiowustite as a function of iron oxide concentration. the electrical conductivity of (mg,fe)o magnesiowustite containing 9 and 27.5 mol % feo has been measured at simultaneously high pressures (30–32 gpa) and temperatures using a diamond anvil cell….

Thermal Conductivity Values Download Table The ratio of thermal memristance between its ‘on’ and ‘off’ states is determined by the emissivity contrast between the insulating and metallic phases of the used oxides 9. the analogy. High pressure temperature electrical conductivity of magnesiowustite as a function of iron oxide concentration. the electrical conductivity of (mg,fe)o magnesiowustite containing 9 and 27.5 mol % feo has been measured at simultaneously high pressures (30–32 gpa) and temperatures using a diamond anvil cell….
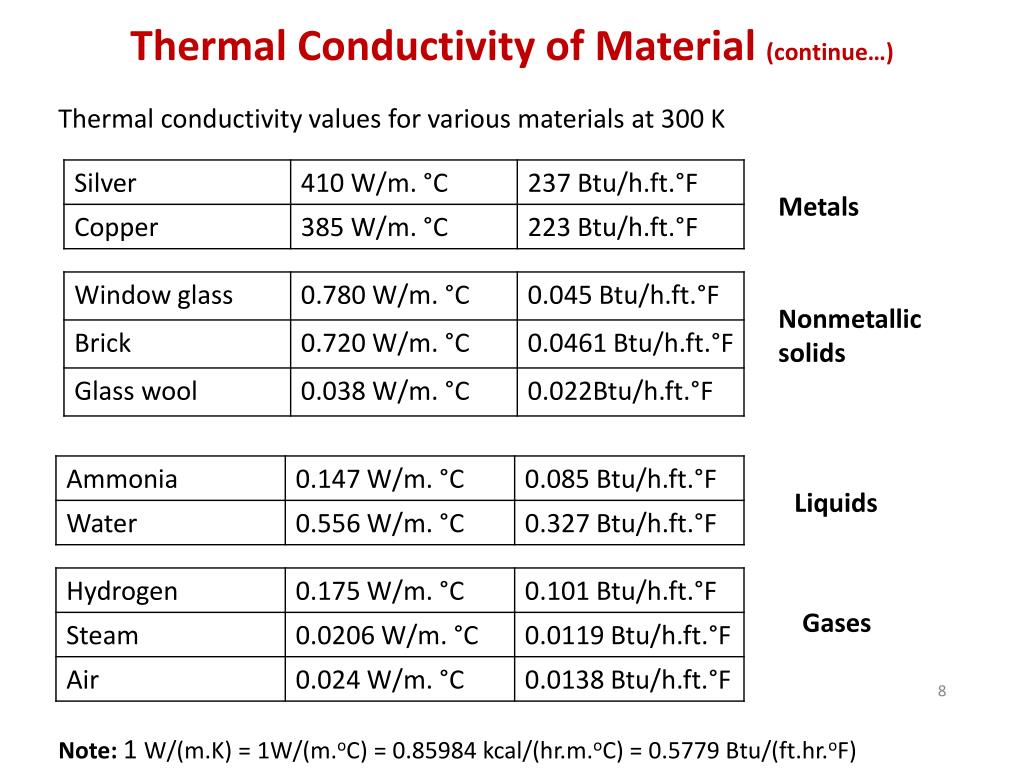
Thermal Conductivity Values

Comments are closed.