What Is A Tertiary Consumers
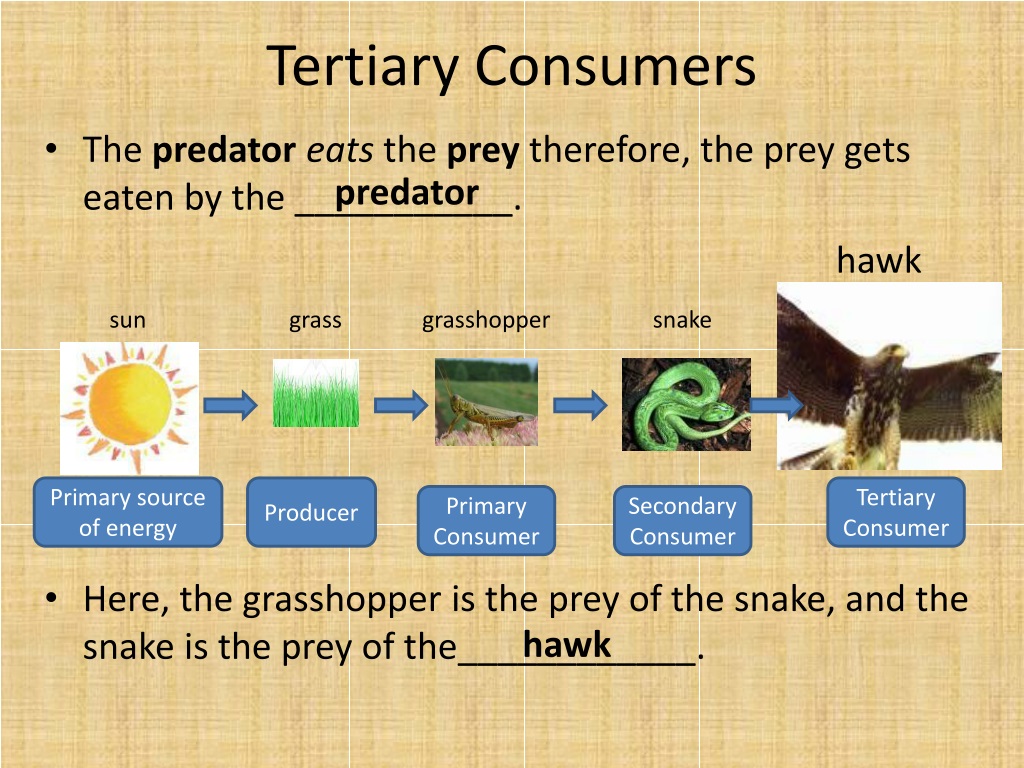
What Is A Tertiary Consumer In A Food Web Tertiary consumer definition. a tertiary consumer is an animal that obtains its nutrition by eating primary consumers and secondary consumers. usually tertiary consumers are carnivorous predators, although they may also be omnivores, which are animals that feed on both meat and plant material. A tertiary consumer is a fourth trophic level after producers, primary consumers, and secondary consumers. it eats both primary and secondary consumers as its main source of food. learn about some examples of tertiary consumers in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems and their ecological roles.
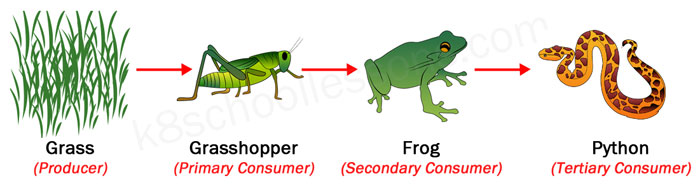
Food Chains And Food Webs Examples Of Food Chains And Food Webs Consumers are organisms that consume (eat) other organisms to sustain themselves. organisms that are consumers include heterotrophs like some animals, fungi, and bacteria. a tertiary consumer is an organism that obtains the energy it needs from consuming other consumers at different levels, from eating primary consumers or secondary consumers. The tertiary consumer is also referred to as the apex predator. such consumers typically exist at the very top of every ecological food chain. moreover, a food chain usually consists of three types of consumers primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers respectively. Primary consumers are the second step, and secondary consumers are the third. this makes a tertiary consumer the fourth step in the food chain because they consume secondary consumers for energy. tertiary consumers can be: herbivores — organisms that eat plants. carnivores — organisms that eat meat. omnivores — organisms that eat plants. A consumer is a living thing that eats other plants and animals. food chain basics: first, a producer – a plant that makes its own food from sunlight. the one after that is the tertiary.
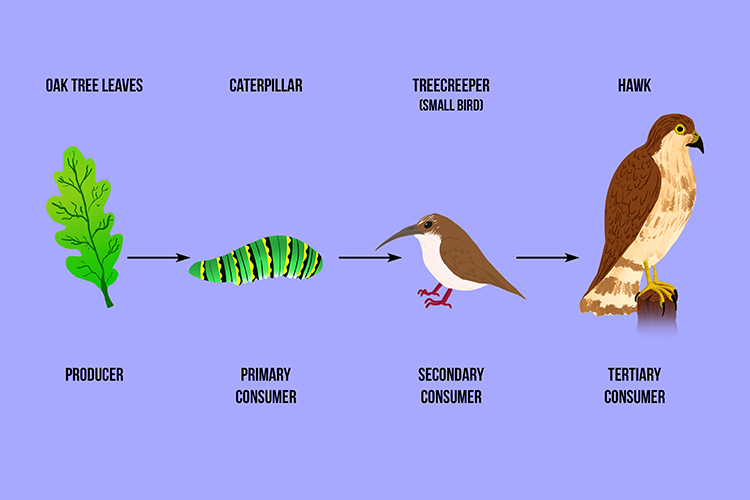
A Tertiary Consumer Eats Secondary Animals In The Food Chain Primary consumers are the second step, and secondary consumers are the third. this makes a tertiary consumer the fourth step in the food chain because they consume secondary consumers for energy. tertiary consumers can be: herbivores — organisms that eat plants. carnivores — organisms that eat meat. omnivores — organisms that eat plants. A consumer is a living thing that eats other plants and animals. food chain basics: first, a producer – a plant that makes its own food from sunlight. the one after that is the tertiary. A tertiary consumer is an animal that obtains its nutrition by eating primary consumers and secondary consumers. usually, tertiary consumers are carnivorous predators, although they may also be omnivores, which are animals that feed on both meat and plant material. Definition. tertiary consumers are organisms that occupy the highest trophic level in a food chain and primarily feed on secondary consumers. they play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems by regulating the populations of species below them in the food chain. in aquatic biomes, tertiary consumers can include large predatory.

Ppt The Food Chain Powerpoint Presentation Id 706666 A tertiary consumer is an animal that obtains its nutrition by eating primary consumers and secondary consumers. usually, tertiary consumers are carnivorous predators, although they may also be omnivores, which are animals that feed on both meat and plant material. Definition. tertiary consumers are organisms that occupy the highest trophic level in a food chain and primarily feed on secondary consumers. they play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems by regulating the populations of species below them in the food chain. in aquatic biomes, tertiary consumers can include large predatory.
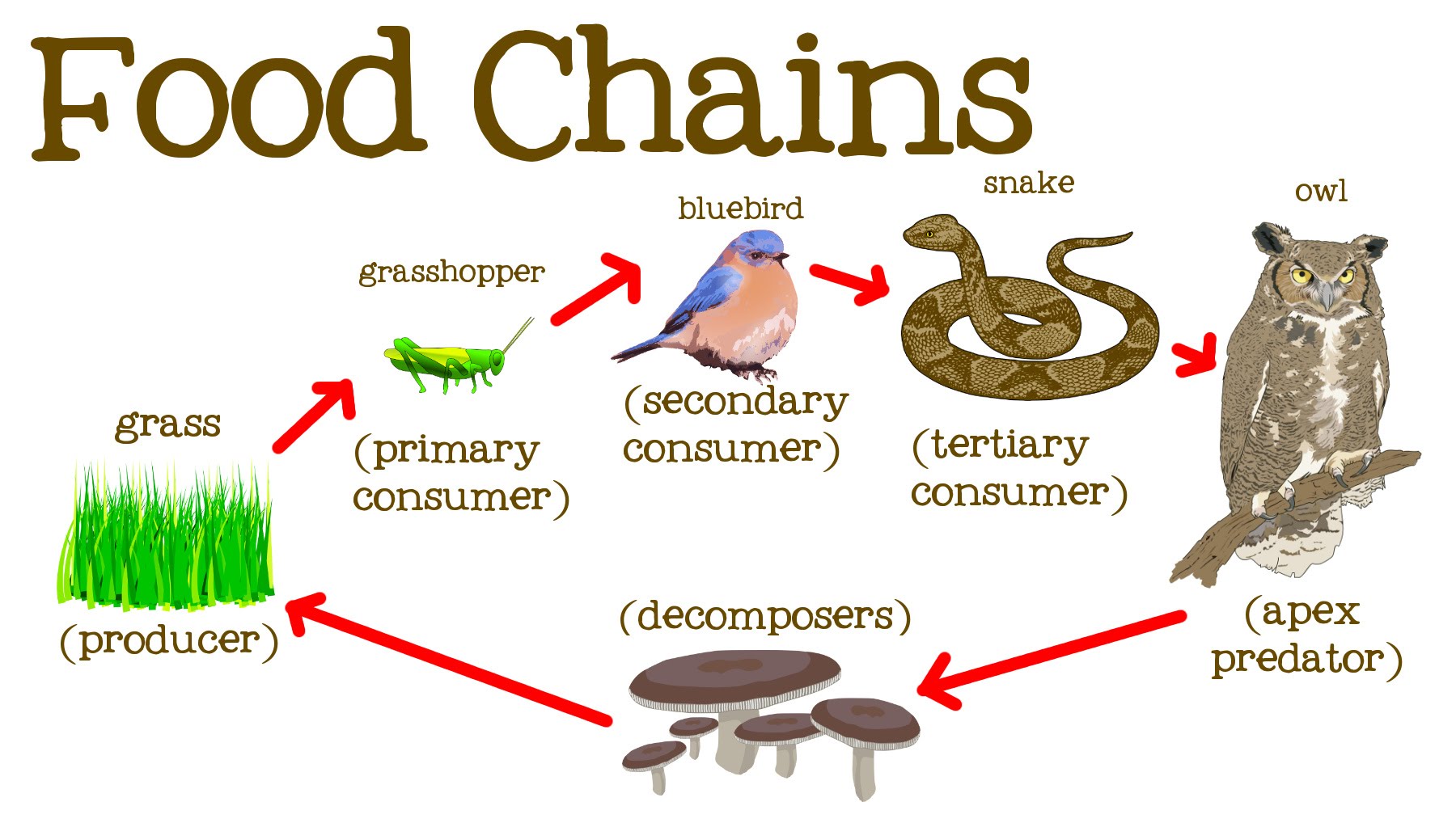
What Is A Tertiary Consumer In An Ecosystem

Comments are closed.