What Is A Secondary Consumers
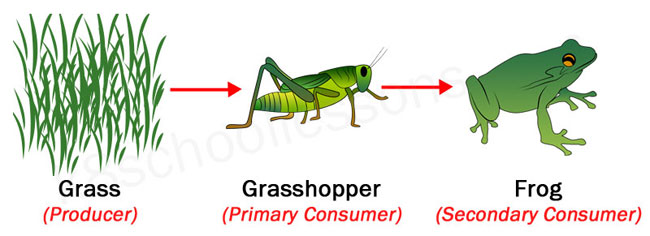
Food Chains And Food Webs Examples Of Food Chains And Food Webs A secondary consumer is an organism that eats primary consumers for energy. primary consumers are herbivores that only eat plants. secondary consumers can be carnivores or omnivores, and they regulate the population of primary consumers and provide energy to tertiary consumers. Secondary consumers can be defined as a group of living organisms that mainly feed on primary consumers or herbivores to get energy. they are placed on the third trophic level in a food chain. some secondary consumers also feed on both producers and primary consumers. so, secondary consumers range from carnivores that consume meat to omnivores.

Secondary Consumer Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary Marine food webs. resource. add to collection. feeding relationships are often shown as simple food chains – in reality, these relationships are much more complex, and the term ‘food web’ more accurately shows the links between producers, consumers and decomposers. a food web diagram illustrates ‘what eats what’ in a particular habitat. Functions of secondary consumers. secondary consumers have an integral role to play in the food network. they are deeply involved in the regulation of the primary consumers’ populations in an ecosystem as they eat them for energy. moreover, secondary consumers also act as a source of nutrients and energy to the tertiary consumers. Definition of secondary consumers. secondary consumers are organisms that primarily feed on primary consumers, which are herbivores, in a food chain. they occupy the third trophic level and can be either carnivores, who eat only other animals, or omnivores, who consume both animal and plant matter. their role is vital in transferring energy. Secondary consumers are those that predate upon primary consumers, and tertiary consumers predate upon secondary consumers. secondary consumers are either carnivores (which eat meat) or omnivores.

Comments are closed.