What Is The Relationship Between Producers And Consumers

Difference Between Producers And Consumers In Biology Differs From Producers and consumers. workers at a factory produce clothes that consumers will buy. a society’s economy is based on creating wealth through selling and buying. the people who do the selling and buying are producers and consumers. producers create, or produce, goods and provide services, and consumers buy those goods and services with money. Consumer and producer are two essential roles in the economic system. a consumer refers to an individual or entity that purchases goods or services for personal use or consumption. they play a crucial role in driving demand and influencing the market. on the other hand, a producer is an individual or organization that creates or manufactures.
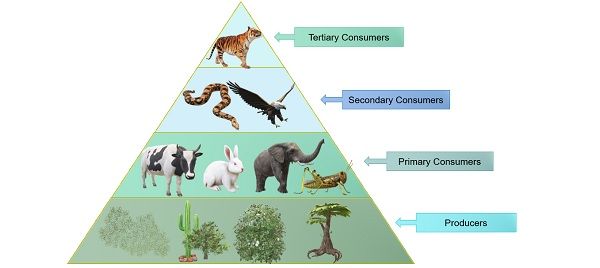
Difference Between Producers And Consumers With Examples And Comparison Chart Bio Differences Consumers buy goods and services to satisfy their wants, and producers make goods and services. this video from the explore economics series for kids helps them understand that people are both consumers and producers. it uses easy to understand examples. kids are encouraged to be producers by making a bookmark, and then to be consumers by using. When the price of a gallon of gasoline increases, for example, people look for ways to reduce their consumption by combining several errands, commuting by carpool or mass transit, or taking weekend or vacation trips closer to home. economists call this inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded the law of demand. the law of demand. Explain the relationship between producers and consumers. flexi says: producers are autotrophs that use energy and inorganic molecules from the environment to build glucose and other organic molecules used as a source of food. primary consumers are usually herbivores that feed on autotrophic plants. secondary consumers are predators that feed. As the price of a good goes up, consumers demand less of it and more supply enters the market. if the price is too high, the supply will be greater than demand, and producers will be stuck with the excess. conversely, as the price of a good goes down, consumers demand more of it and less supply enters the market.

Comments are closed.