What Is A Tertiary Consumer In A Food Chain
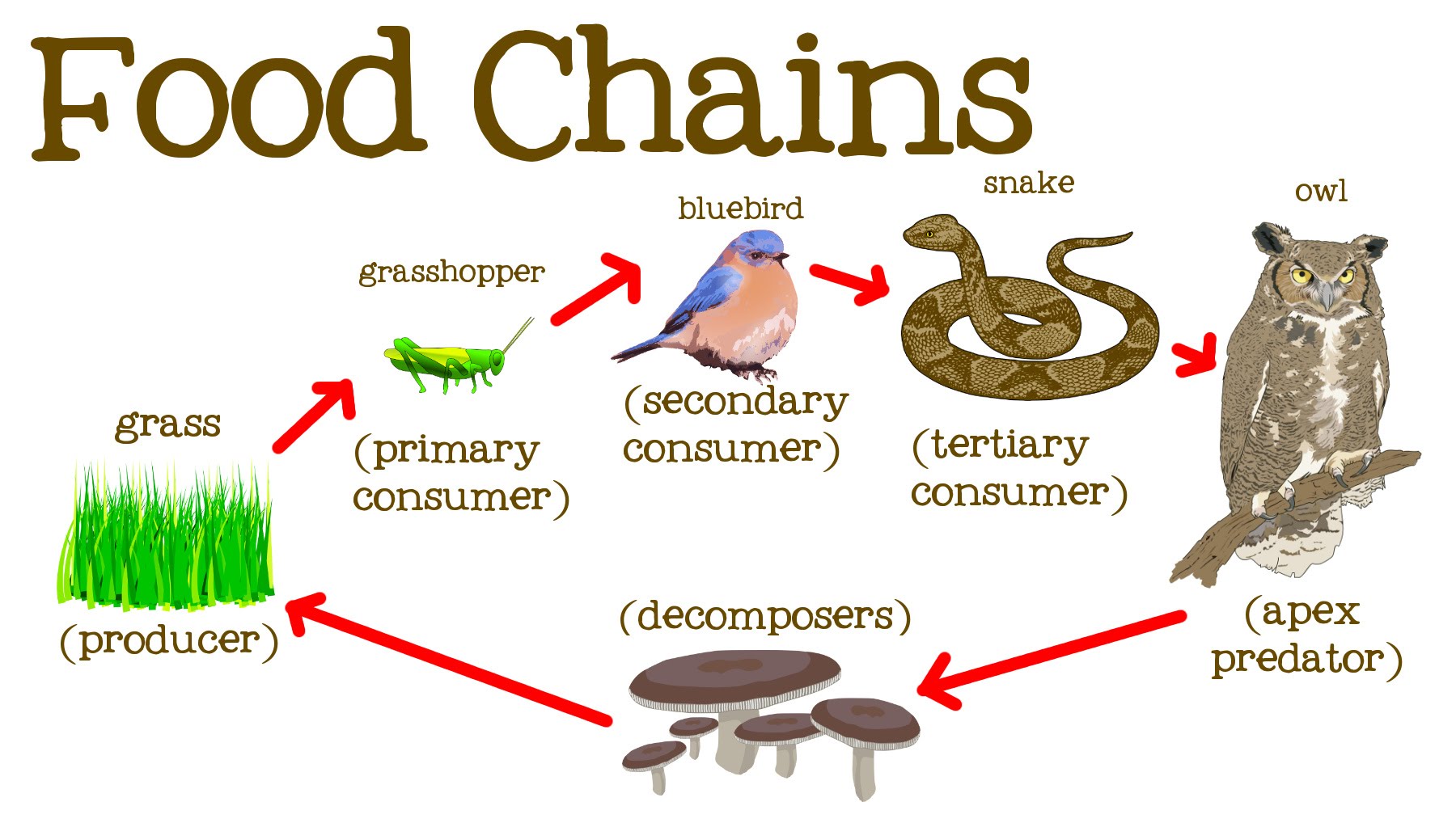
Food Chain Grade Three A tertiary consumer is an animal that eats primary and secondary consumers, usually a carnivore or an omnivore. learn about the ecological role of tertiary consumers, such as big cats, sharks, whales and humans, and how they affect the food chain and the ecosystem. A tertiary consumer is a fourth trophic level after producers, primary consumers, and secondary consumers. it eats both primary and secondary consumers as its main source of food. learn about some examples of tertiary consumers in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems and their ecological roles.

Food Chain Grade Three Primary consumers are the second step, and secondary consumers are the third. this makes a tertiary consumer the fourth step in the food chain because they consume secondary consumers for energy. tertiary consumers can be: herbivores — organisms that eat plants. carnivores — organisms that eat meat. omnivores — organisms that eat plants. The cow and human are consumers. a food chain is a list of organisms in a. habitat. that shows their feeding relationship, i.e what eats what. the organisms are joined by arrows which show the. A consumer in a food chain is a living creature that eats organisms from a different population. a consumer is a heterotroph and a producer is an autotroph. like sea angels, they take in organic moles by consuming other organisms, so they are commonly called consumers. heterotrophs can be classified by what they usually eat as herbivores. Learn about trophic interactions, trophic levels, and food chains and webs in ecology. a tertiary consumer is a carnivore that eats other carnivores, such as a hawk or a lion.
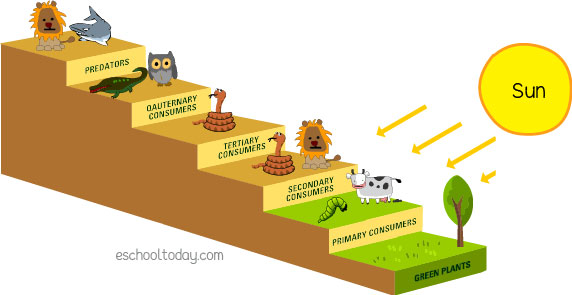
Food Chain With 5 Trophic Levels A consumer in a food chain is a living creature that eats organisms from a different population. a consumer is a heterotroph and a producer is an autotroph. like sea angels, they take in organic moles by consuming other organisms, so they are commonly called consumers. heterotrophs can be classified by what they usually eat as herbivores. Learn about trophic interactions, trophic levels, and food chains and webs in ecology. a tertiary consumer is a carnivore that eats other carnivores, such as a hawk or a lion. Tertiary consumers. examples of tertiary consumers are hawks, snakes, crocodiles and some big cats. tertiary consumers can be either omnivorous or carnivorous. they feed on primary and secondary consumers, and may also eat producers (plants). for a food chain to have a tertiary consumer, there must be a secondary consumer available for it to eat. A tertiary consumer is an animal that obtains its nutrition by eating primary consumers and secondary consumers. usually, tertiary consumers are carnivorous predators, although they may also be omnivores, which are animals that feed on both meat and plant material.

Mpalalive Tertiary consumers. examples of tertiary consumers are hawks, snakes, crocodiles and some big cats. tertiary consumers can be either omnivorous or carnivorous. they feed on primary and secondary consumers, and may also eat producers (plants). for a food chain to have a tertiary consumer, there must be a secondary consumer available for it to eat. A tertiary consumer is an animal that obtains its nutrition by eating primary consumers and secondary consumers. usually, tertiary consumers are carnivorous predators, although they may also be omnivores, which are animals that feed on both meat and plant material.

Comments are closed.